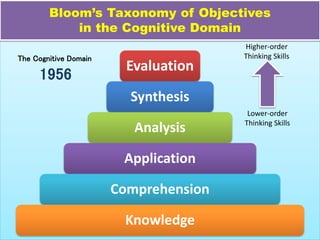
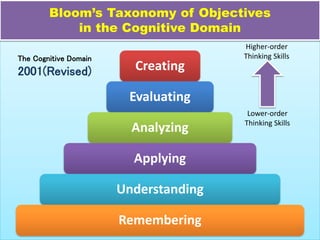
This document discusses Benjamin Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives. It explains that Bloom developed a classification of learning objectives within the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. The cognitive domain involves knowledge and intellectual skills and was revised in 2001 to focus on higher-order thinking skills like analysis, evaluation and creation. The affective domain involves attitudes, emotions and values. The psychomotor domain includes physical skills and movements. The document provides details on Bloom's taxonomy within each of these domains.