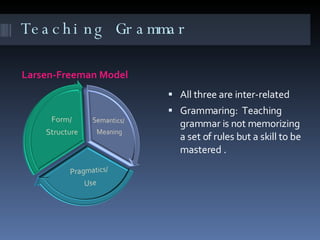
This document discusses various topics related to teaching English to adult learners, including the Pygmalion effect, teaching grammar, the learning process, the teaching process, teaching vocabulary, and strategies for teaching vocabulary. It notes that teaching grammar is a skill, not just memorizing rules. Learning is gradual and errors are normal. Teachers should provide feedback and opportunities for meaningful practice. When teaching vocabulary, explicit instruction is important initially but most learning later becomes incidental through reading. Strategies include guessing, mnemonics, notebooks, and focusing on cognates and collocations.