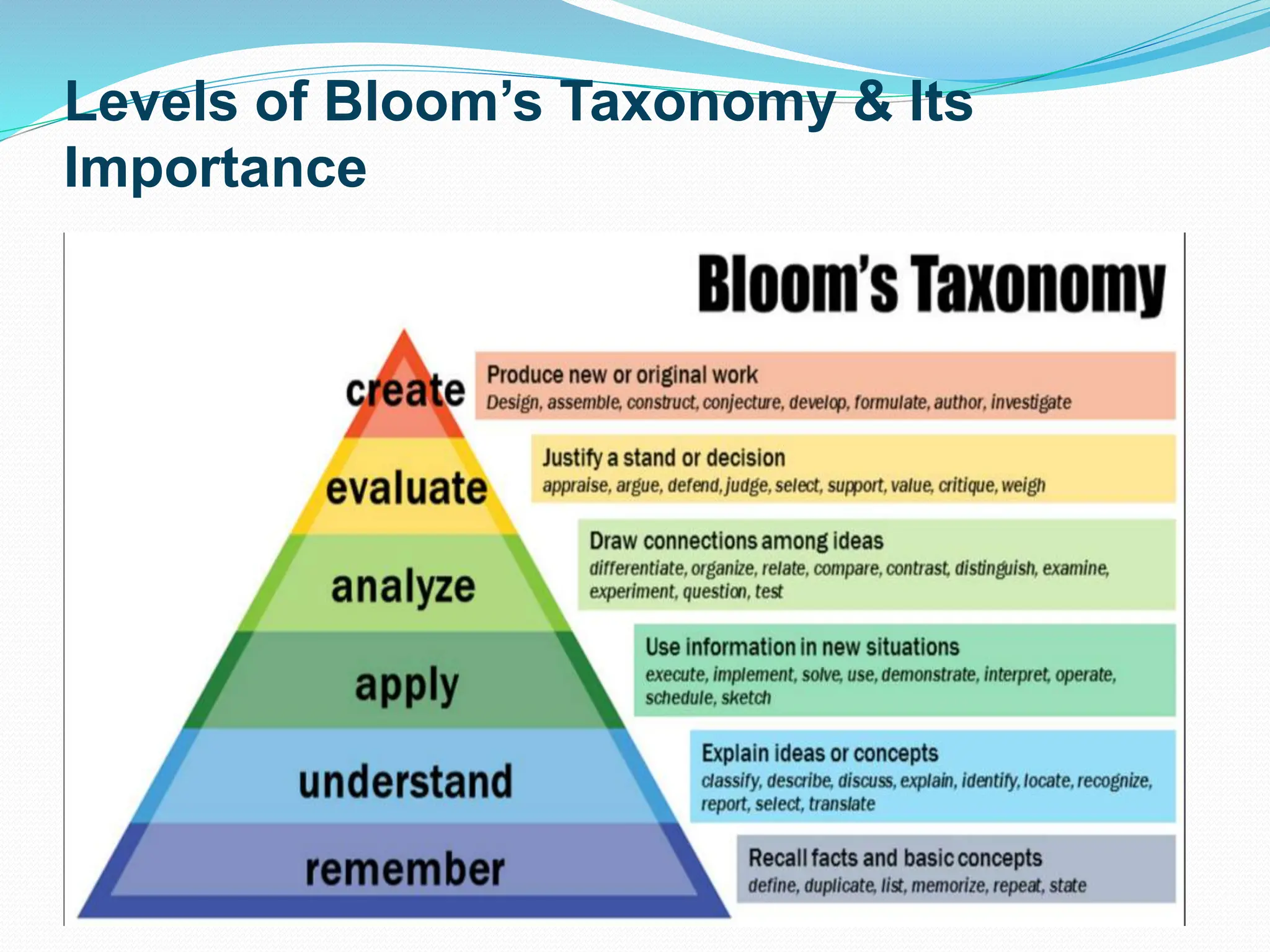
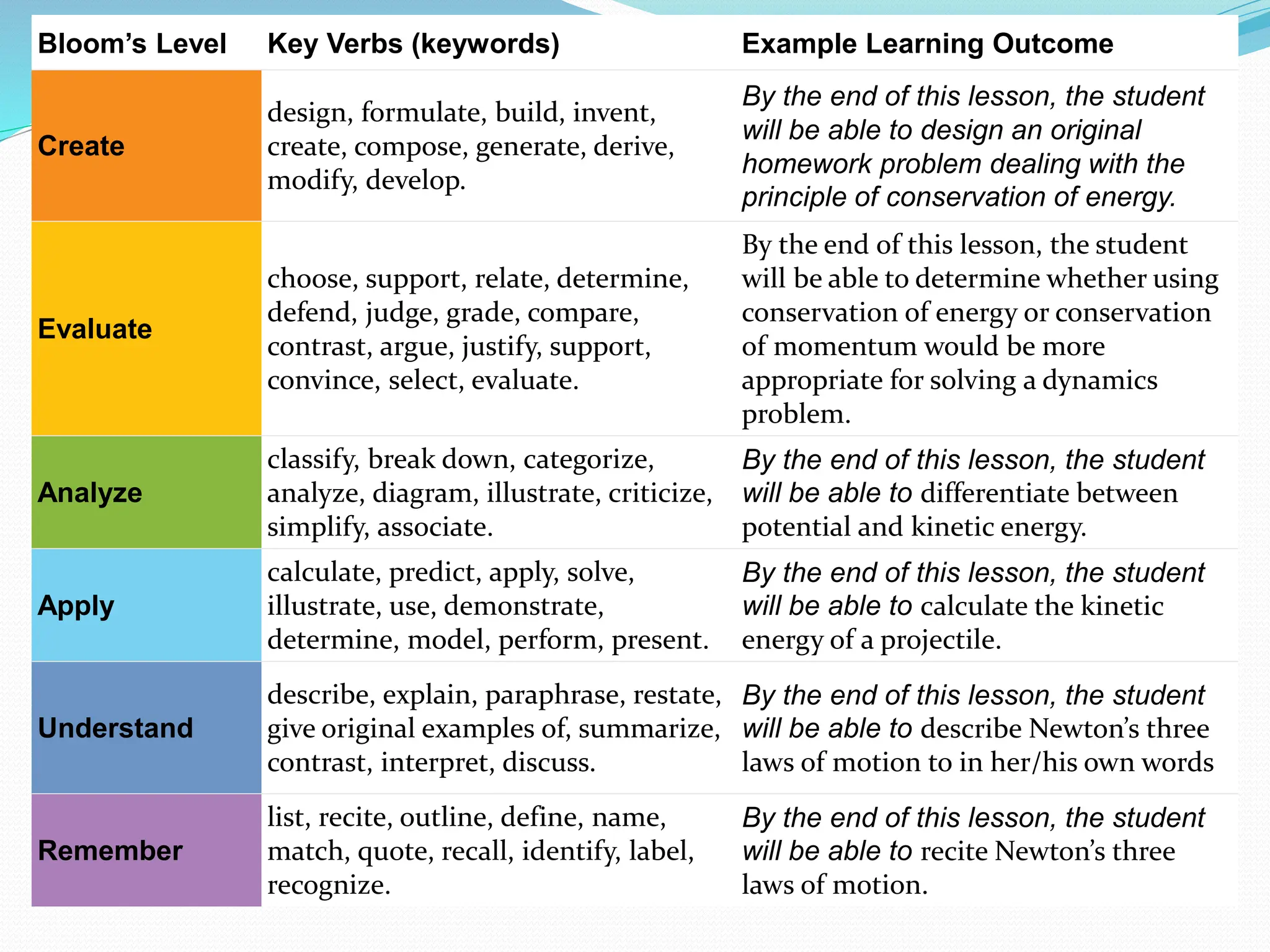
Blooms Taxonomy is a classification system used to define levels of cognition such as thinking, learning, and understanding. Educators use Bloom's Taxonomy to inform curriculum development, assessments, and teaching methods. Originally introduced in 1956 by Benjamin Bloom, it categorizes educational goals from basic recall to higher order thinking skills, including creating. The taxonomy is helpful for ensuring all levels of thinking are addressed and for developing balanced assessments.