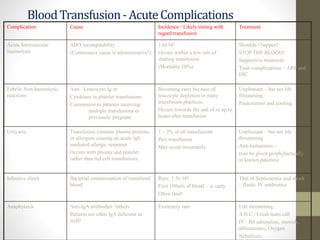
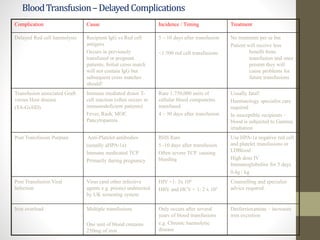
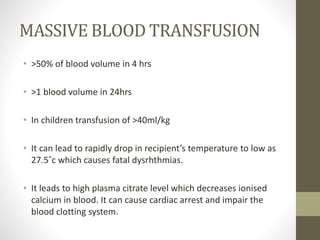
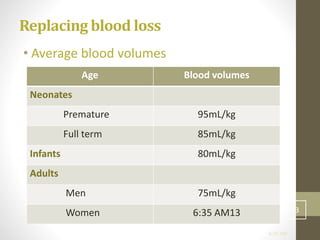
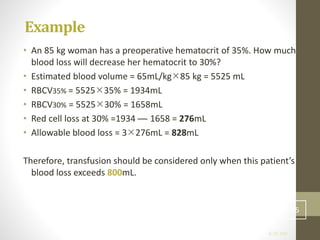
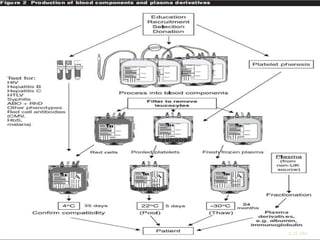
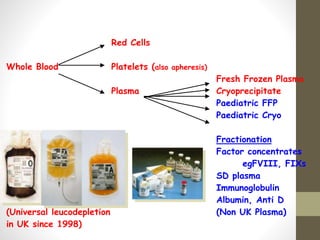
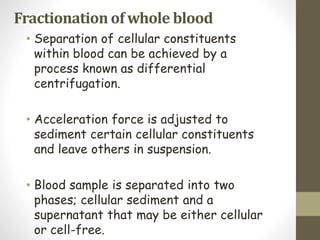
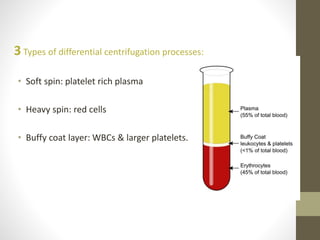
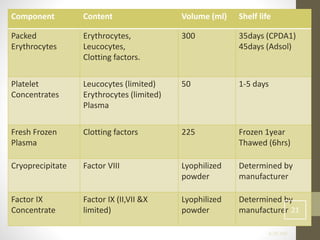
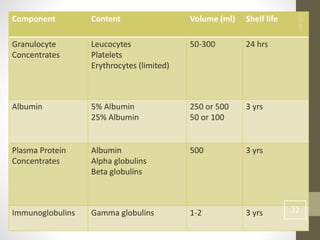
This document discusses blood transfusion and its components. It begins by outlining the characteristics of an ideal blood substitute. It then discusses the principal aims of blood transfusion, including improving oxygen carrying capacity and reducing hypovolaemia. It provides guidance on blood transfusion, including recommendations from WHO and the Council of Europe. It details the process of blood grouping and cross-matching. Finally, it discusses various blood components that can be transfused, including packed red blood cells, platelets, fresh frozen plasma, cryoprecipitate, and granulocyte concentrates, along with their indications, contents, shelf lives, and administration considerations.





















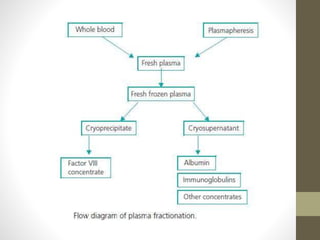





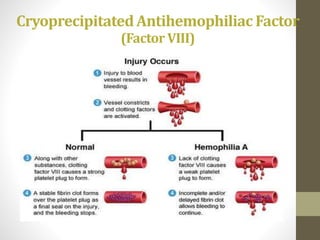
![USES
• Hemophilia A
[high concentrations of factor VIII (80 to 120 units) in a
volume of only about 10 ml]
• In non bleeding patients with congenital fibrinogen deficiency or
Von Willebrands disease not responding to desmopressin.
• Bleeding patients with VWD.
• In massively transfused patients with fibrinogen concentrates <80-
100 mg/dl.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bloodtransfusion-170317063509/85/Blood-transfusion-38-320.jpg)