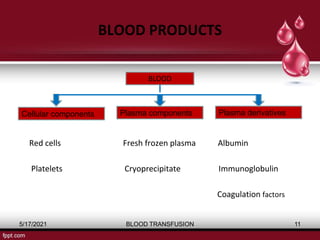
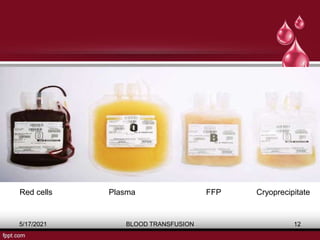
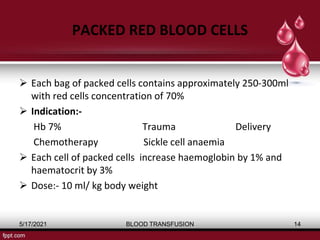
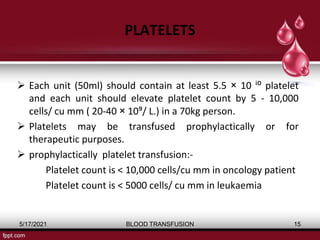
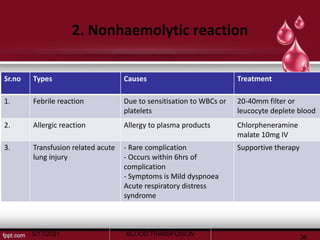
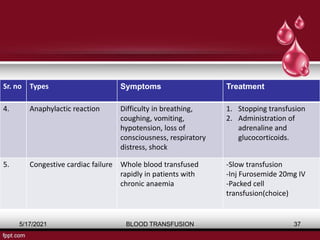
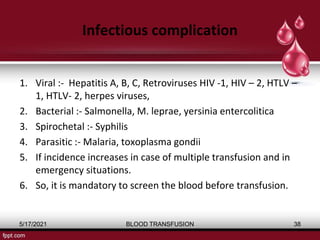
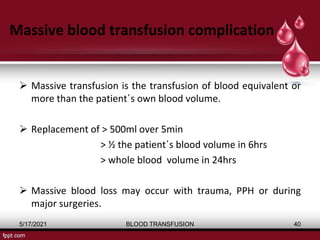
The document discusses blood transfusion, a life-saving procedure for transferring blood or its components from one person to another. It details the history of blood transfusion, types of transfusions, the various blood products, administration protocols, potential complications, donor selection criteria, and necessary precautions for screening and storage. Key topics include allogeneic and autogenic transfusions, types of blood products like red cells and plasma, and adverse reactions associated with transfusions.