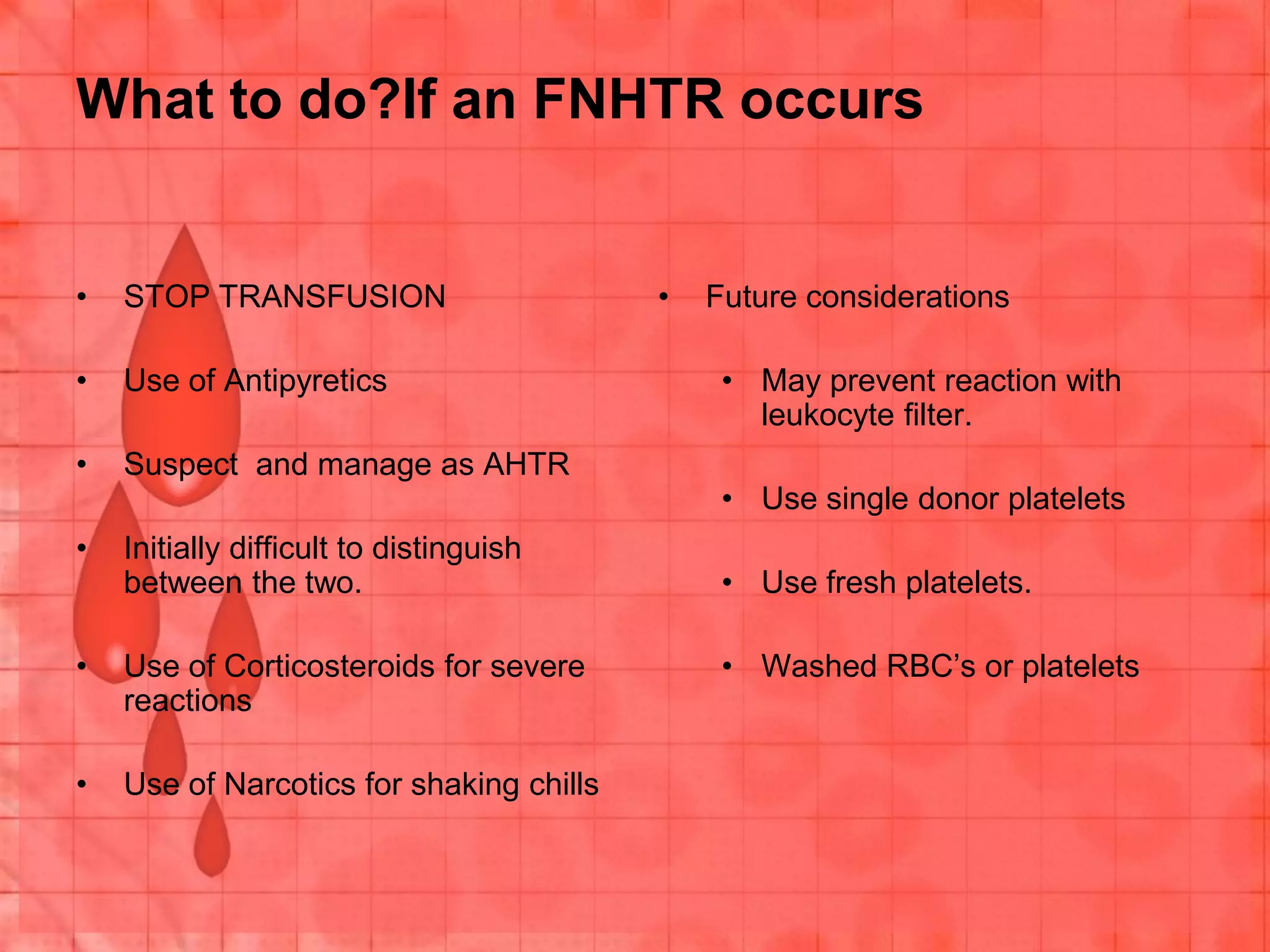
This document discusses transfusion therapy for a 22-year-old man with multiple penetrating chest wounds who has drained 1500mL of blood from his right chest. The most appropriate next step is to arrange transfusion and transfer to the operating theater. Transfusion therapy involves administering blood components like packed red blood cells, fresh frozen plasma, platelets, and cryoprecipitate to replace lost blood and clotting factors. The risks and complications of transfusion include acute reactions like hemolytic, febrile, allergic, and transfusion-related acute lung injury as well as delayed issues such as alloimmunization, iron overload, and transfusion-transmitted infections.