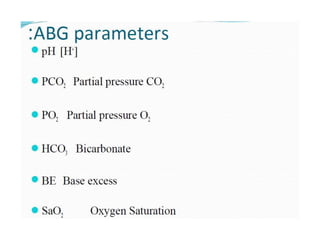
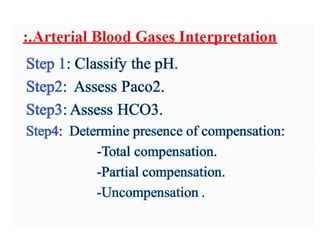
The document discusses acid-base balance and pH regulation in the human body. It covers:
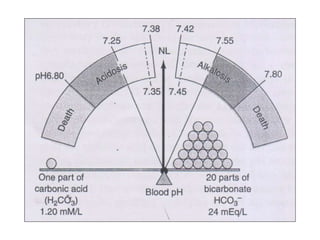
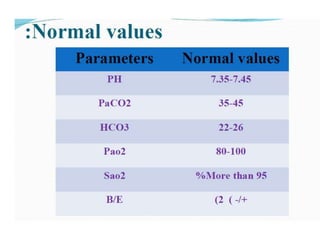
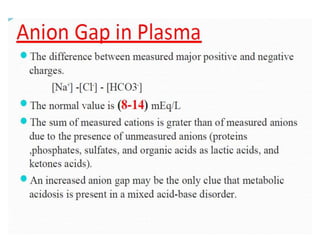
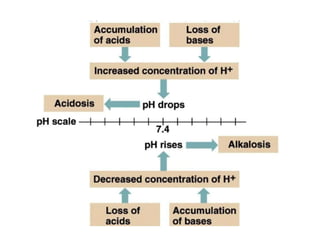
- The normal pH range of 7.35-7.45 and what constitutes acidosis and alkalosis.
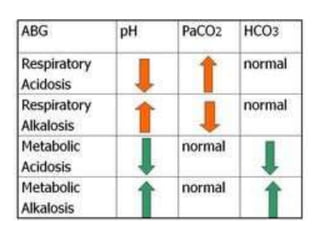
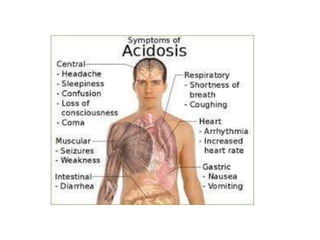
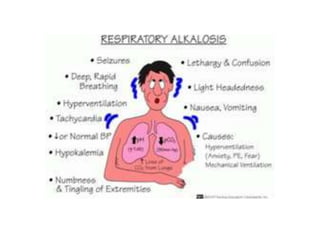
- The four main types of acid-base disorders: metabolic acidosis, metabolic alkalosis, respiratory acidosis, and respiratory alkalosis.
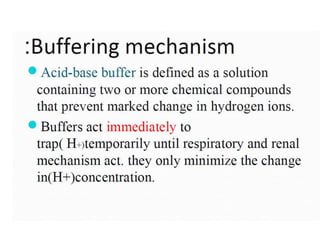
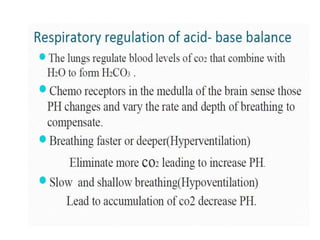
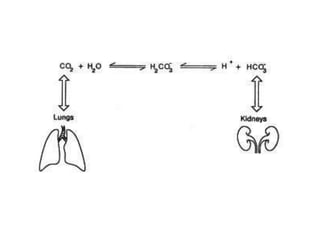
- The kidney and lung systems play key roles in pH regulation through bicarbonate reabsorption/excretion and carbon dioxide expiration.
- Maintaining normal pH is essential for oxygen delivery, protein structure, and biochemical reactions in the body.