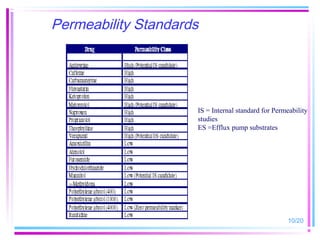
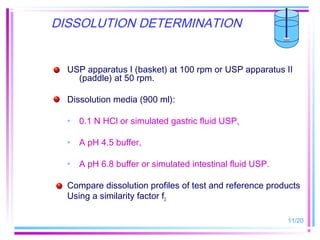
The document discusses biowaivers for solid oral dosage forms based on the Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS). It describes the four BCS classes based on a drug's solubility and permeability characteristics. For highly soluble, highly permeable Class 1 drugs, in vivo bioavailability/bioequivalence studies can be waived if the test and reference products have rapid dissolution. The document outlines methods for determining solubility and permeability to classify drugs. It also discusses potential biowaiver extensions for Class 3 drugs or drugs with pH-dependent solubility if dissolution is very rapid.