This document discusses bioequivalence studies, which compare the bioavailability of generic drugs to their branded counterparts. It covers key aspects of study design, including assessing pharmacokinetic parameters like AUC and Cmax in fasting and fed states using single and multiple dose studies. Analytical methods must be validated to measure drug concentrations accurately. Statistical tests like ANOVA are used to determine if generic and branded versions are bioequivalent by having equivalent rates and extents of drug absorption. The goal is to demonstrate generic drugs deliver the same therapeutic effects as the original drug.







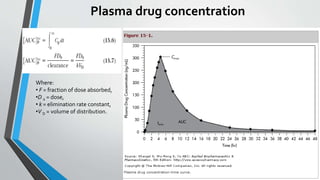
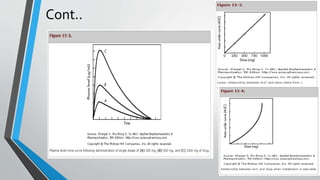


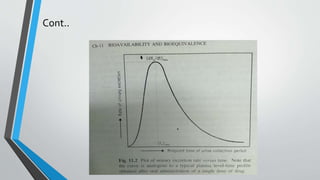
















![Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of the Data
• For single-dose studies, including a fasting study or a food intervention
study, the pharmacokinetic analyses include calculation for each subject
• For multiple-dose studies, pharmacokinetic analysis includes calculation for
each subject of the steady-state area under the curve, (AUC0–t), T max, C min,
C max, and
• The percent fluctuation [100 x (C max – C min)/C min].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioeqivelence-190310141630/85/Bioequivalence-study-29-320.jpg)


