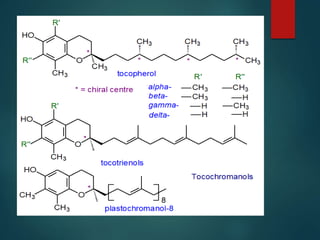
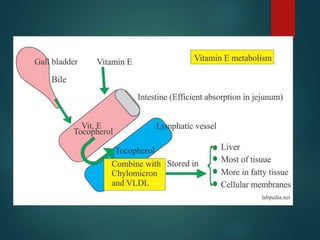
This document discusses vitamin E, including its dietary sources, biochemical functions, absorption and transport, recommended daily allowance, deficiency symptoms, and toxicity. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin and antioxidant that prevents lipid peroxidation and protects cell membranes. Key dietary sources include nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables. The RDA for vitamin E is 15 mg/day for adults. Deficiency can cause neurological and muscle problems, while toxicity is rare and requires extremely high doses over 1000 mg/day.