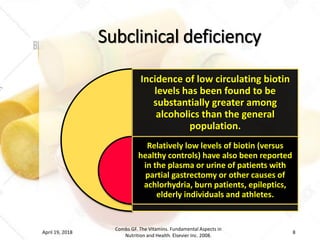
Biotin deficiency is rare because biotin is found widely in foods and synthesized by gut bacteria. Deficiencies can be caused by antagonists or inadequate intake from mother's milk or intravenous nutrition. Symptoms include skin rashes, tongue inflammation, loss of appetite, nausea, depression, and lipid metabolism issues. One case was caused by a child eating raw eggs for six years, as the protein avidin in raw eggs binds biotin and prevents absorption. Marginal biotin levels may play a role in sudden infant death syndrome. While biotin toxicity is very low, excess biotin may help reduce diabetes symptoms.