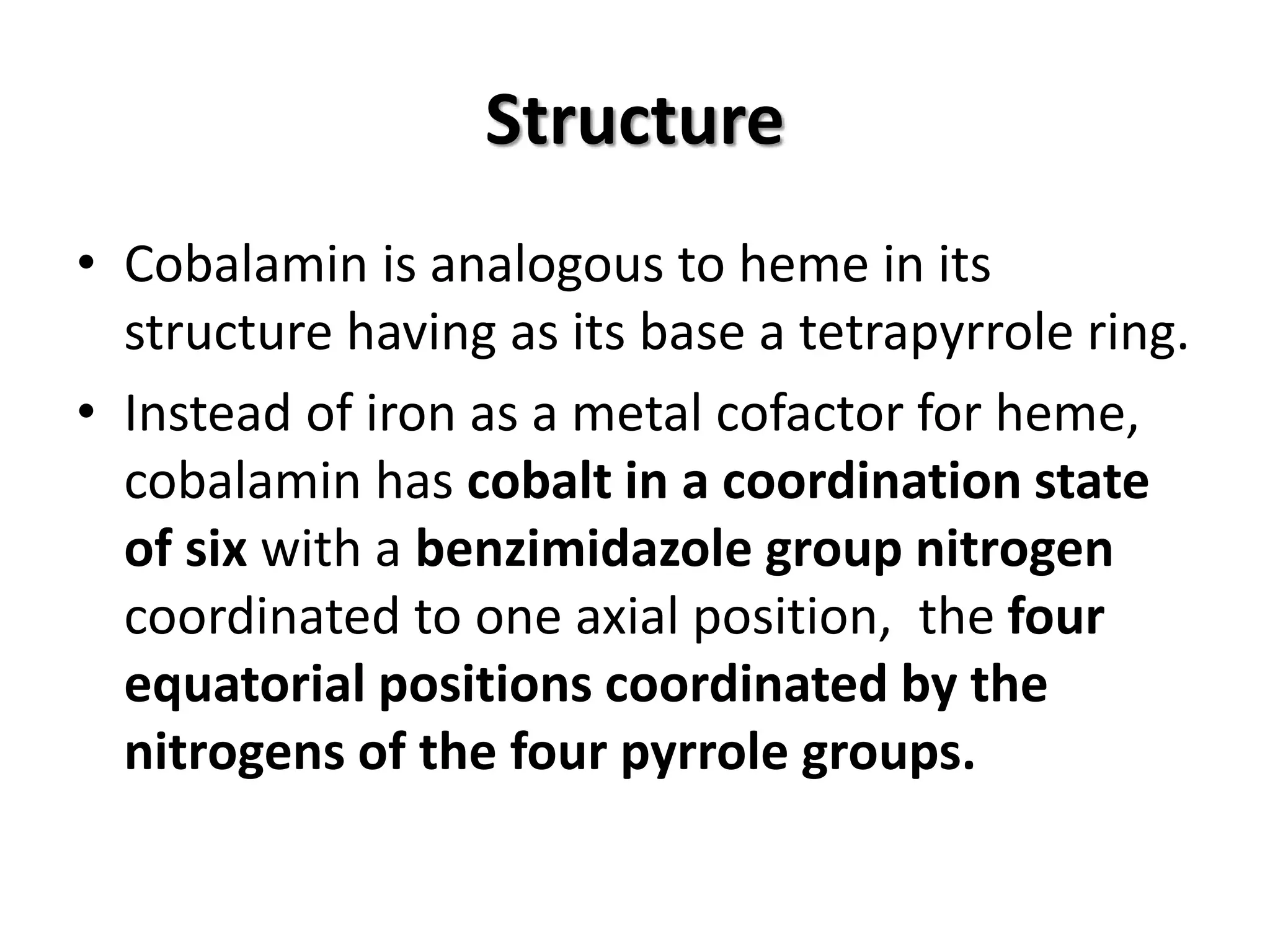
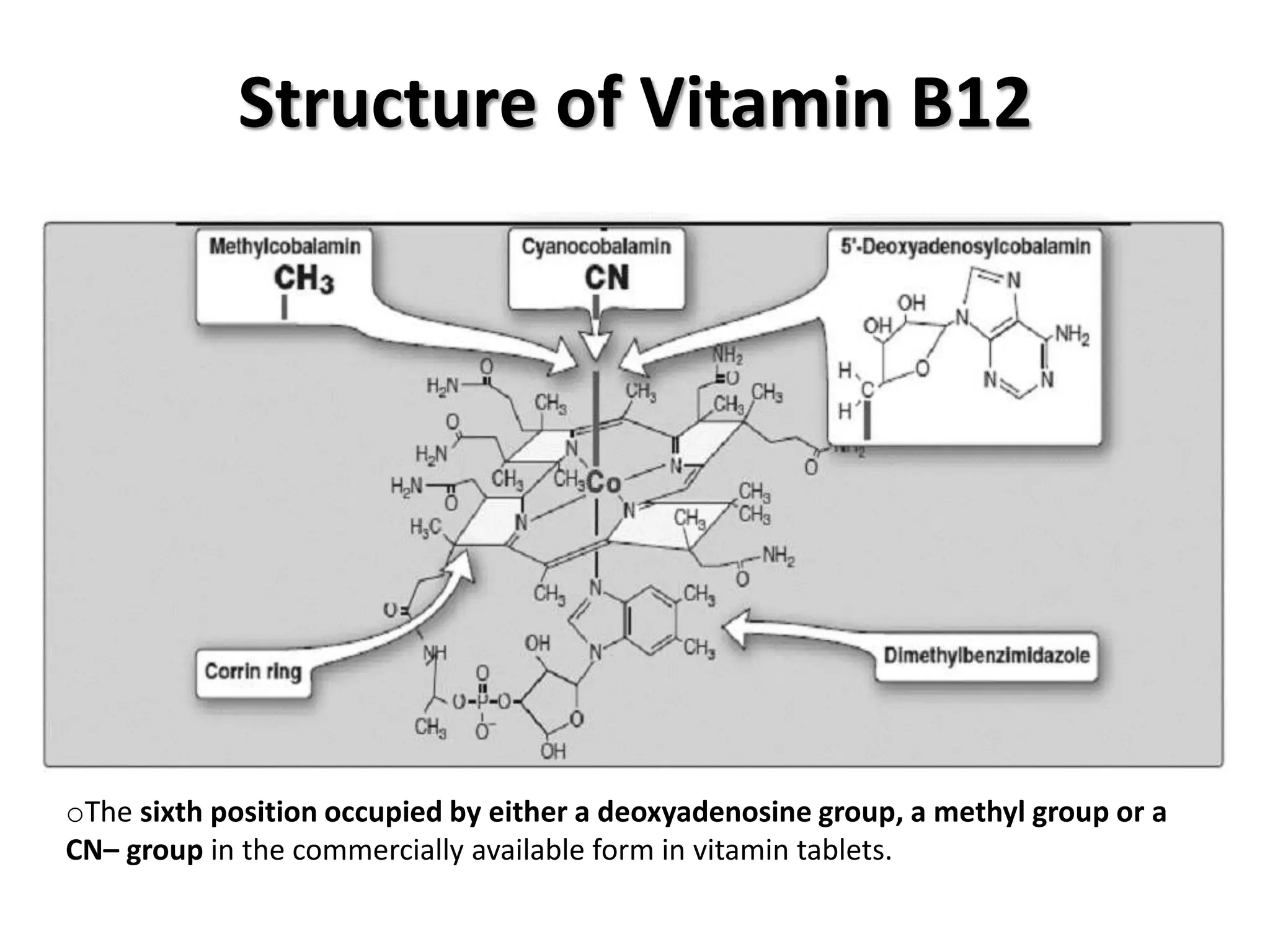
This document discusses vitamin B12 deficiency, including its structure, dietary sources, absorption, transport, storage, and metabolic roles. It also covers the causes, manifestations, and laboratory findings of B12 deficiency. The key points are:
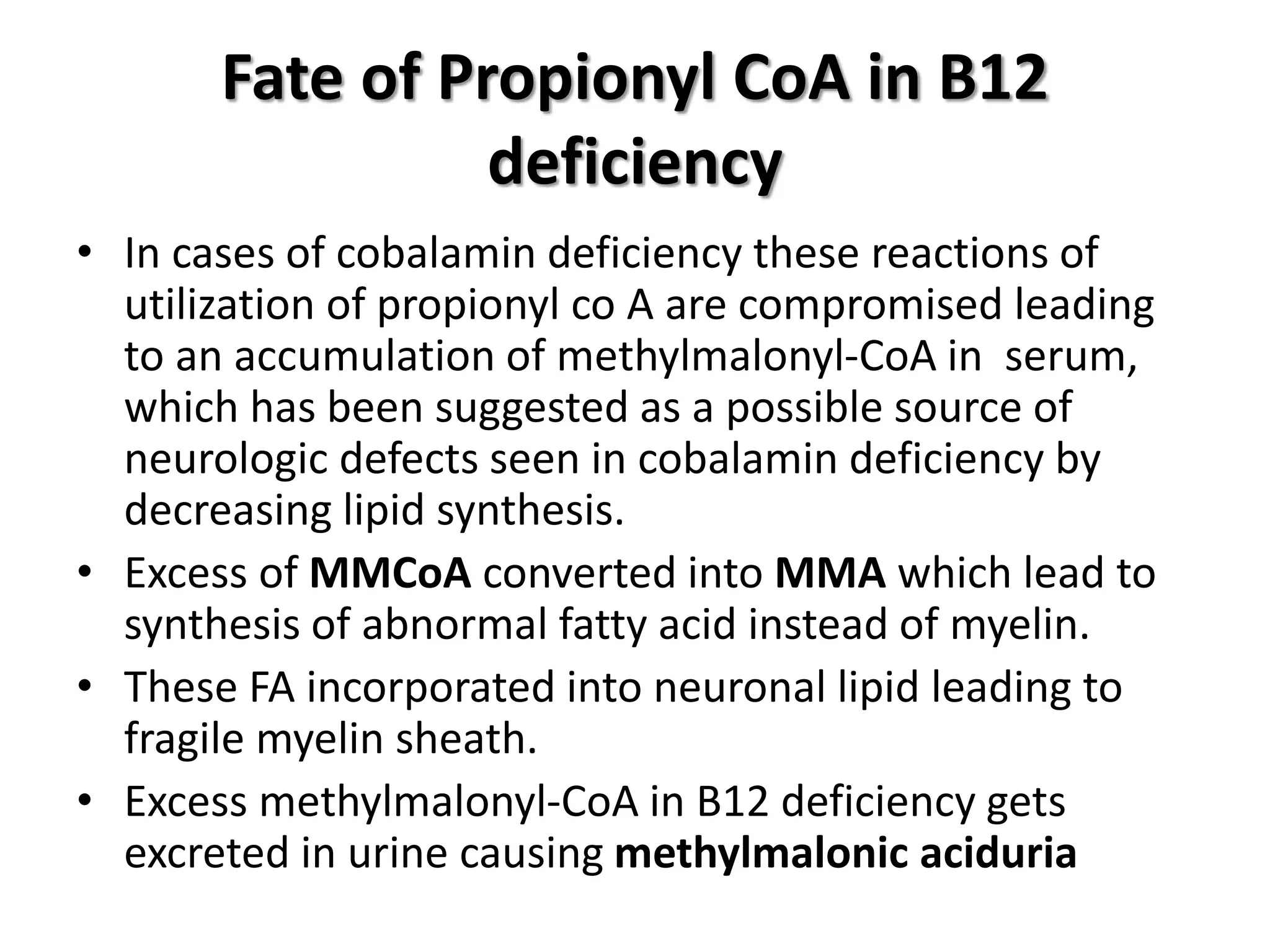
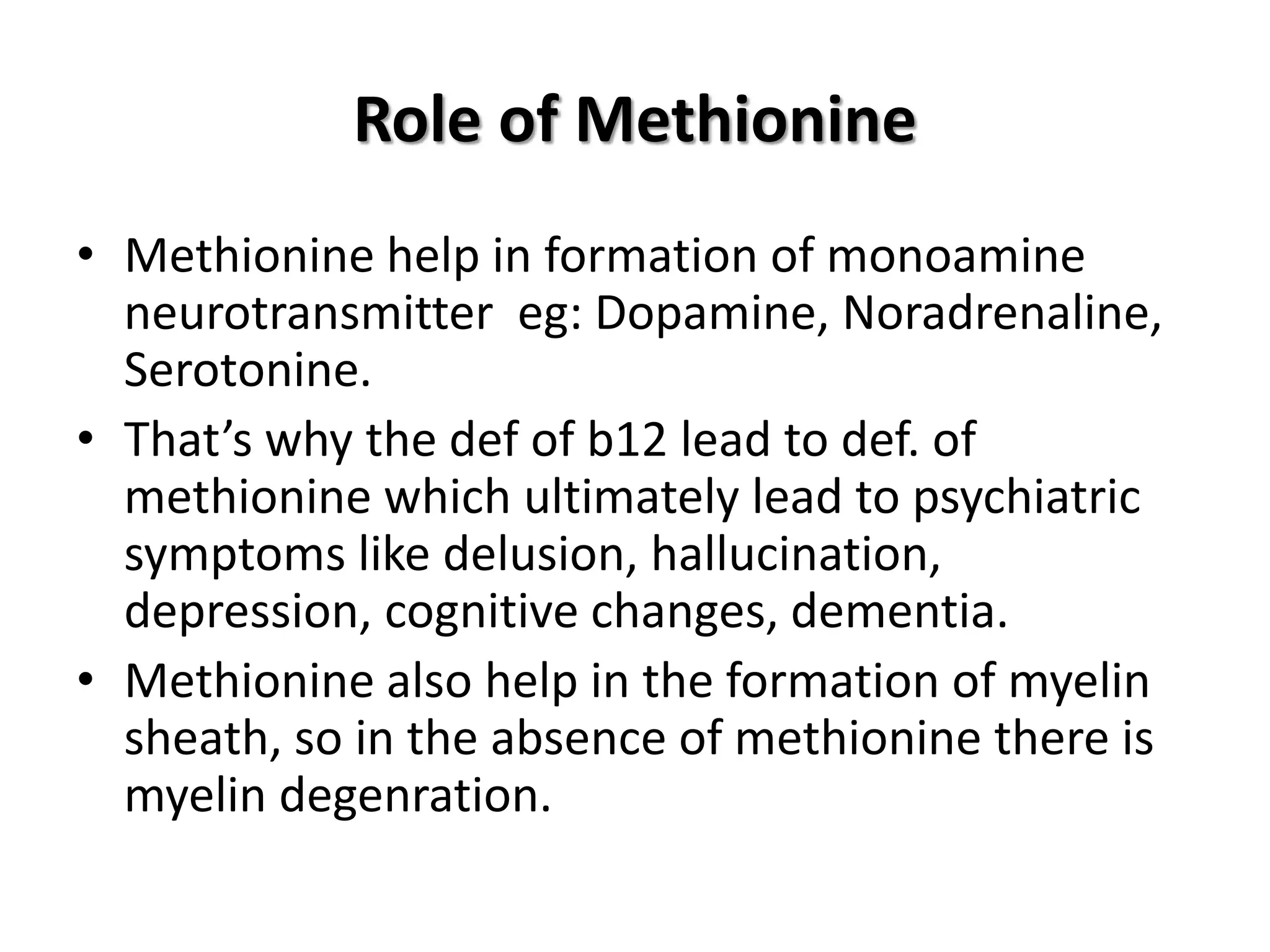
1. Vitamin B12 is essential for DNA synthesis and fatty acid/amino acid metabolism. Deficiency can cause megaloblastic anemia and neurological issues.
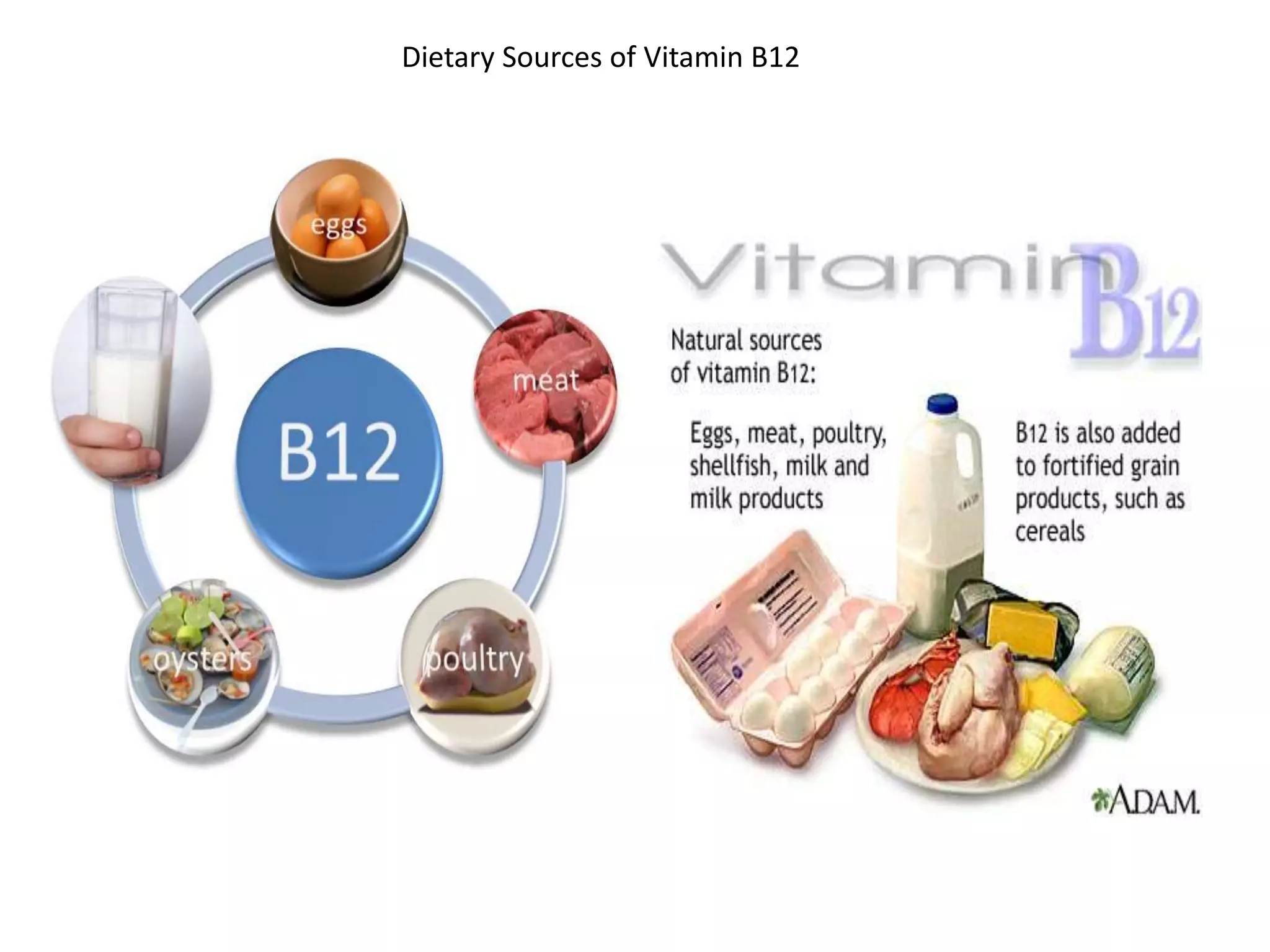
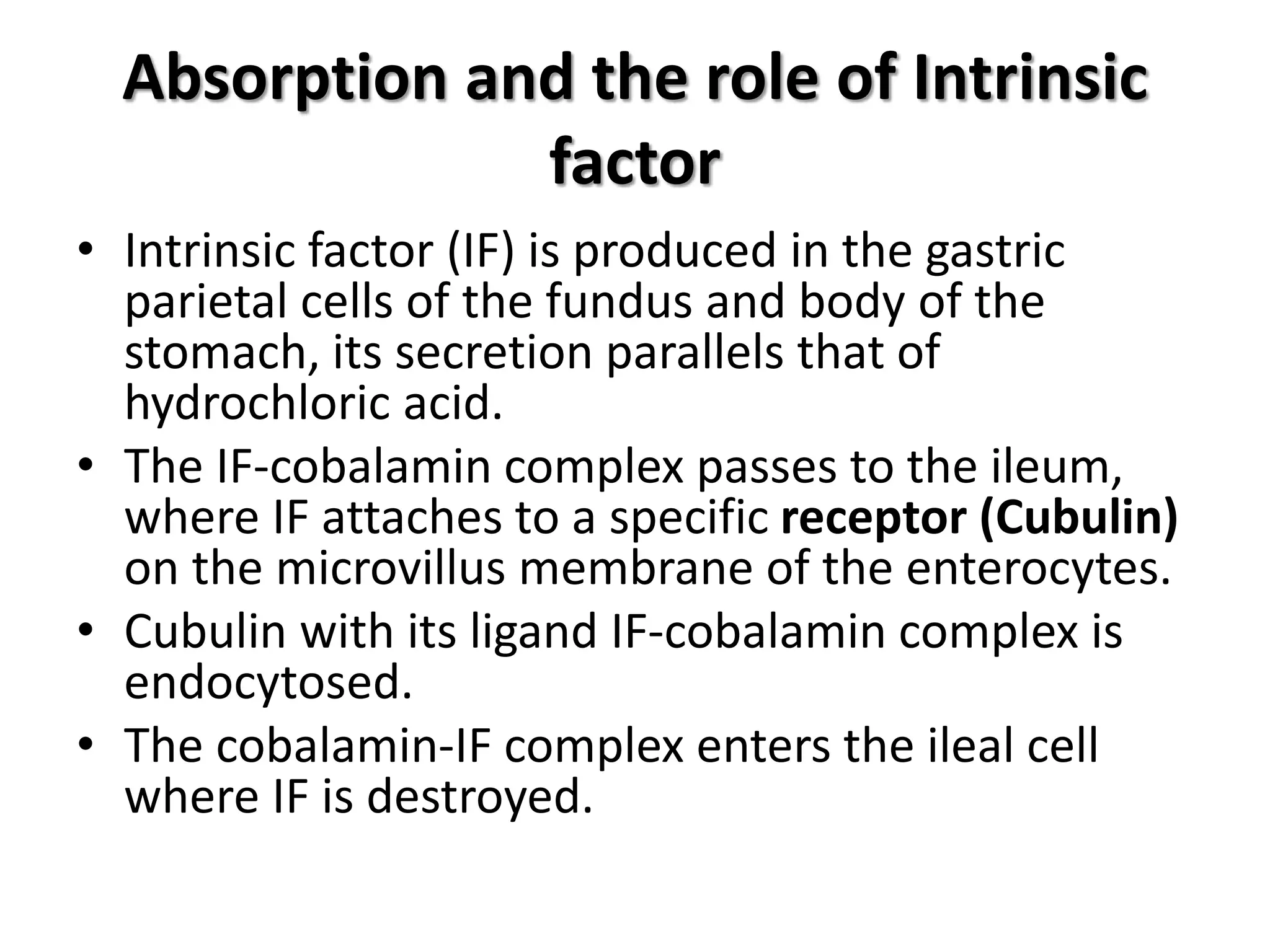
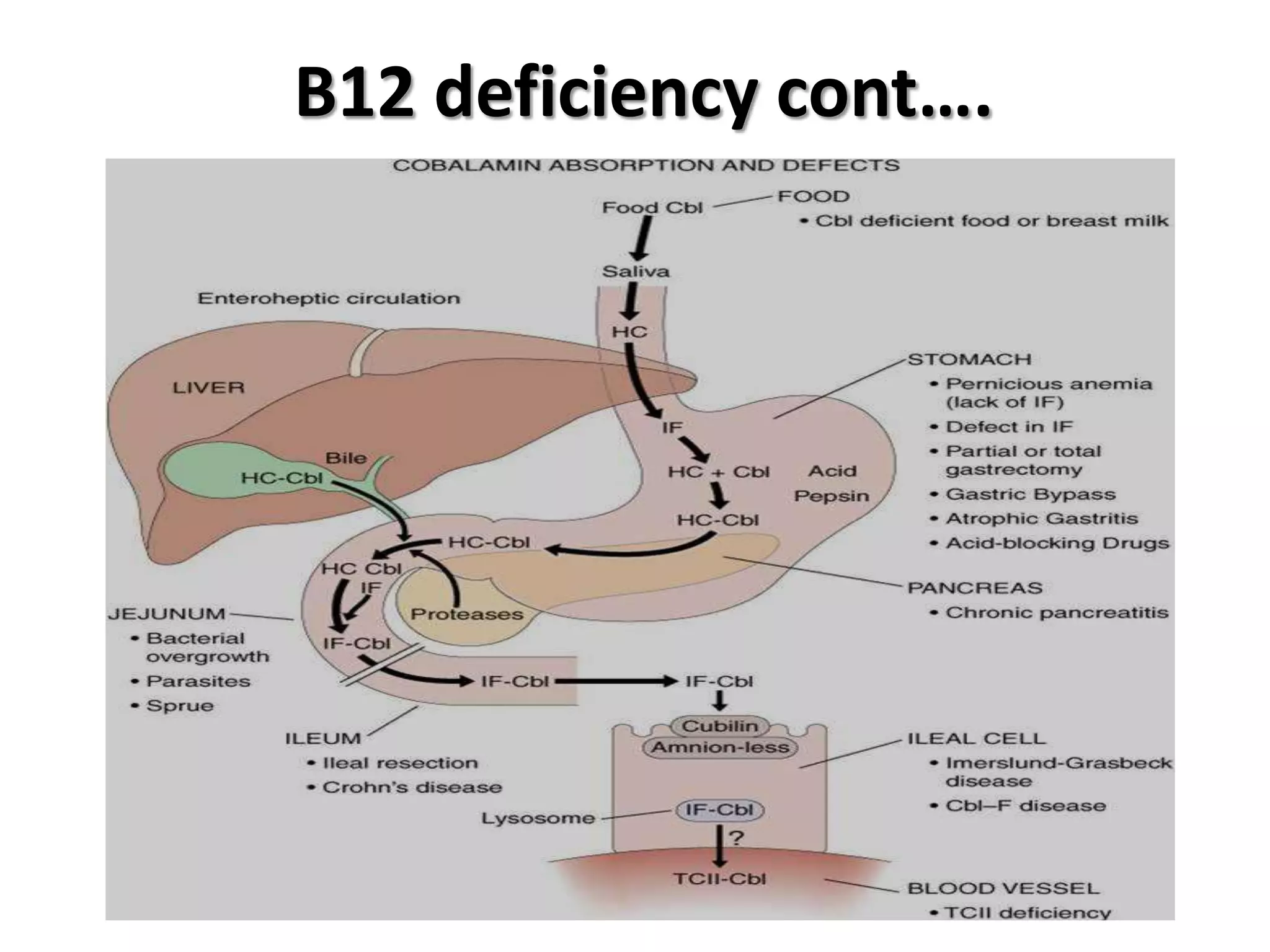
2. Dietary sources are animal products. Absorption requires intrinsic factor in the ileum. Deficiency can be caused by pernicious anemia or other issues impairing absorption.
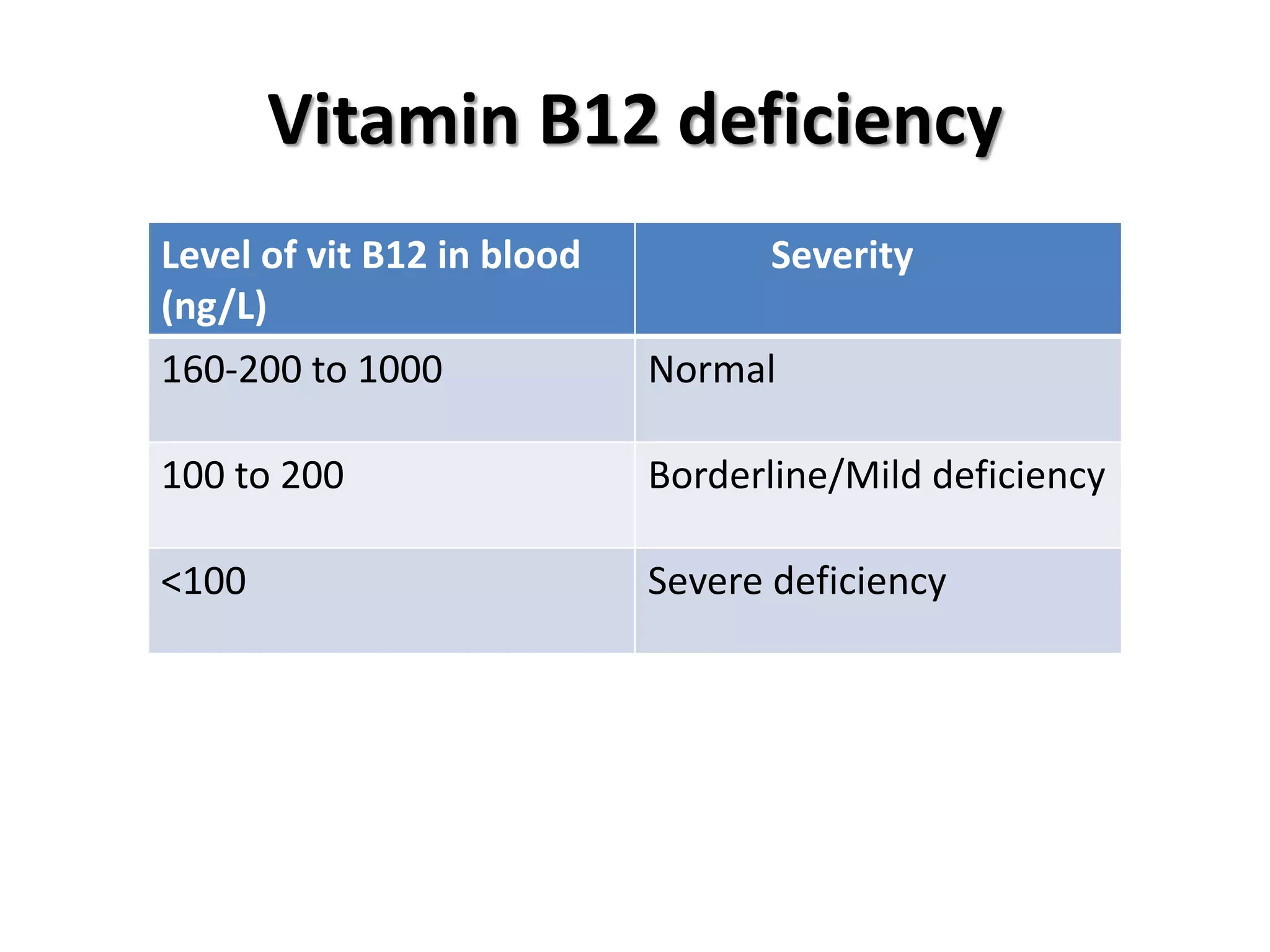
3. Manifestations include megaloblastic anemia, neurological changes, and other issues. Laboratory findings show macro