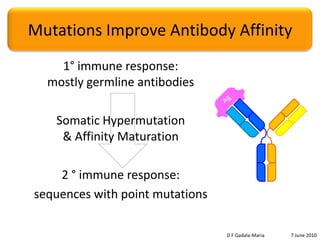
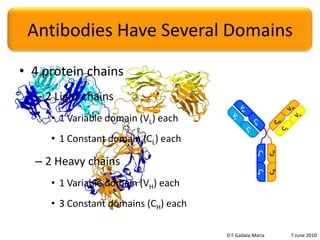
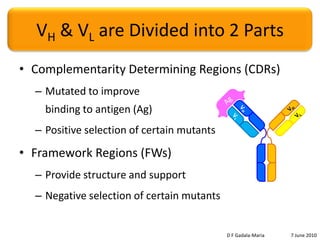
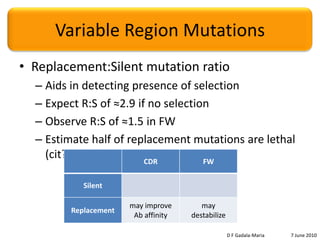
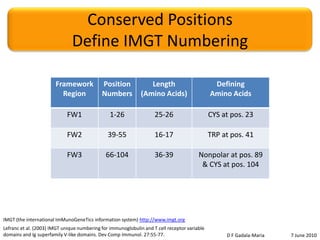
The document discusses the conservation of residues in the variable region of antibodies, focusing on somatic hypermutation and affinity maturation in the immune response. It presents estimates that approximately half of the replacement mutations in framework regions are lethal, categorizing mutations into invariant, conservative, and non-conservative types. Future directions include the need for more sequence data and better alignments to further analyze and understand antibody diversity.