Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times







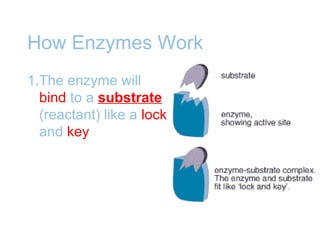


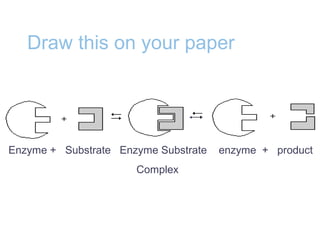
Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms in substances to form different products. Chemical equations show the reactants and products, with the same number and type of atoms on both sides. Chemical reactions require activation energy to occur, and can release or absorb energy. Enzymes are biological catalysts that lower the activation energy needed for reactions in living things by binding to reactants at an active site and facilitating the formation of products.










