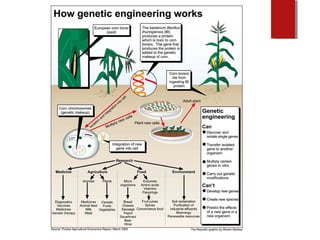
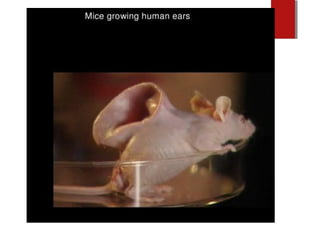
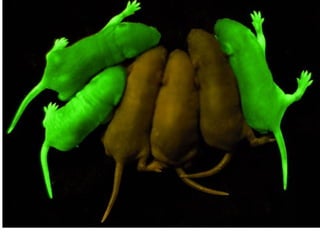
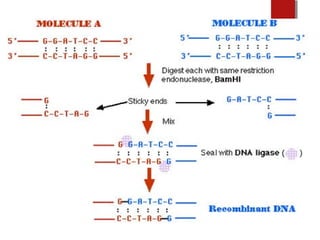
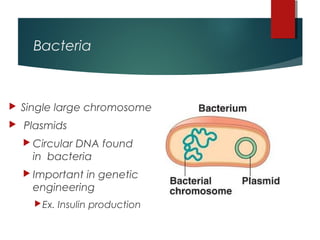
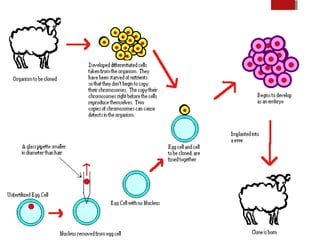
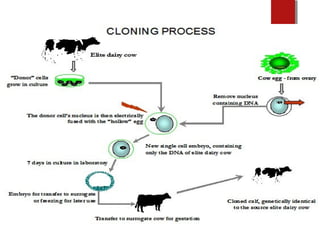
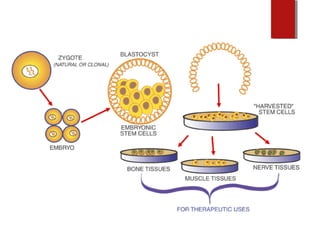
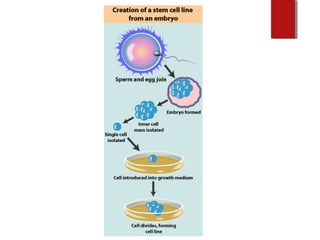
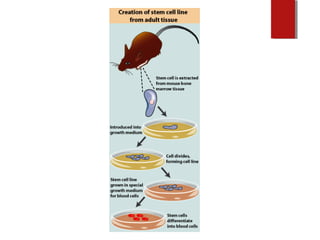
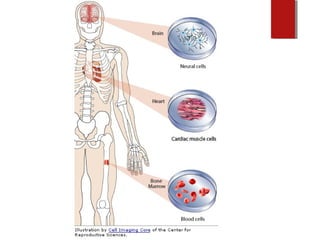
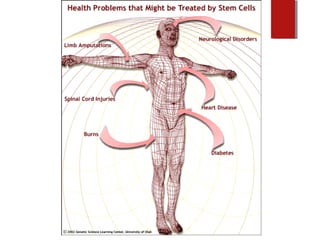
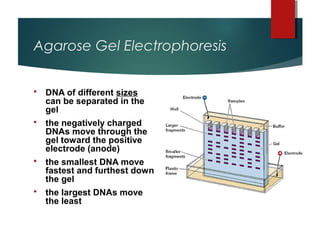
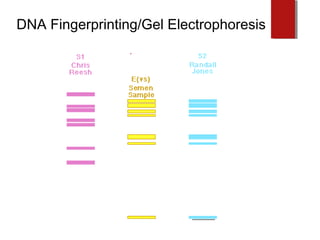
The document discusses various topics in biotechnology including the human genome project, genetic engineering, cloning, stem cells, and DNA fingerprinting. It provides details on how scientists mapped the human genome using techniques like DNA sequencing, restriction fragment-length polymorphisms, yeast and bacterial artificial chromosomes, polymerase chain reaction, and electrophoresis. Genetic engineering techniques like gene splicing and restriction enzymes are described. Applications and debates around cloning, genetic engineering, and stem cells are also summarized.