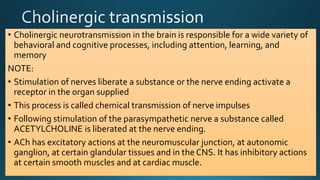
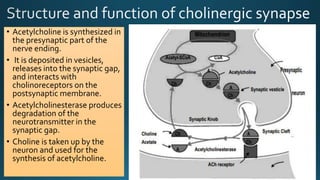
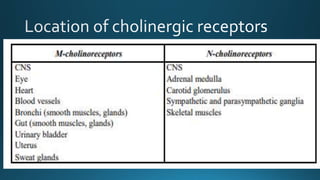
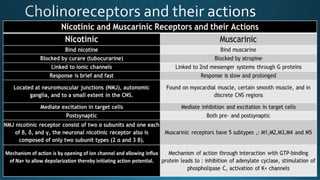
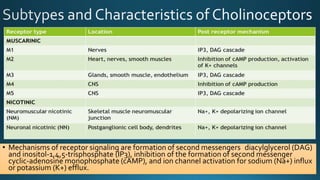
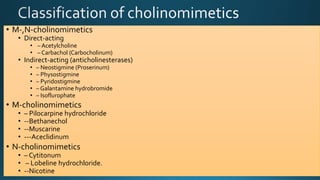
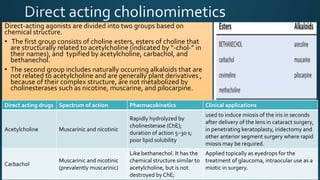
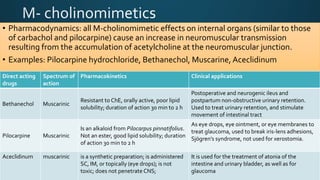
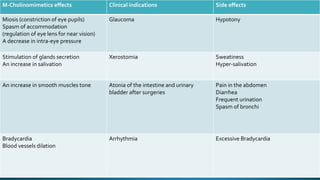
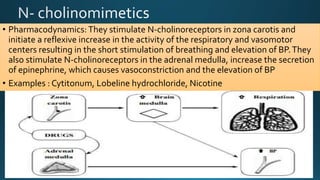
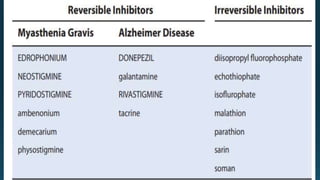
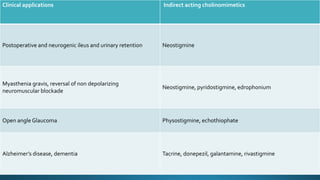
The document discusses acetylcholine (ACh), the first neurotransmitter discovered. ACh is synthesized in the presynaptic part of neurons from choline and acetyl-CoA. It is stored in vesicles and released into the synaptic cleft upon neuronal stimulation. In the cleft, ACh binds to cholinergic receptors on the postsynaptic membrane before being degraded by acetylcholinesterase. ACh acts as a neurotransmitter in both the central and peripheral nervous systems, including at neuromuscular junctions, autonomic ganglia, and various organs. The document outlines the synthesis, storage, release, mechanisms of action, and degradation of ACh. It also discusses cholinergic drugs that can act as