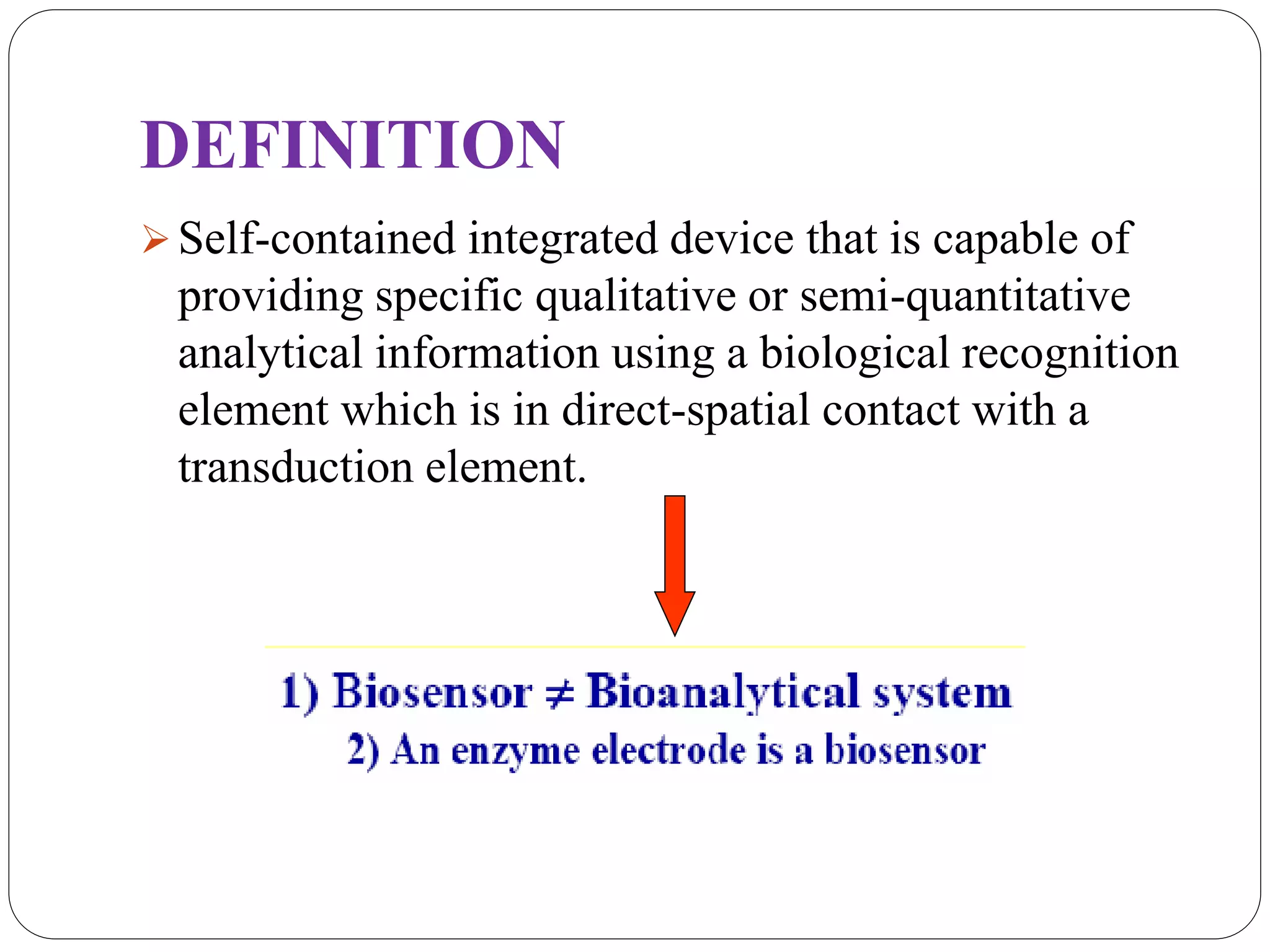
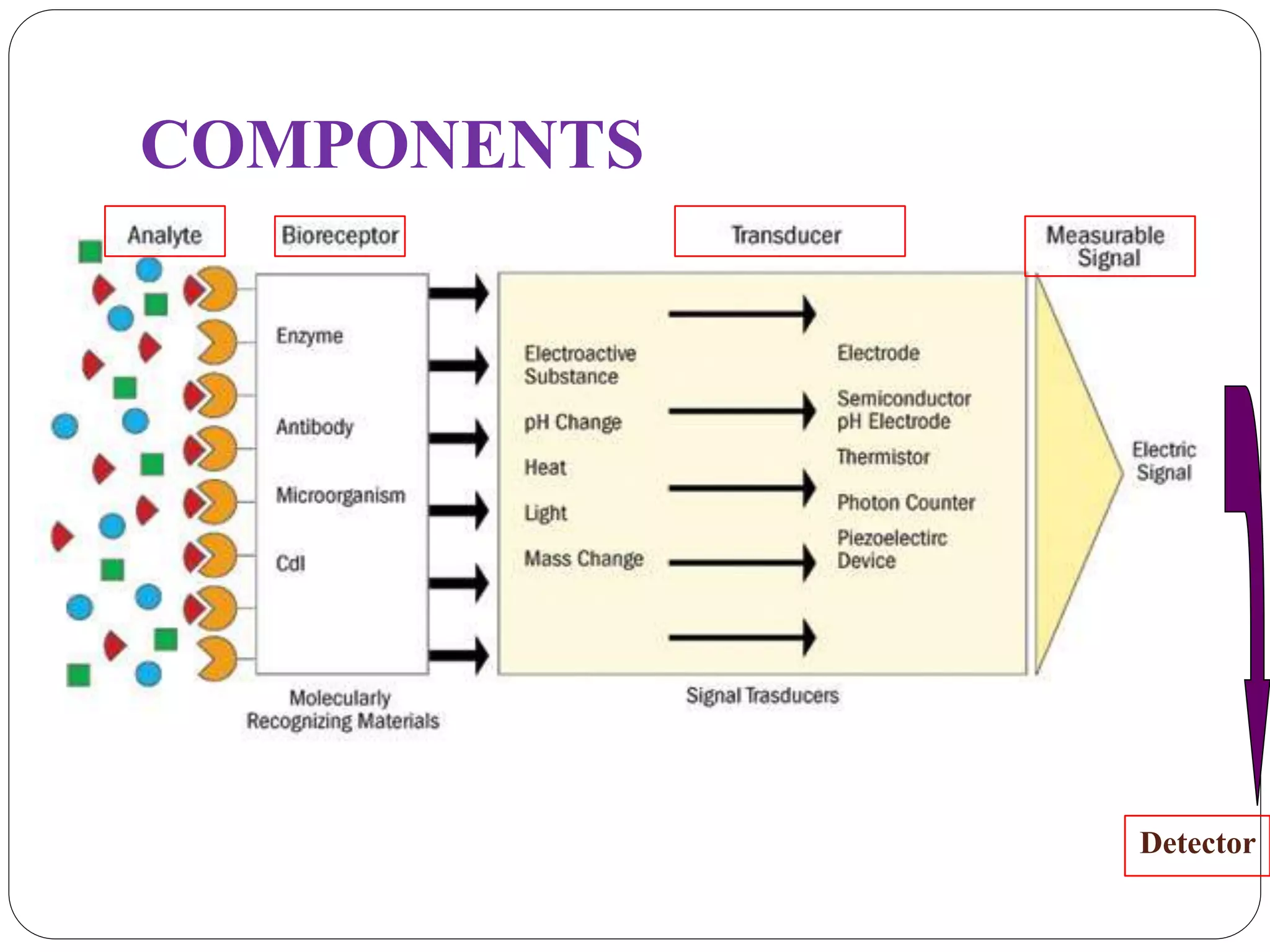
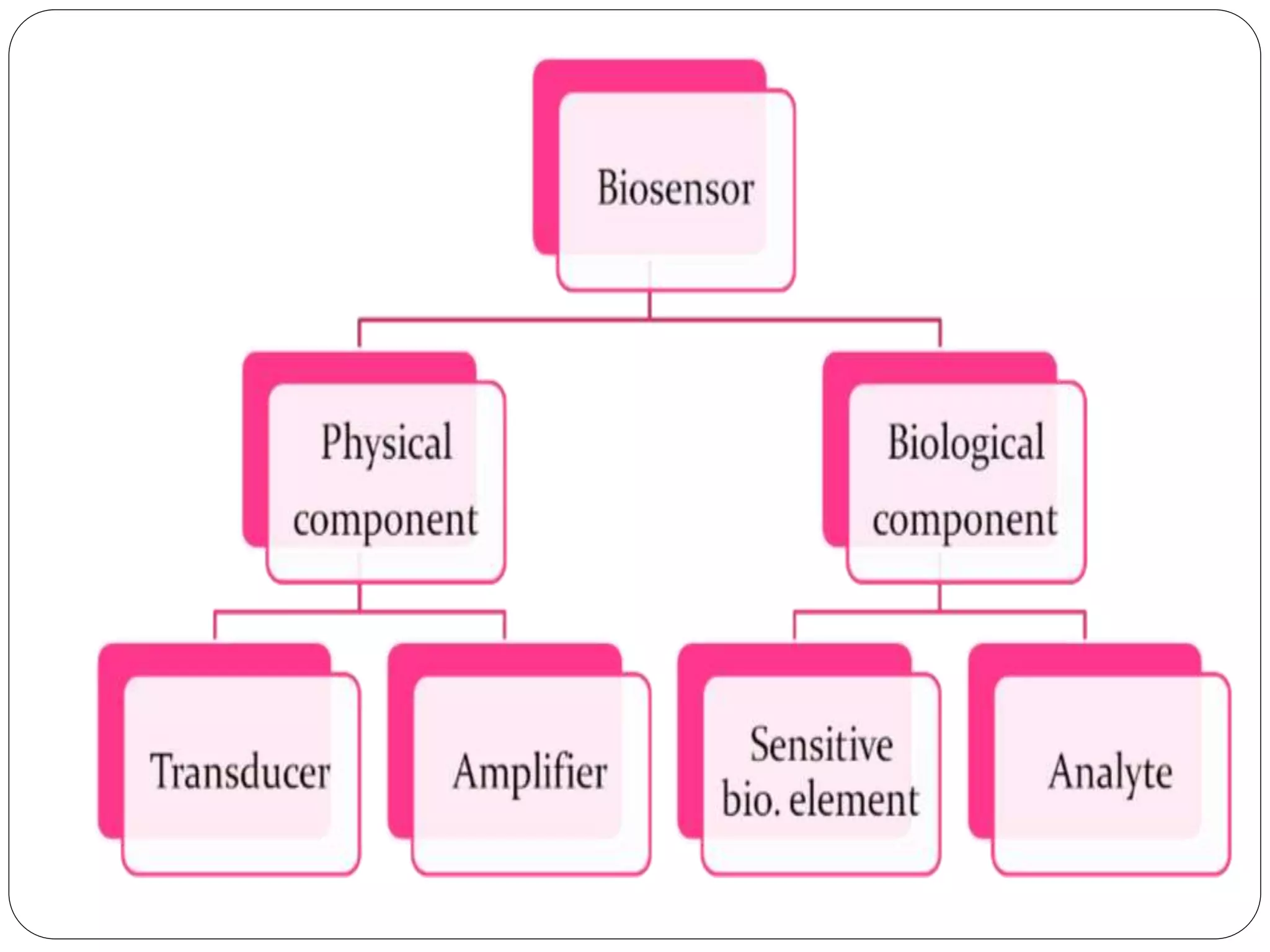
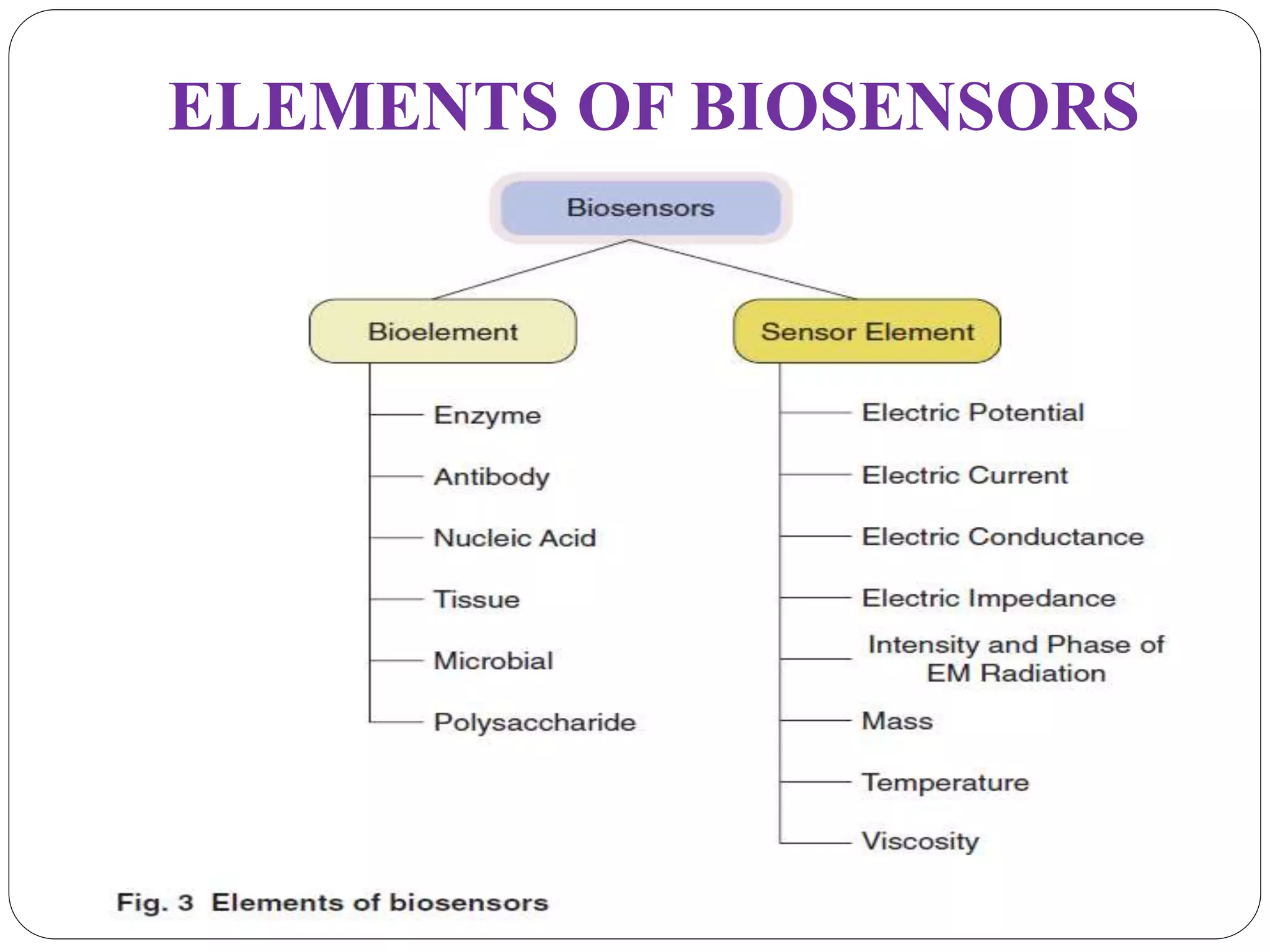
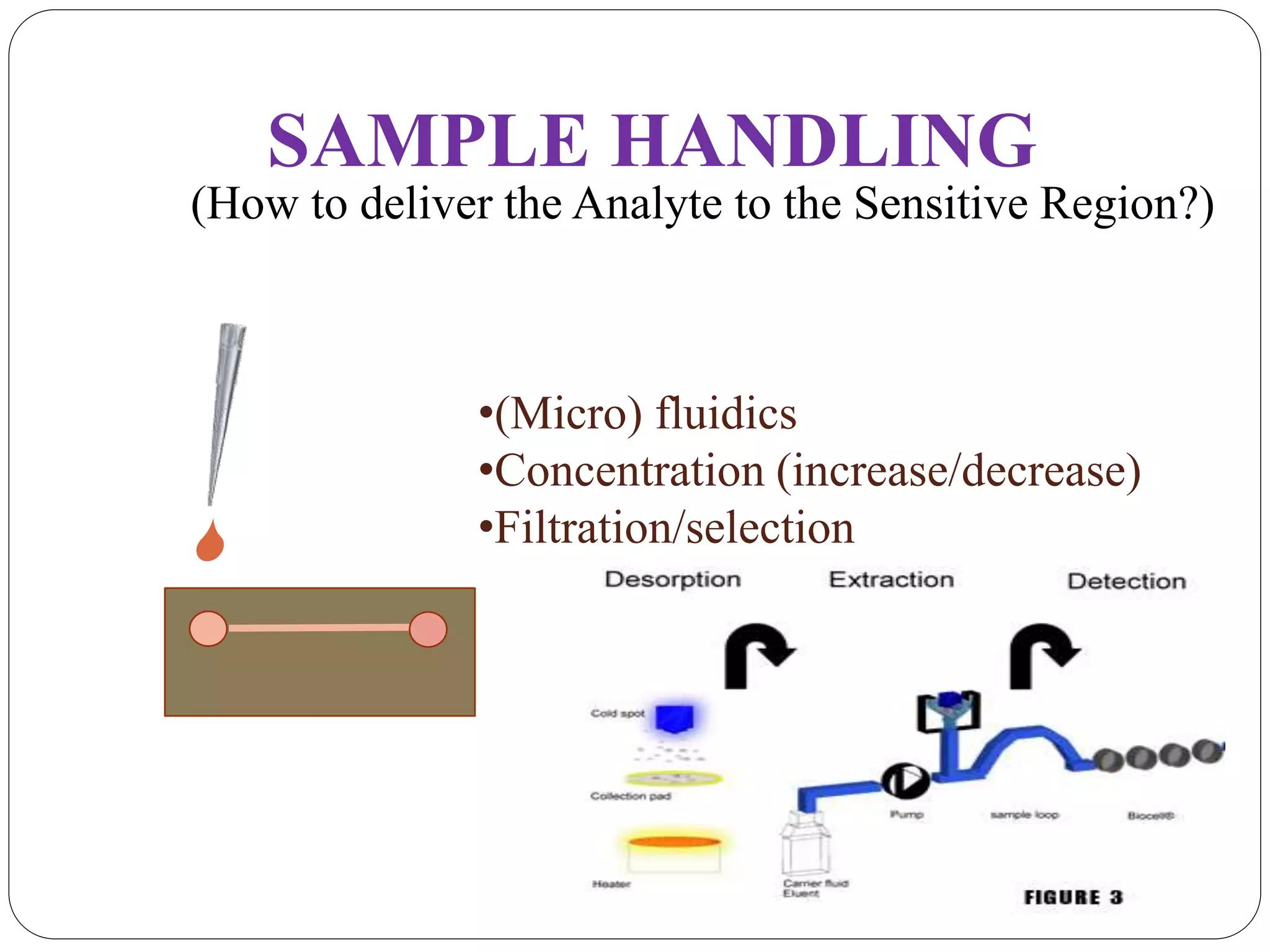
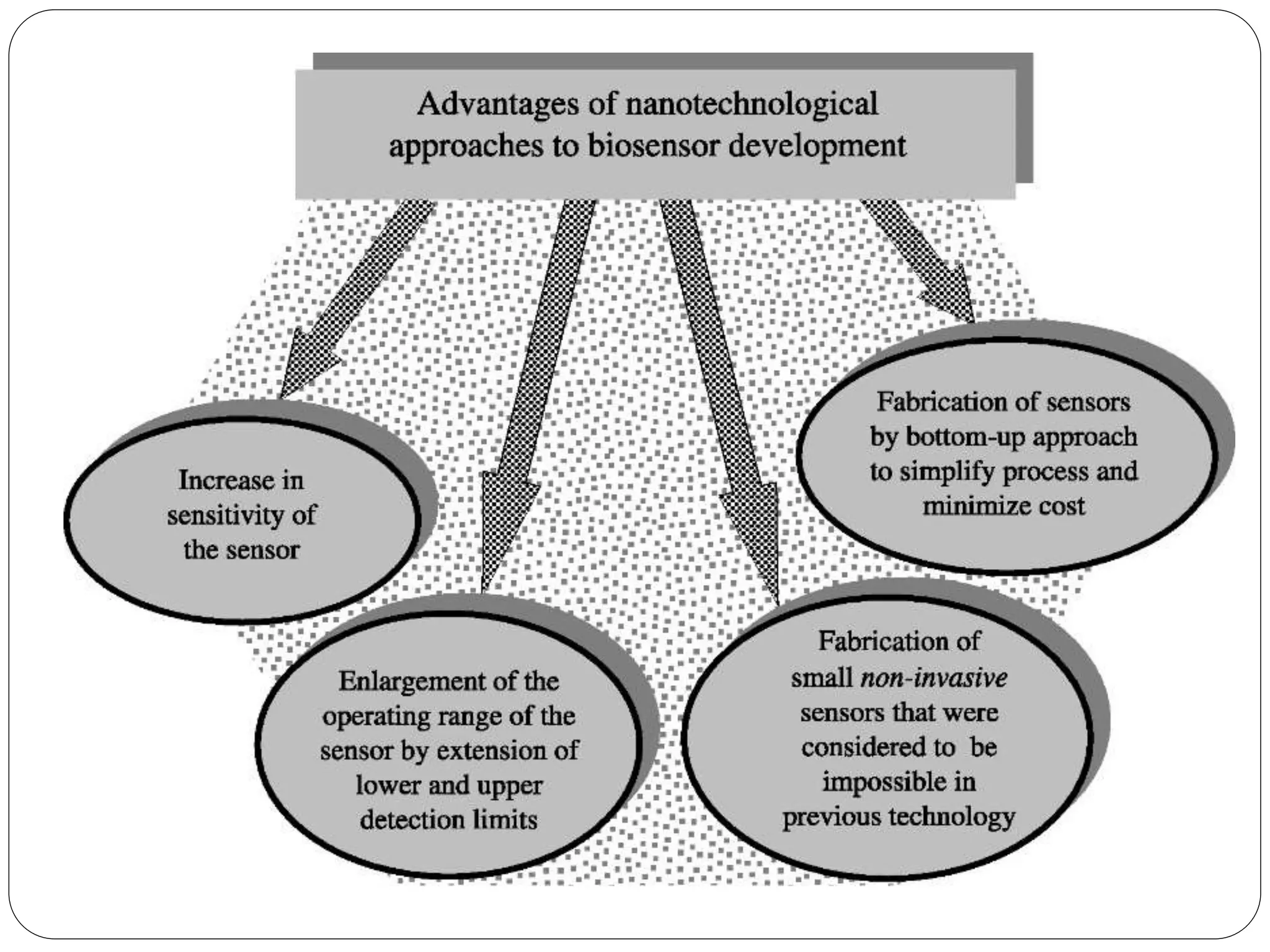
Biosensors integrate a biological component with a transducer to produce an electronic signal proportional to the concentration of an analyte. They have various applications including detecting glucose levels, pregnancy, infectious diseases, and hereditary conditions. Common components are a biological recognition element, transducer to convert biological response into a quantifiable signal, and detector. Examples of sensing techniques include fluorescence, SPR, impedance spectroscopy, and electrochemical methods like amperometric, potentiometric, and conductimetric. Advantages are specificity, small sample size, rapid results, and portability.