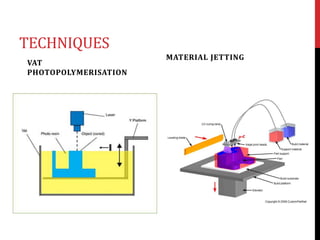
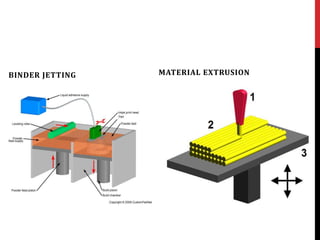
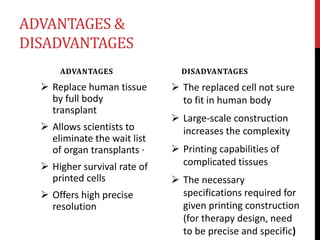
3D bioprinting is a technique that uses 3D printing and viable living cells to print tissue for medical use, such as reconstructive surgery. It works by collecting cells and turning them into "bioink" which is then printed, layer by layer, with hydrogel, to build tissue. Advantages include replacing human tissue without transplants and higher survival rates of printed cells. Disadvantages include ensuring the printed cells properly fit in the body and the complexity of printing complicated tissues. Applications include creating living organs for transplants, testing new drugs on printed cells rather than animals, and direct printing of cells onto the human body.