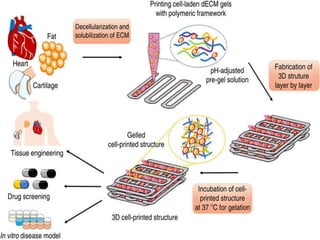
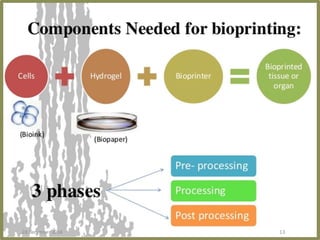
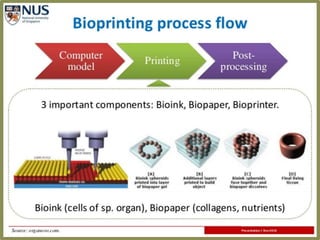
3D bioprinting uses ink made from living cells in a layer-by-layer process to construct human tissues and organs. It begins with bioink and hydrogel loaded into a bioprinter to print the materials onto a biopaper substrate according to a digital model. The biopaper dissolves and layers blend together to build structures which can then undergo stimulation to further develop. Bioprinting addresses the shortage of organ donors for transplantation but faces challenges with keeping cells alive and high costs. Potential applications include tissue engineering and personalized drug delivery.