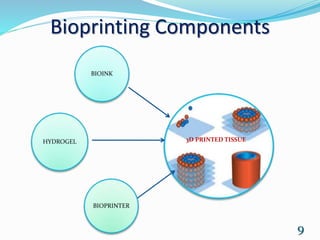
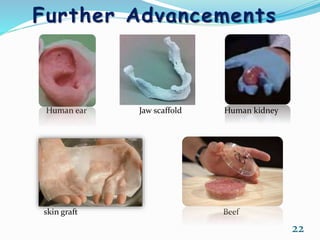
3D bioprinting is a process that uses 3D printing technologies to deposit bioinks containing living cells in layers to create tissue structures while maintaining cell viability. It has applications in printing tissues and organs, drug testing, and scaffolds. The process involves pre-bioprinting steps like obtaining medical scans and preparing cells and bioinks, bioprinting which deposits the materials layer by layer, and post-bioprinting incubation and stimulation to develop cell interactions and tissue growth. There are three main bioprinting approaches - biomimicry which duplicates natural structures, self-assembly using embryonic development models, and mini-tissue building blocks. Inkjet and robotic printers are commonly used to deposit materials. Ch