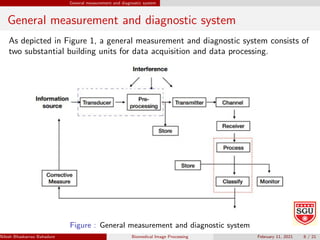
Nilesh Bhaskarrao Bahadure presents information on biomedical image processing and signal analysis. The document discusses biomedical signals, their origin and dynamics, and processing techniques. It explains that physiological processes produce signals that can provide information about health and disease states. Advanced signal processing is needed to extract clinically relevant data from complex biomedical signals. The document also describes computer-aided diagnosis systems, which apply computer technology to medical imaging to assist physicians' clinical decision making and improve diagnostic accuracy.