This document provides an overview of topics in biomedical instrumentation and signal processing including:
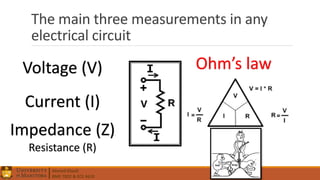
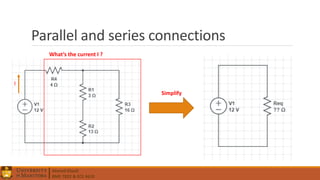
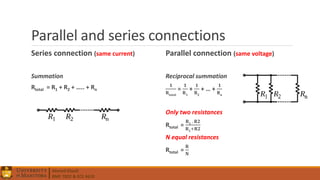
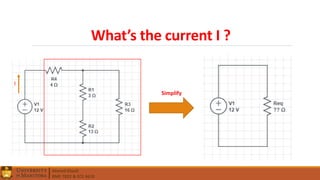
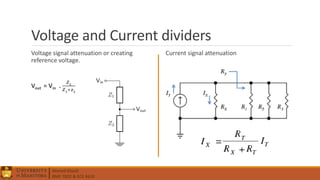
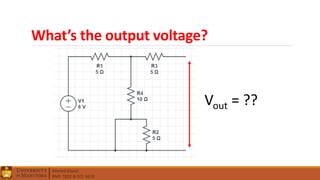
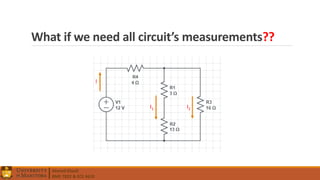
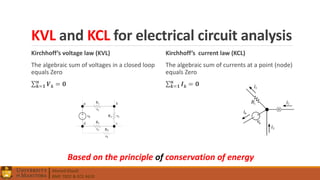
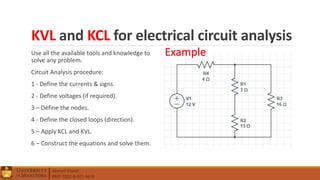
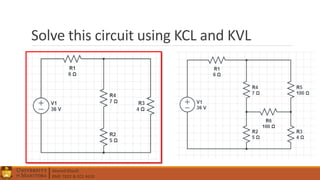
1. Circuit analysis concepts such as Ohm's Law, series and parallel connections, voltage and current dividers, and using Kirchhoff's laws.
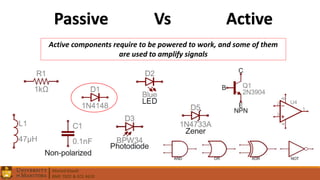
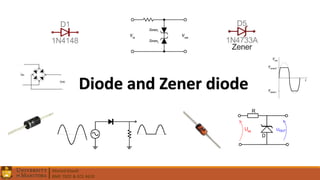
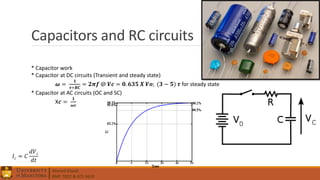
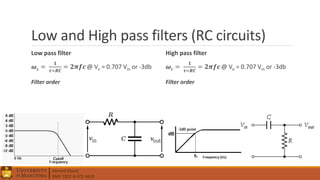
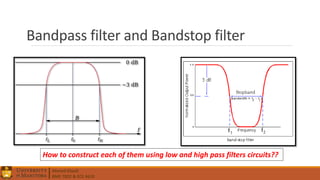
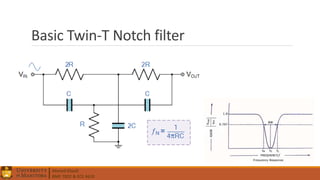
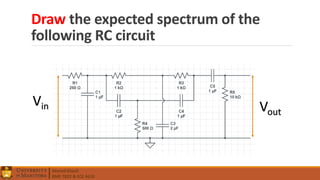
2. Electrical components like diodes, capacitors, and filters.
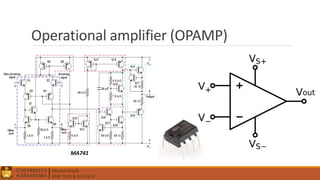
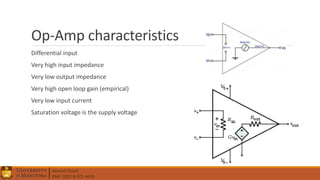
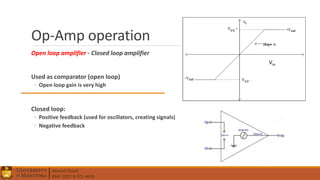
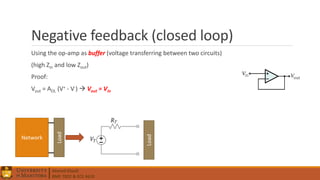
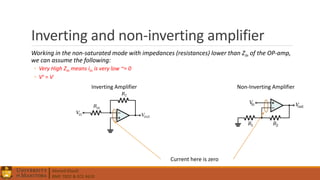
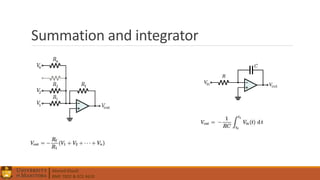
3. Operational amplifiers including their characteristics, operation in open and closed loop configurations, and applications like inverting and non-inverting amplifiers.
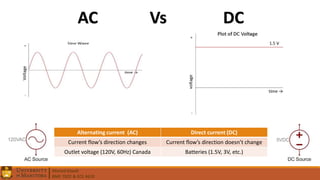
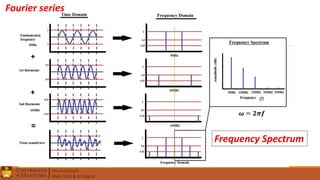
4. Differences between AC and DC signals, passive and active components, and tutorials on specific circuits and concepts.
The document serves as a tutorial covering fundamental electrical engineering and signal processing concepts relevant to biomedical applications.