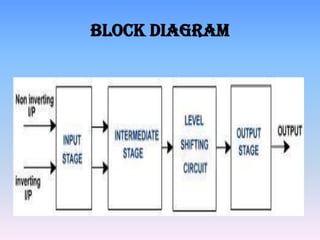
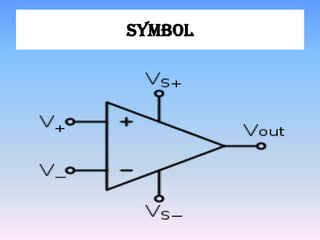
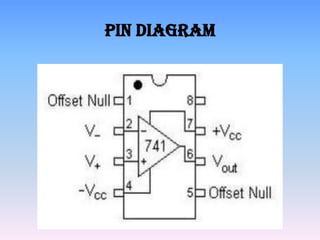
This document discusses operational amplifiers (op-amps). It defines an op-amp as a high-gain direct coupled amplifier consisting of one or more differential amplifiers. It provides a block diagram and symbol for an op-amp. It then explains how an op-amp works by amplifying the difference between its input terminals. Next, it lists several ideal specifications and features of an op-amp including infinite gain, bandwidth, input impedance and more. The document discusses advantages like easy gain adjustment with negative feedback. It provides examples of applications such as filters, oscillators and converters. Finally, it provides references for more information.