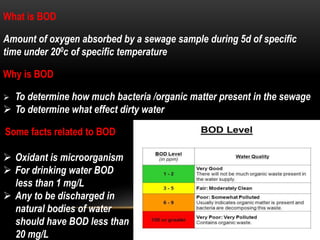
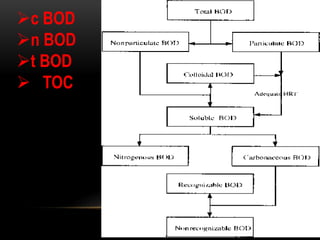
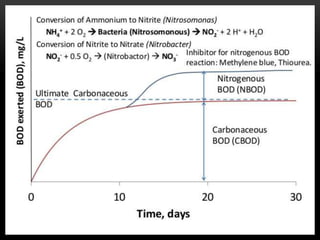
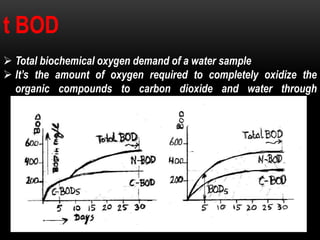
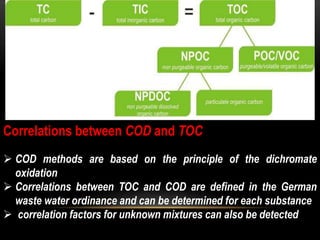
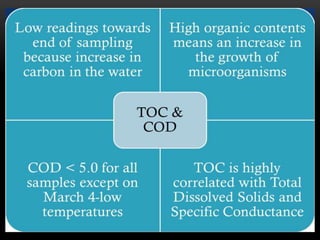
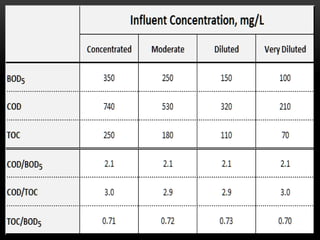
BOD types include carbonaceous BOD (cBOD), nitrogenous BOD (nBOD), and total BOD (tBOD). cBOD measures oxygen depletion from biological organisms breaking down carbonaceous pollutants. nBOD measures oxygen used by autotrophic bacteria to convert ammonia to nitrates through nutrient enrichment. tBOD is the total oxygen required to oxidize all organic compounds through microbial growth. Total organic carbon (TOC) has been standardized to assess organic pollution in water and can correlate to chemical oxygen demand (COD) measurements through dichromate oxidation correlations defined for different substances.