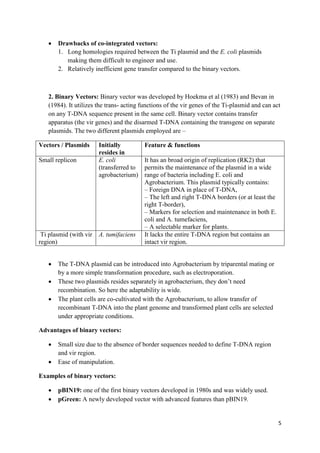
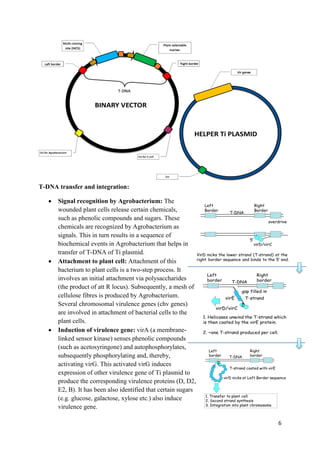
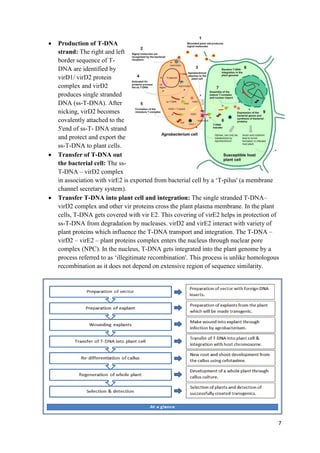
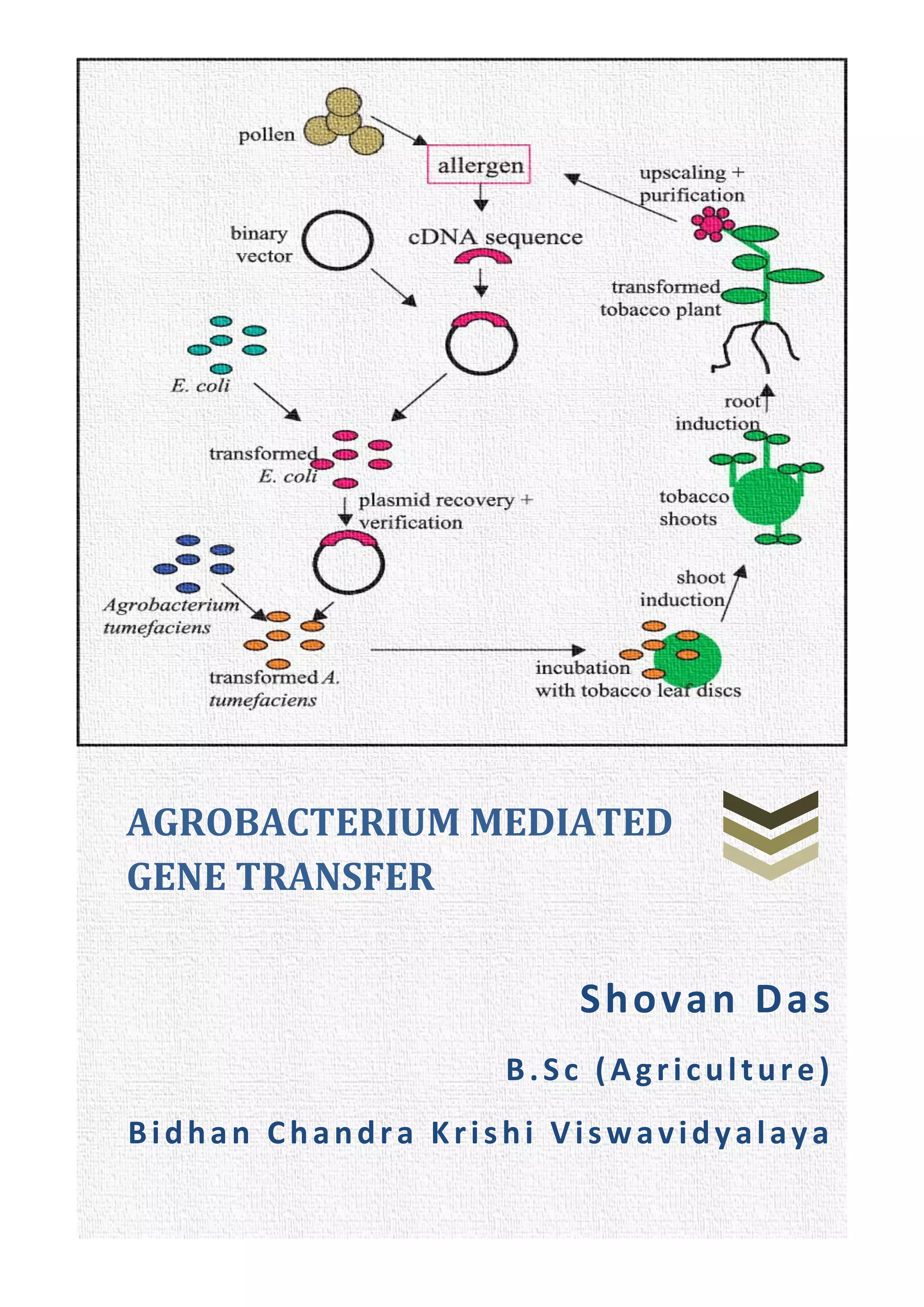
Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer is a method for incorporating foreign genes into organisms, primarily used in plants, where Agrobacterium species serve as vectors to facilitate the transfer. The process involves the use of two types of plasmids: binary vectors and co-integrated vectors, with the binary vectors being more efficient and easier to manipulate. Key features include the role of virulence genes in the transfer process, the structure of the T-DNA, and the significance of signal molecules released from wounded plant cells.

![3
trns2 (iaaM, auxB) Indoleacetamide hydrolase Auxin synthesis
trnr (ipt, cyt) Isopentyltransferase Cytokinin synthesis
trnL Unknown Unknown, mutations affect
tumour size
frs Fructopine synthase Opine synthesis
mas Mannopine synthase Opine synthesis
ags Agropine synthase Opine synthesis
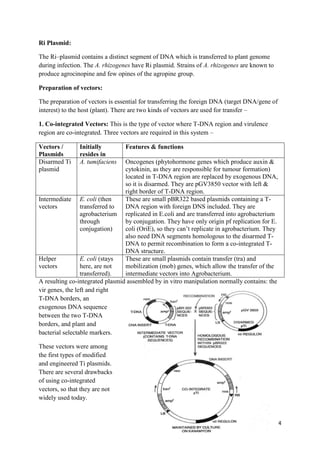
Opine catabolism region: Genes are carried on this region allow the bacterium to
utilize opines as nutrient.
Origin of replication (Ori): Replication of DNA of that plasmid starts from here.
Virulence region: Virulence region (30 kb) consists of 24 genes which code for
proteins that prepare the T-DNA and the bacterium for transfer. Virulence genes are
located in 8 operons from virA to virH. vir A,F,G are monocistronic operons, whereas
vir B,C,D,E,H are polycistronic.
Operons Function/s
virA Chemoreceptor (senses acitosyringone & alpha hydroxy acitosyringone),
activator of virG. It is activated after binding with phenolic compound and
cause auto-phosphorylation due to auto-kinase activity on histidine residue
of vir A.
virB Transmembrane complex (conjugational pores between plant cell and
bacteria). VirB11 has ATPase activity and generate ATP needed for the
delivery of T-DNA into the plant cells.
virC Host-range specificity. Helps in DNA transfer (VirC1 specifically binds to
overdrive sequence and stimulates the transfer process. Agrobacterium
tumefaciens uses type IV secretion system [T4SS] to transfer T-DNA
complex to its host cells. T4SS also known as mating pair formation
apparatus is a cell envelope spanning complex. T4SS form a pore or
channel).
virD Site-specific endonuclease, essential for cleavage of super coiled stranded
substrate. VirD1 has topoisomerase activity and VirD2 has endonuclease
activity.
virE T-DNA processing and protection (it bind to the single stranded DNA and
protect it from nuclease action).
virF Host range specificity. It directs the T-complex (virD4, virB1, virB2, T4SS)
protein for destruction in proteosomes.
virG Positive regulator of vir B, C, D, E, F. (virA cause phosphorylation to VirG
protein and bind with virG forming dimer and then induce the expression of
other operons.
virH Encodes P-450 type monooxygenases protein. Associated with
detoxification of a variety of compound.
Agrobacterium tumeficiens strains generally produce octapine (arginine + alanine) or
nopaline (arginine + glutamine).
Agrobacterium rhizogenes produce either agropine or mannopine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agrobacteriummediatedgenetransfer-200913160405/85/Agrobacterium-mediated-gene-transfer-LIKE-NEVER-BEFORE-4-320.jpg)