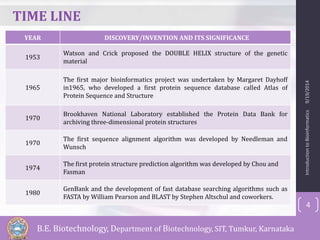
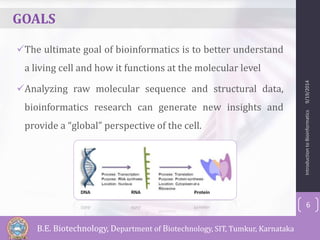
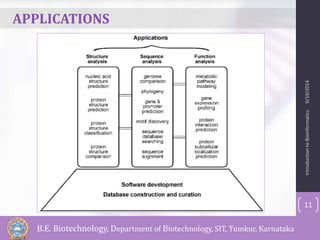
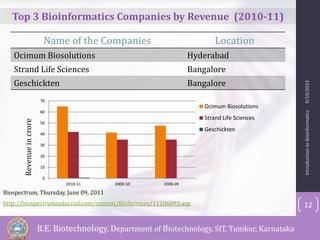
Bioinformatics is defined as the field that studies biology using computers and information technology. It involves the collection, storage, and analysis of molecular biological data using techniques from computer science and statistics. Some key events in bioinformatics include Watson and Crick proposing the DNA double helix structure in 1953, and the development of sequence alignment and structure prediction algorithms in the 1970s. Bioinformatics aims to better understand living cells at the molecular level by analyzing raw molecular sequence and structure data. It provides globally accessible databases and analysis tools to enable sharing and study of biological data.