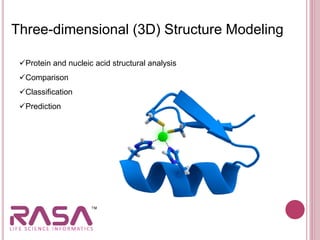
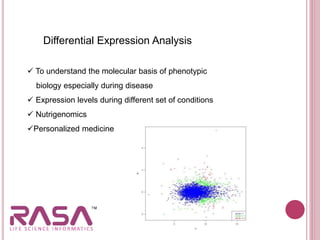
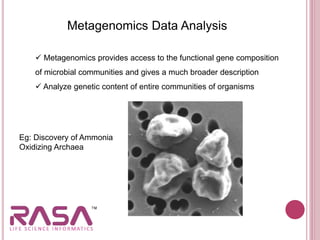
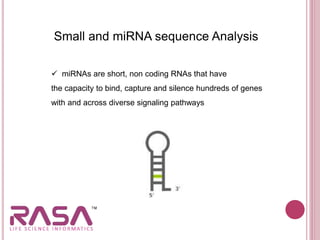
This document discusses the role of bioinformatics in biotechnology applications. It summarizes that bioinformatics has become essential for analyzing the vast amounts of genomic data generated from sequencing projects. It provides examples of how bioinformatics tools can be applied to microbial genome analysis, molecular medicine, drug development, next generation sequencing, and more. The document also outlines two major fields of bioinformatics - developing computational tools and databases, and generating biological knowledge to understand living systems.







![The Bioinformatics Market
The global bioinformatics market is estimated to reach $13.3 billion by 2020.
Factors for growth :
1] Increasing government initiatives and funding,
2] Growing use of bioinformatics in drug discovery and
biomarkers development
The Hindrance :
1] Factors such as dearth of skilled personnel to ensure proper use of
bioinformatics tools, and
2] lack of integration of a wide variety of data generated through
various bioinformatics platforms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d87bb1f8-6df2-44ee-bf18-aab345e2c83c-151120104139-lva1-app6892/85/Bioinformatics-Applications-in-Biotechnology-16-320.jpg)


