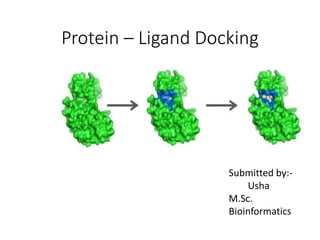
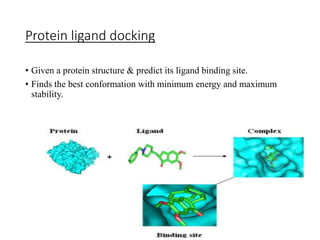
Protein-ligand docking predicts the binding orientation of one molecule to another to form a stable complex. It finds the best conformation with minimum energy and maximum stability by generating multiple poses and scoring them based on binding affinity. Common docking algorithms like AutoDock and GOLD use search methods like genetic algorithms and simulated annealing to find the best binding pose. They evaluate binding free energy terms like hydrogen bonding, electrostatics, and solvation to score and select conformations.