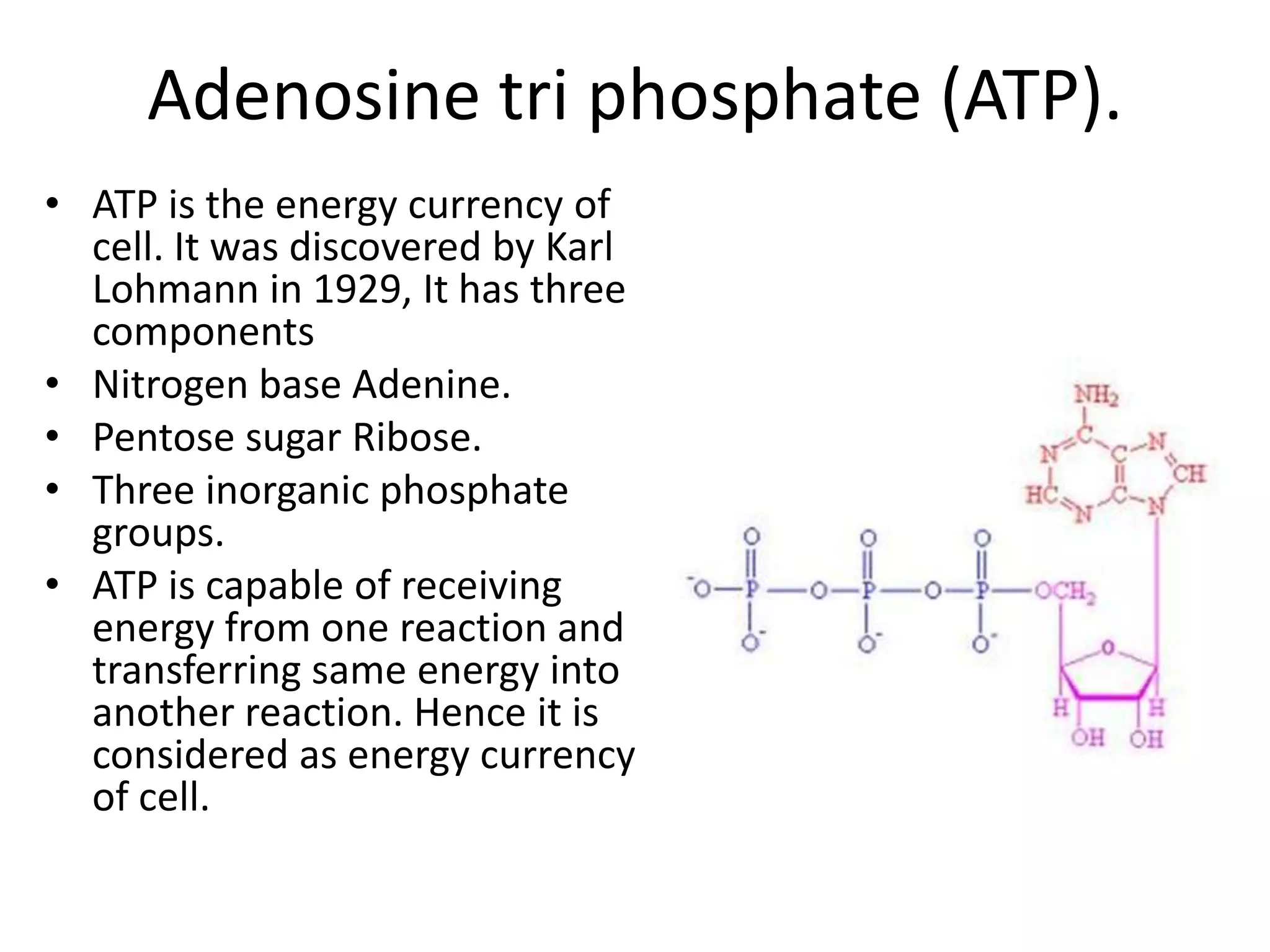
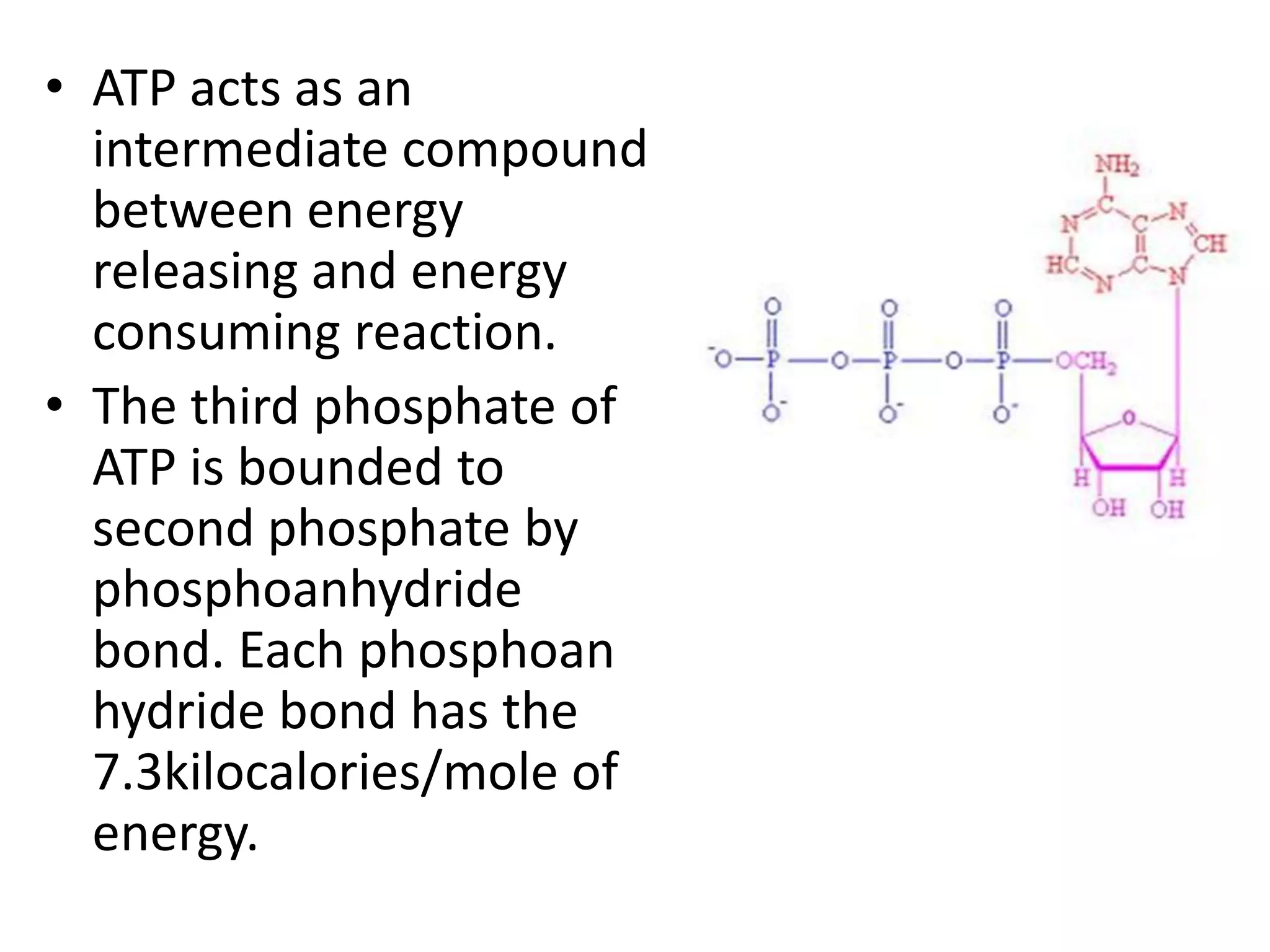
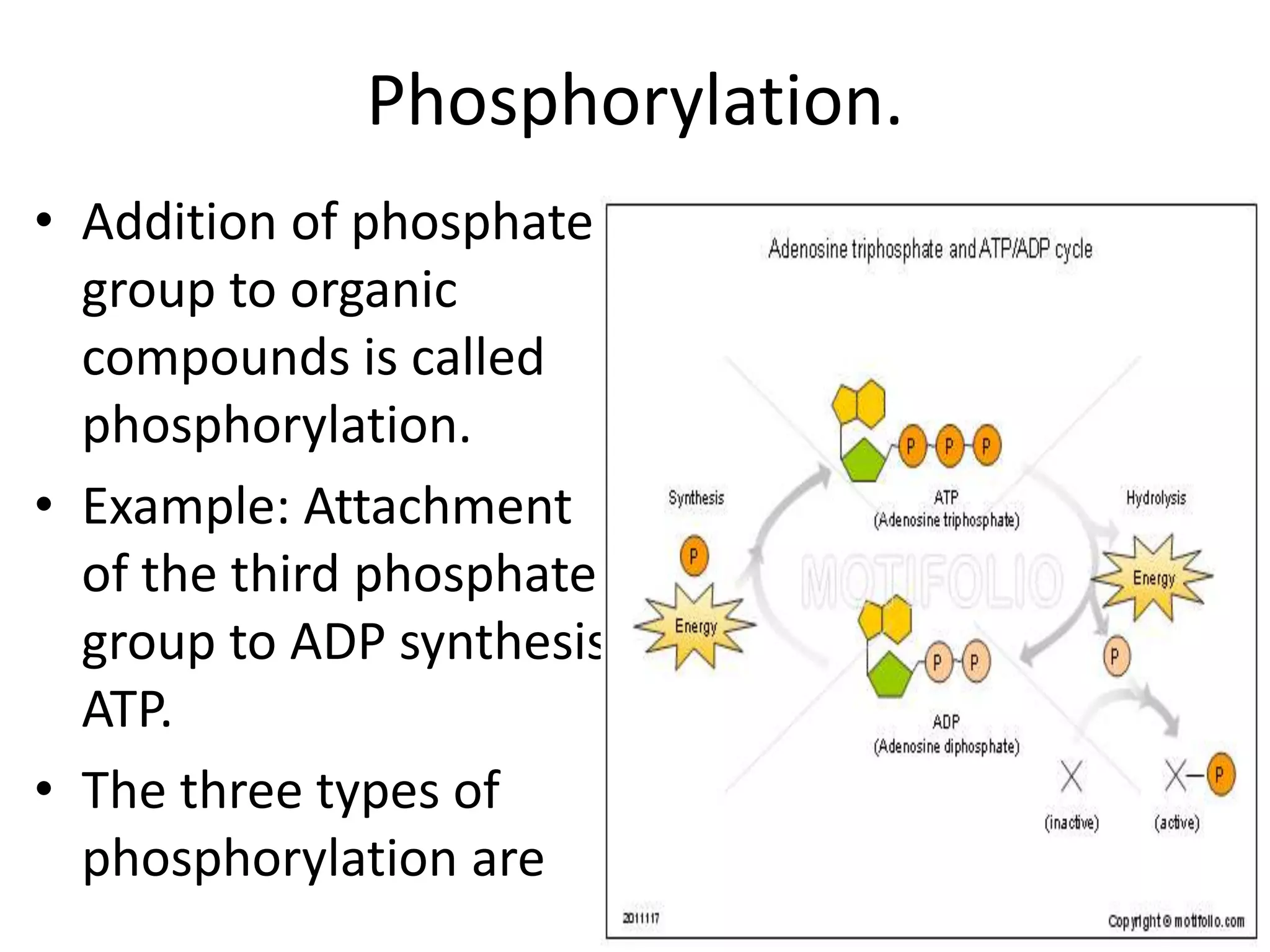
Bioenergetics is the study of energy transformations in living systems. Organisms need energy for physiological activities, which involve chemical reactions. Energy is utilized or generated in these reactions according to the laws of thermodynamics. Light provides energy for all organisms, as green plants capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy stored in glucose. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) acts as the energy currency of cells, containing energy in its phosphate bonds. ATP transfers energy between energy-releasing and energy-consuming reactions through phosphorylation, the addition of phosphate groups. There are three types of phosphorylation: photophosphorylation using sunlight, and oxidative and substrate phosphorylation using energy from oxidation or substrate hydrolysis.