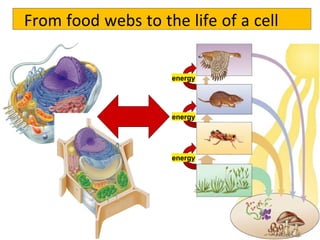
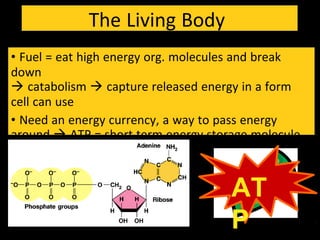
1) All living systems require a constant input of free energy which is obtained from food and transformed through a series of chemical reactions from one form to another.
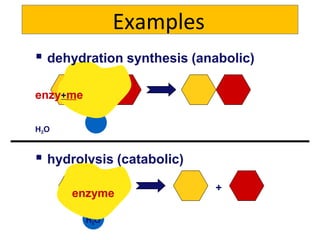
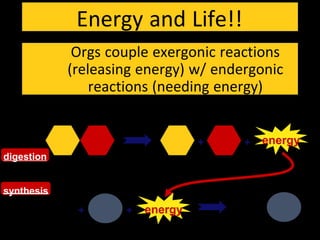
2) Energy is released through exergonic (catabolic) reactions like cellular respiration which break bonds, while endergonic (anabolic) reactions like synthesis require energy to form bonds.
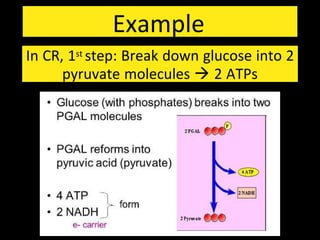
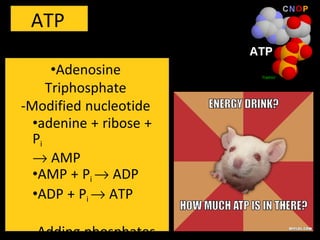
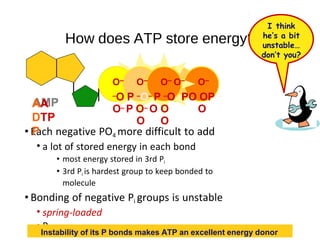
3) ATP acts as a short-term energy storage molecule, transferring energy between reactions by having a phosphate bond that is easily broken to drive endergonic reactions in cells.