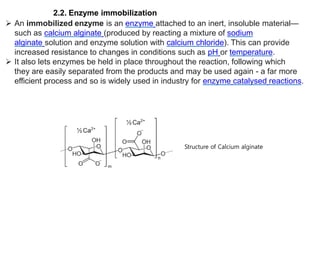
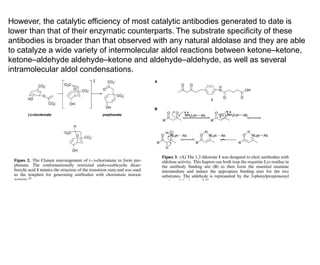
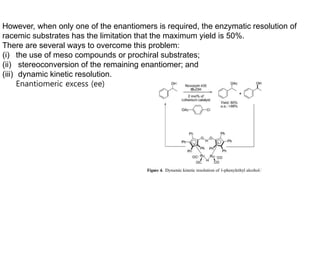
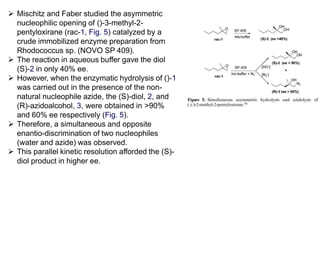
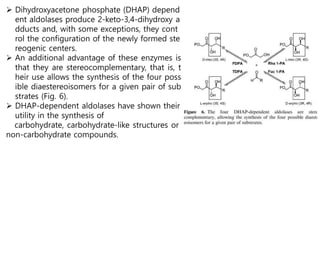
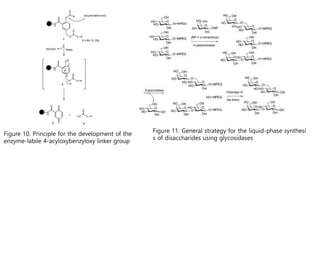
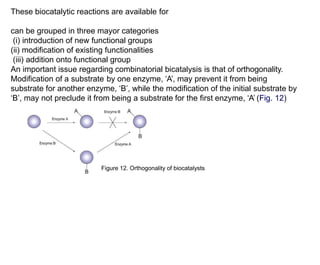
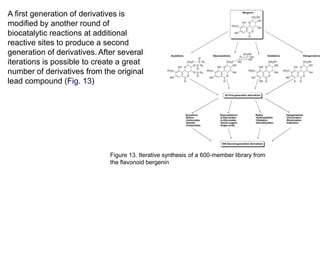
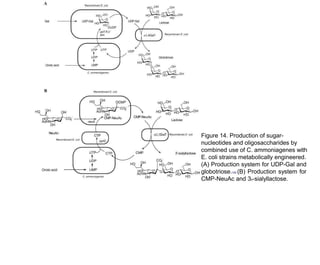
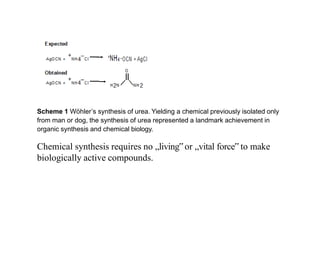
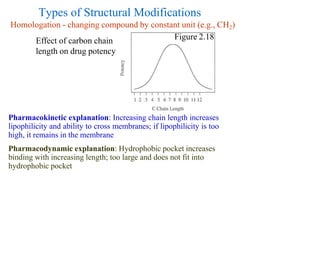
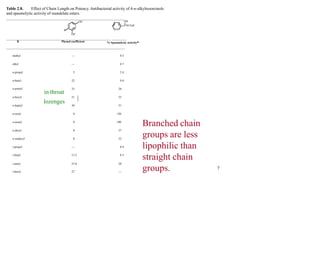
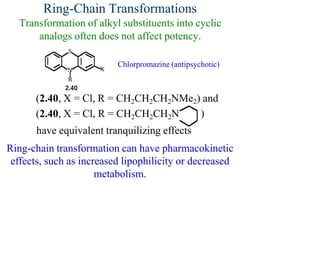
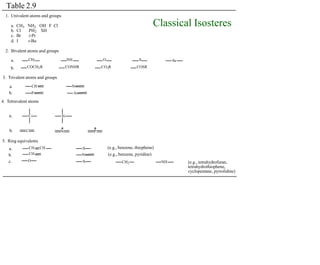
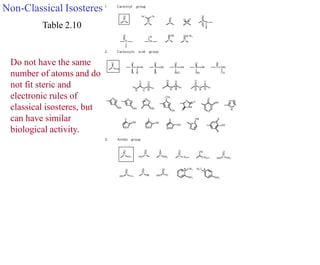
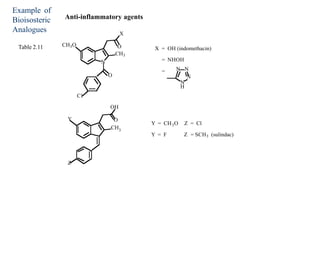
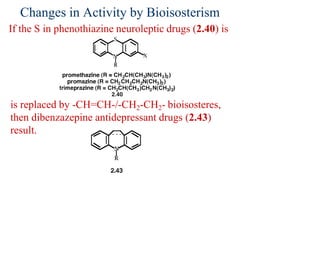
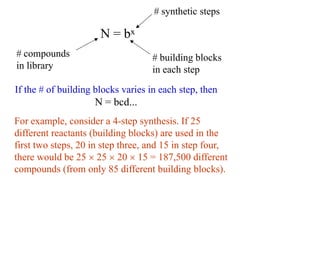
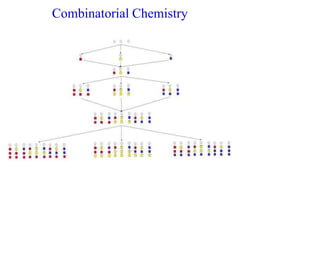
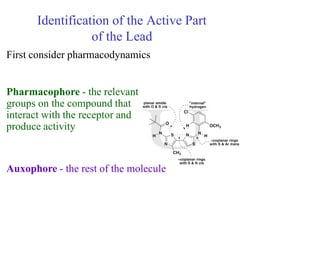
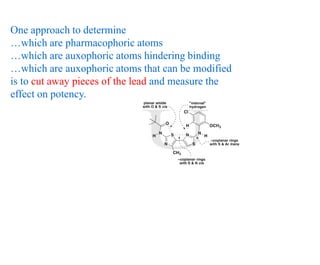
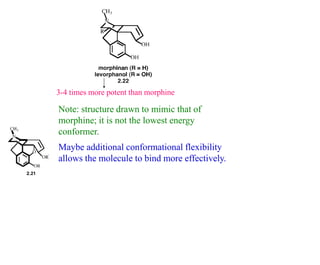
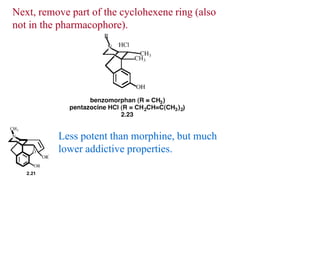
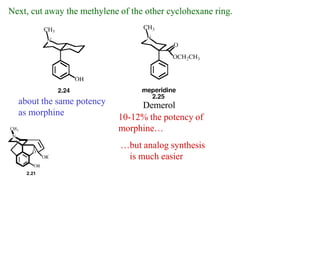
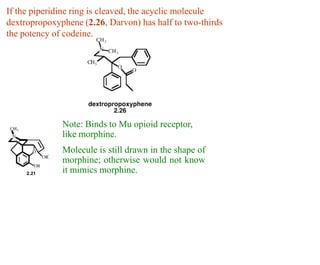
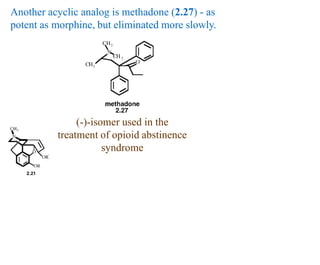
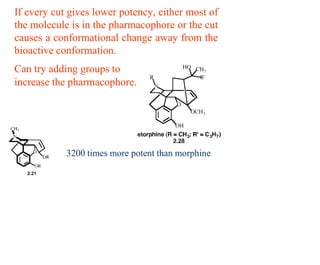
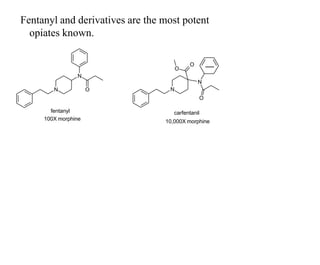
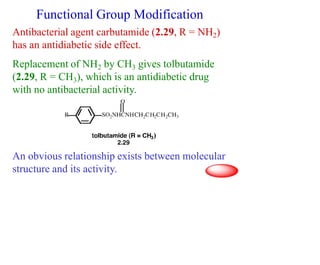
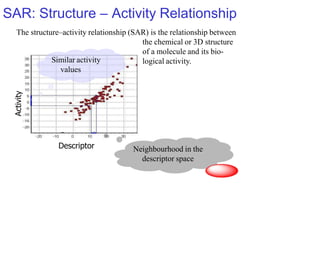
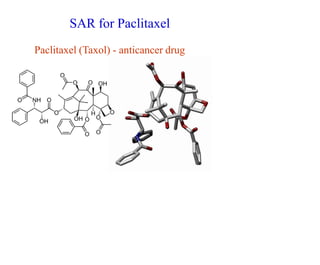
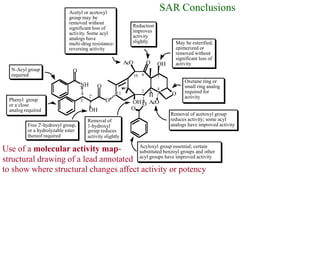
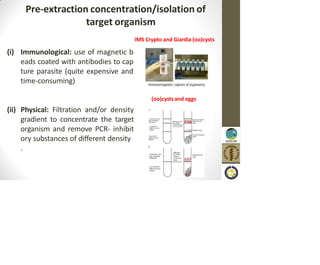
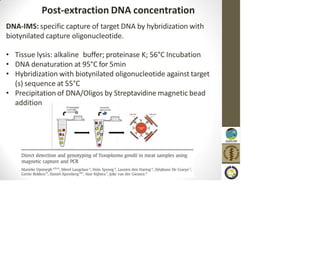
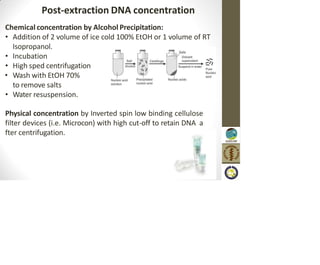
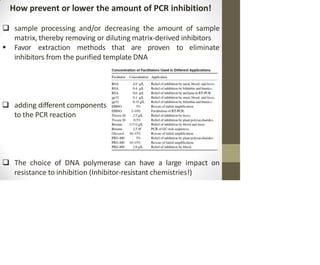
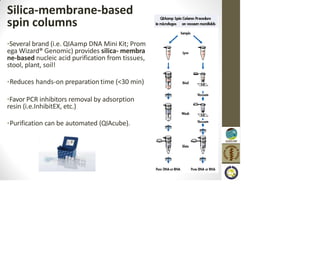
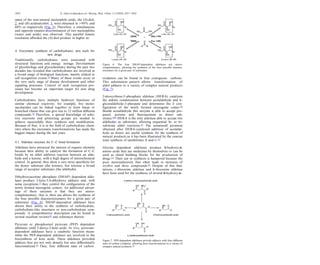
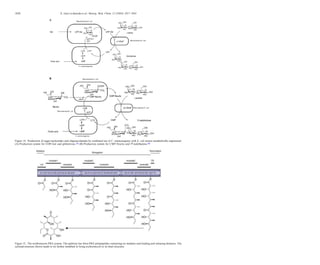
This document discusses the use of enzymes in the synthesis of bioactive compounds. It begins by noting the advantages of enzymes as catalysts such as their selectivity and ability to work under mild conditions. However, their narrow substrate specificity and instability have limited their application. Advances in biocatalysis over the last 20 years have helped address these drawbacks through immobilization, use of enzymes in non-aqueous solvents, and directed evolution. The document then discusses various applications of enzymes including in non-aqueous solvents, immobilization, directed evolution to modify substrate specificity and stability, synthesis of carbohydrates and chiral drugs, and their use in combinatorial chemistry.