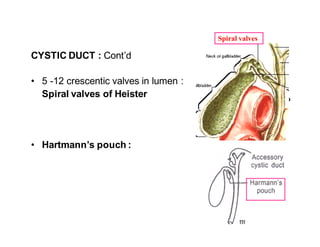
The biliary apparatus includes passages that store and convey bile from the liver to the duodenum. It has two parts: the intrahepatic and extrahepatic parts. The intrahepatic part includes the duct system within the liver while the extrahepatic part includes the right and left hepatic ducts, common hepatic duct, cystic duct, bile duct, and gallbladder. The common hepatic duct joins the cystic duct near the first part of the duodenum to form the bile duct, which opens at the major duodenal papilla. The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile before releasing it through the cystic duct into the common hepatic duct on contraction.