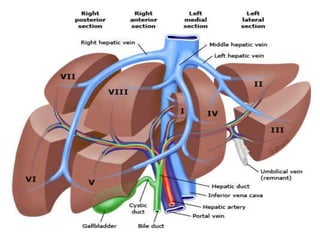
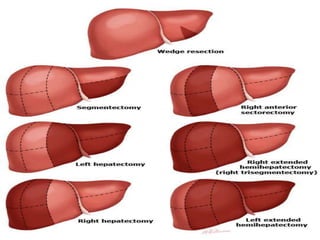
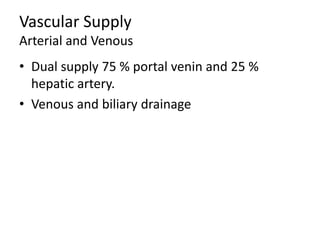
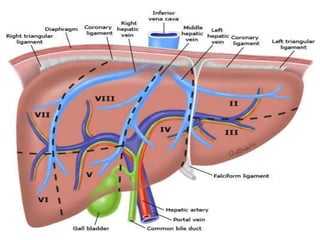
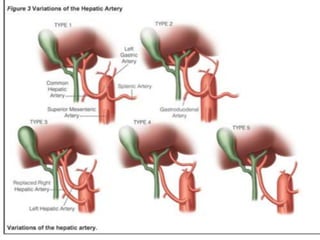
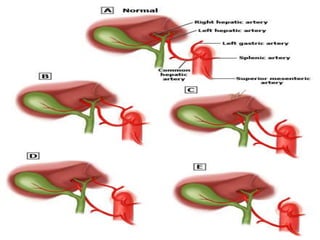
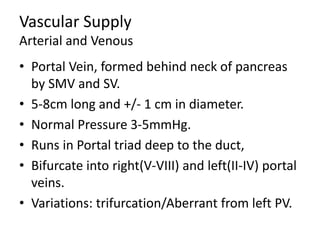
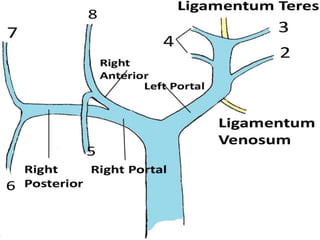
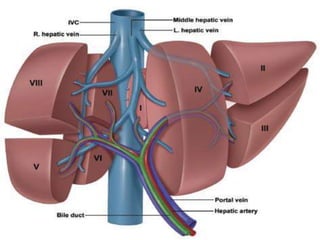
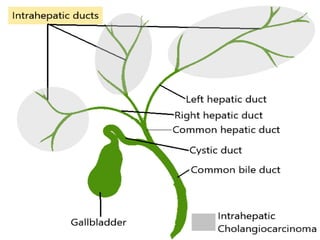
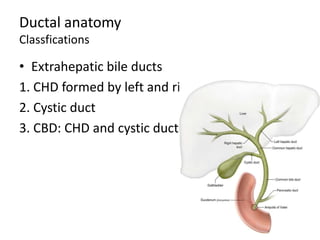
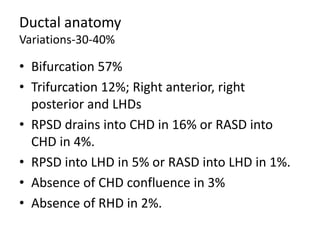
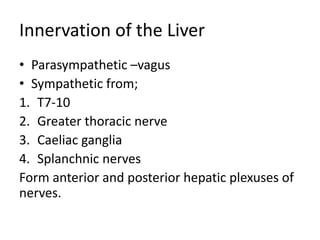
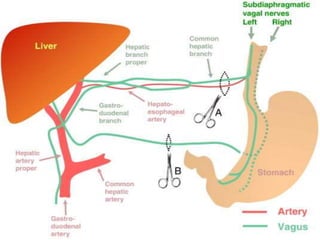
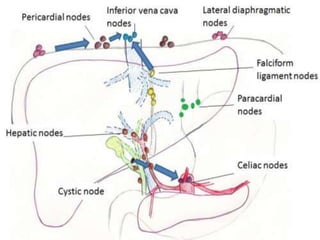
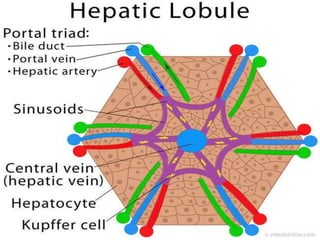
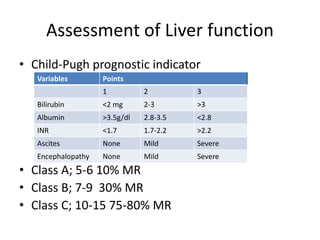
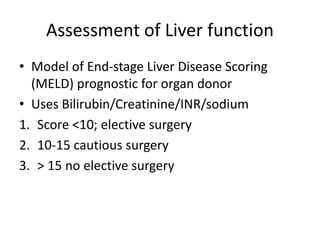
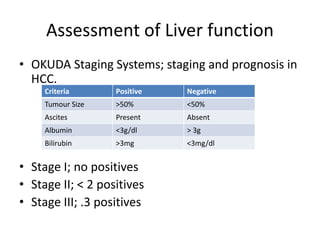
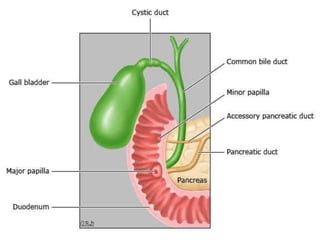
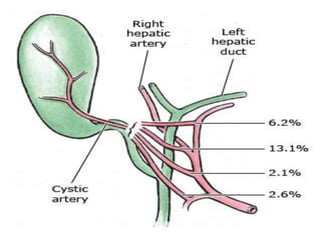
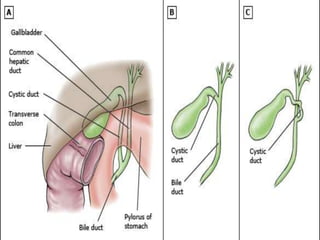
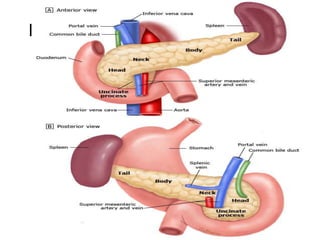
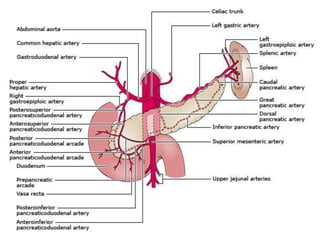
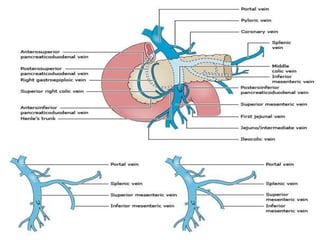
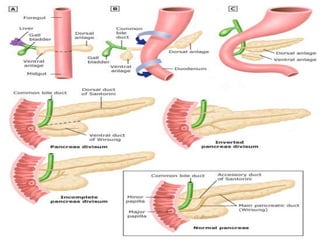
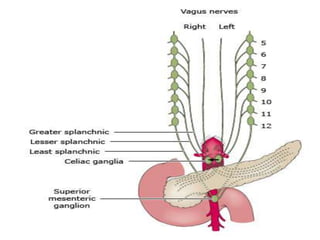
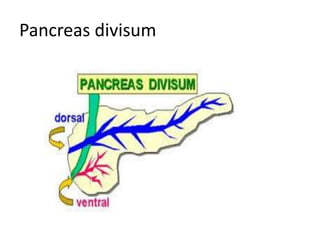
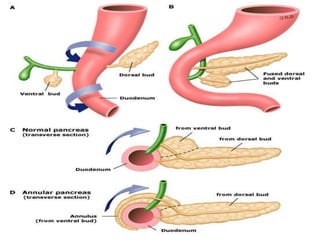
The document provides an overview of hepatobiliary anatomy including the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, pancreas, and spleen. It describes the location, structure, vasculature, innervation, and variations of each organ. Key points include that the liver is the largest organ located under the diaphragm, the gallbladder stores and concentrates bile, and the pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine functions including insulin and enzyme production. Anatomical variations are also discussed for each structure.