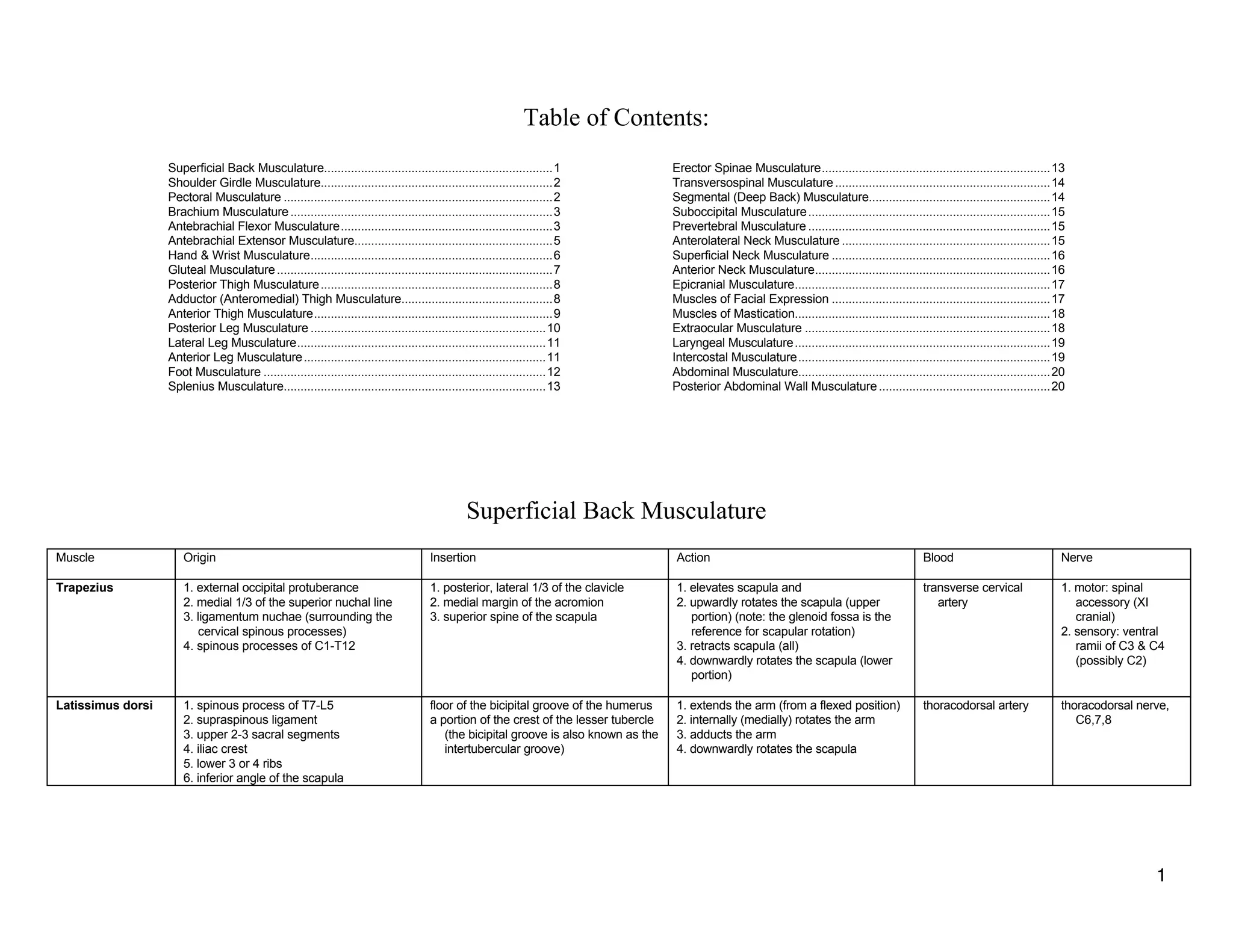
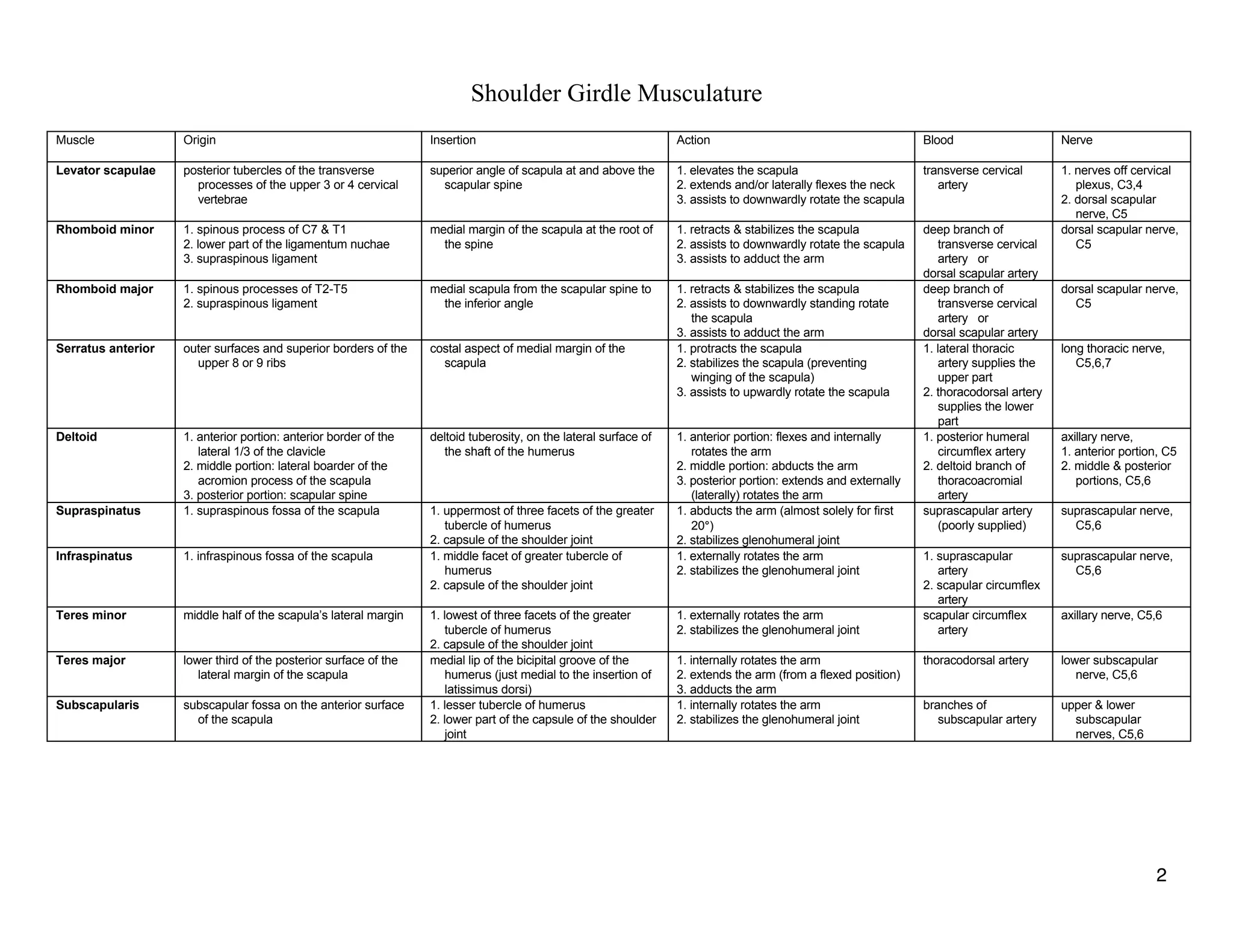
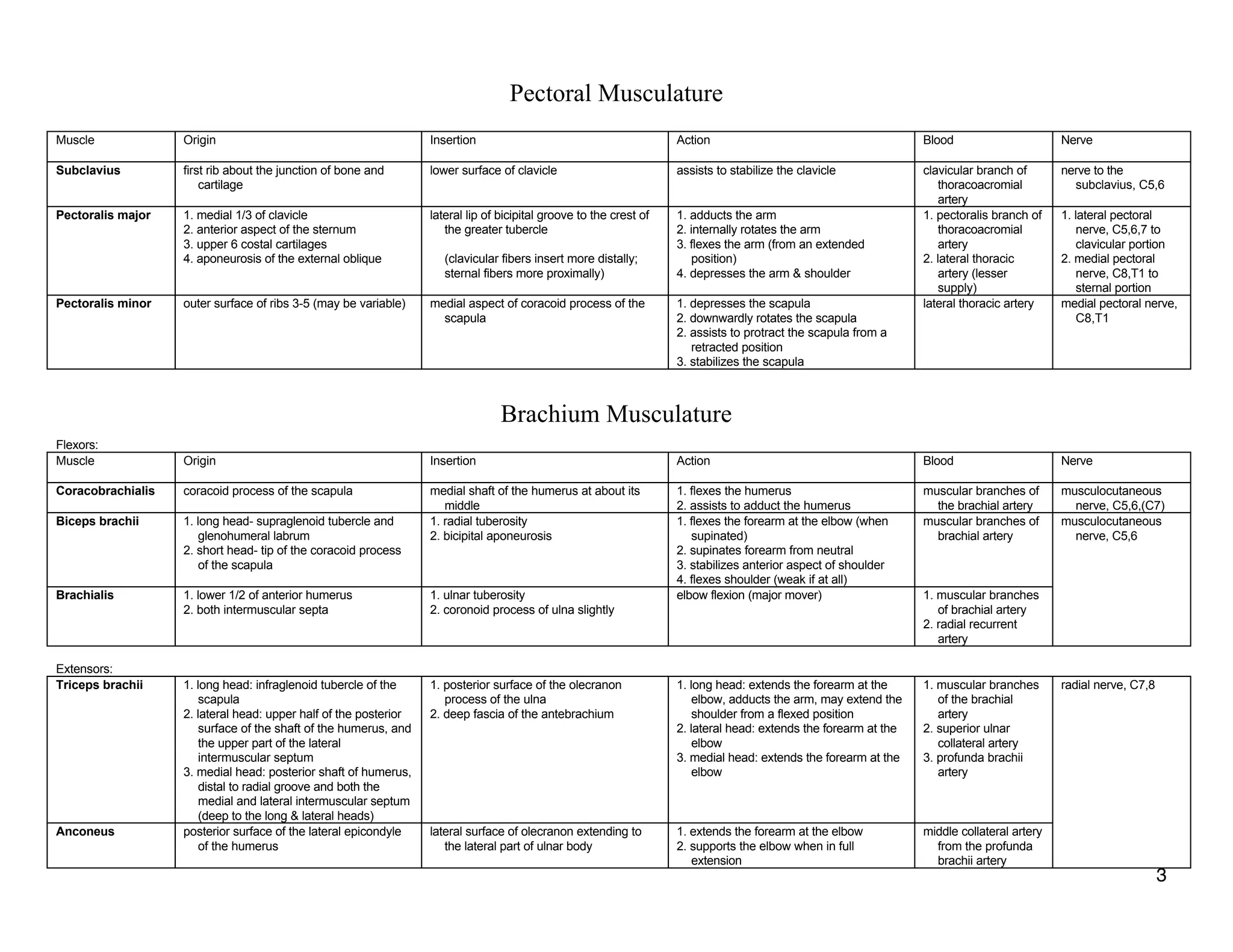
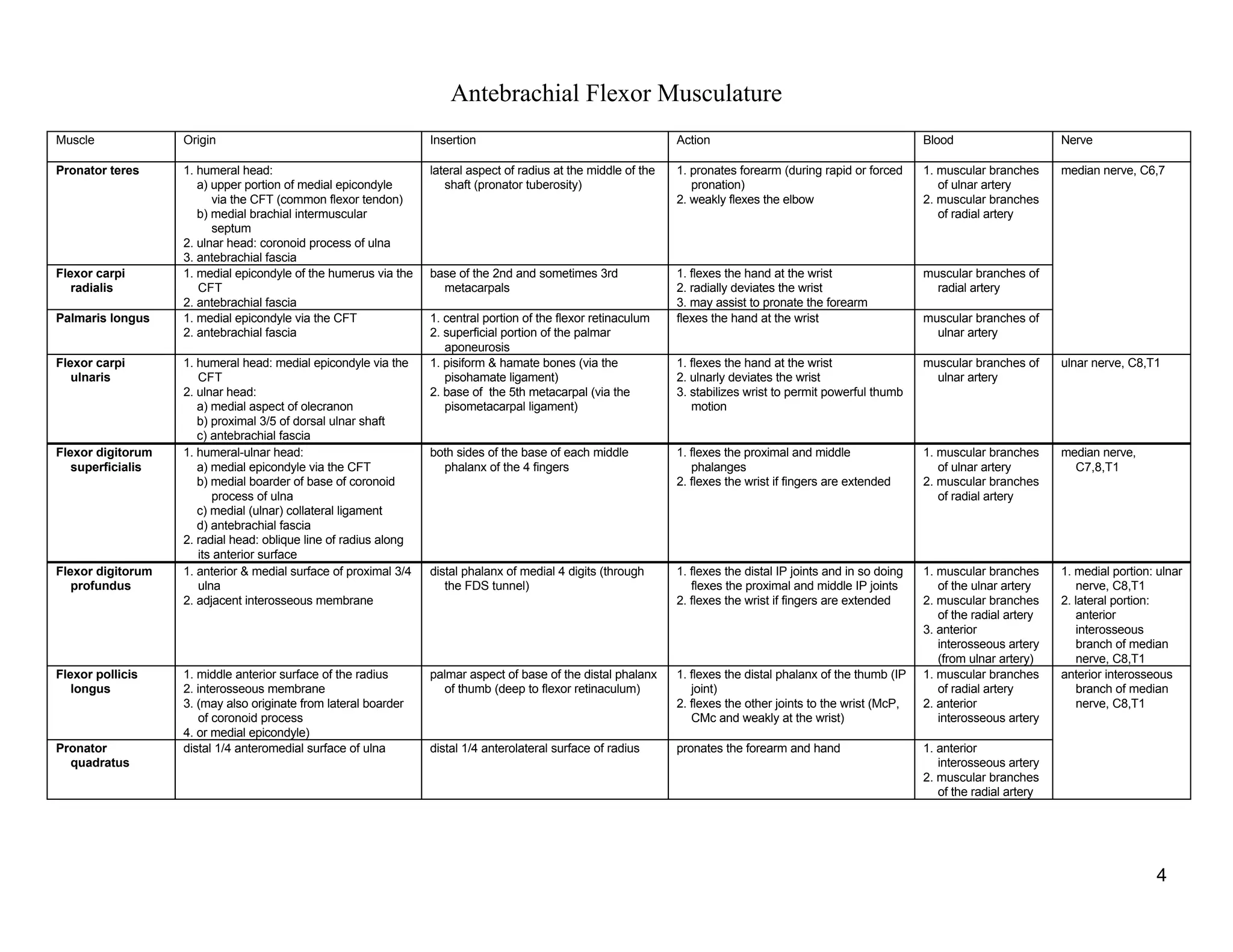
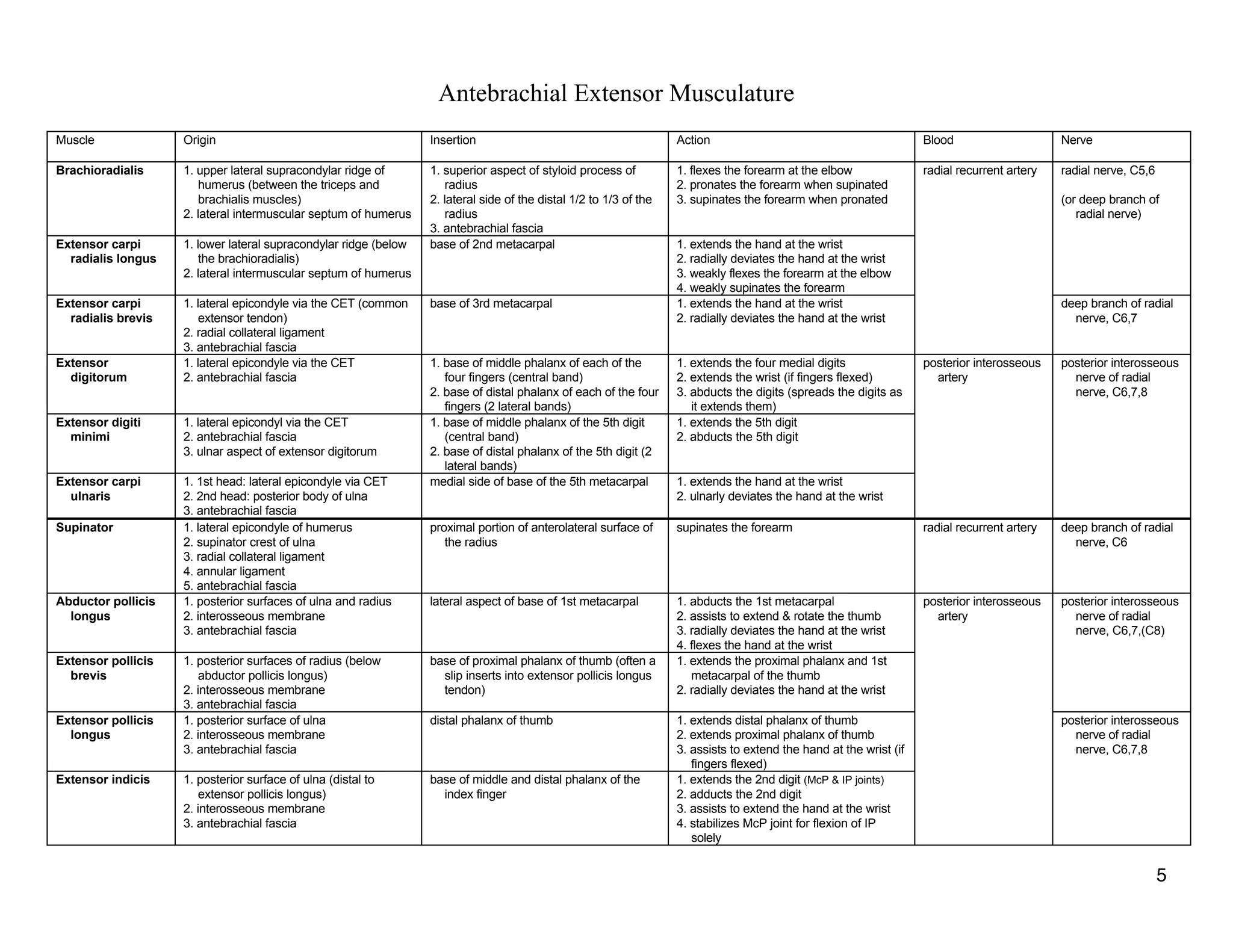
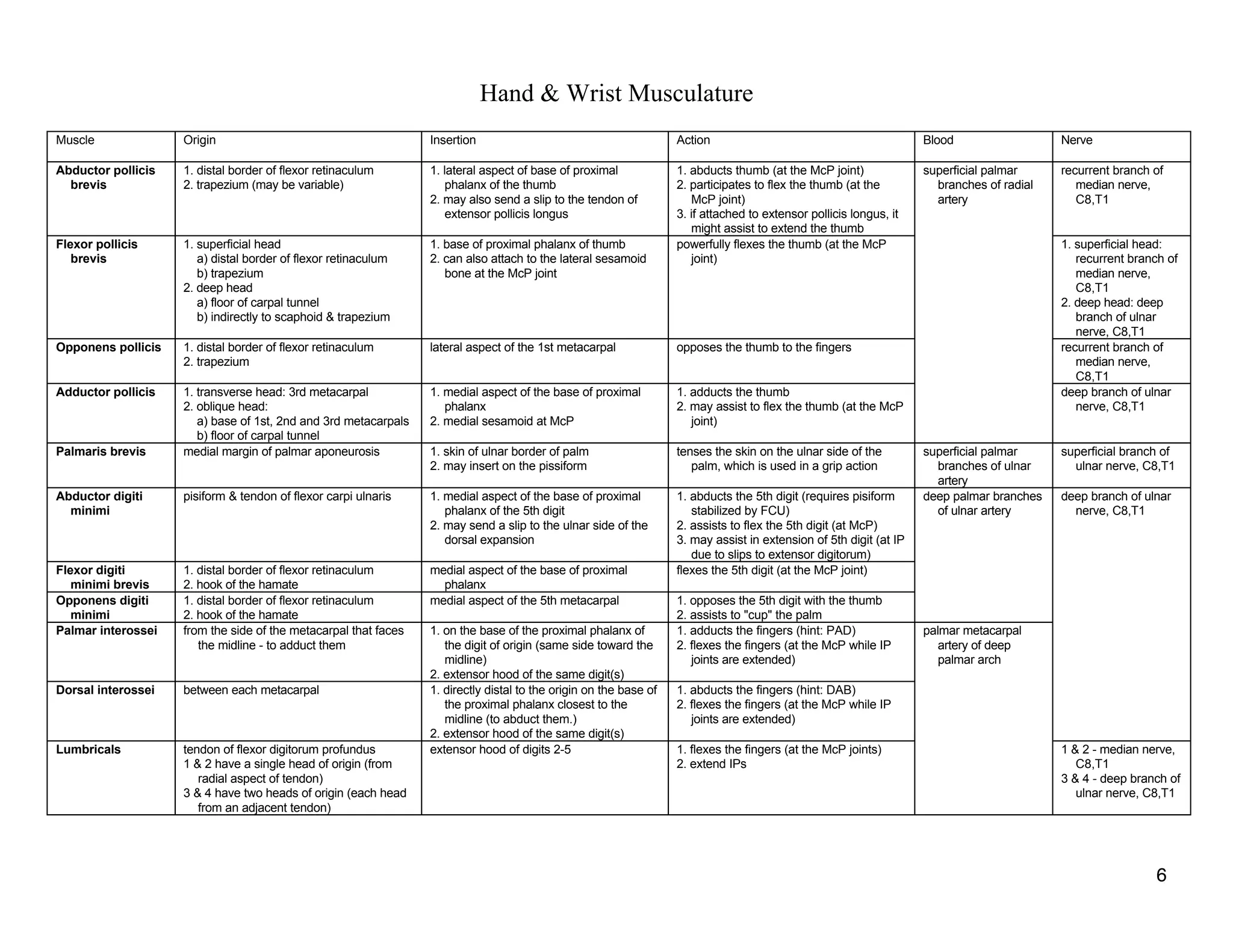
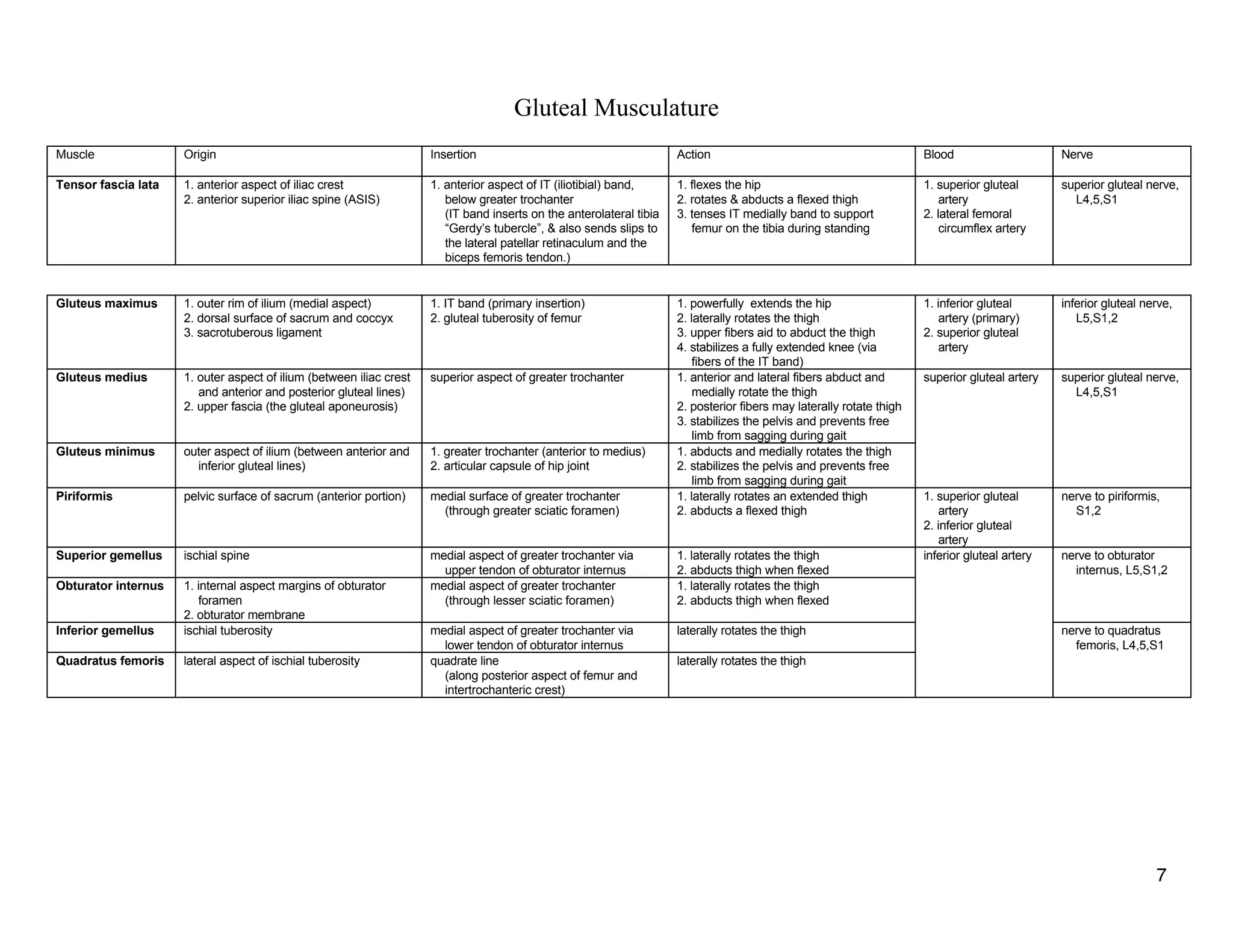
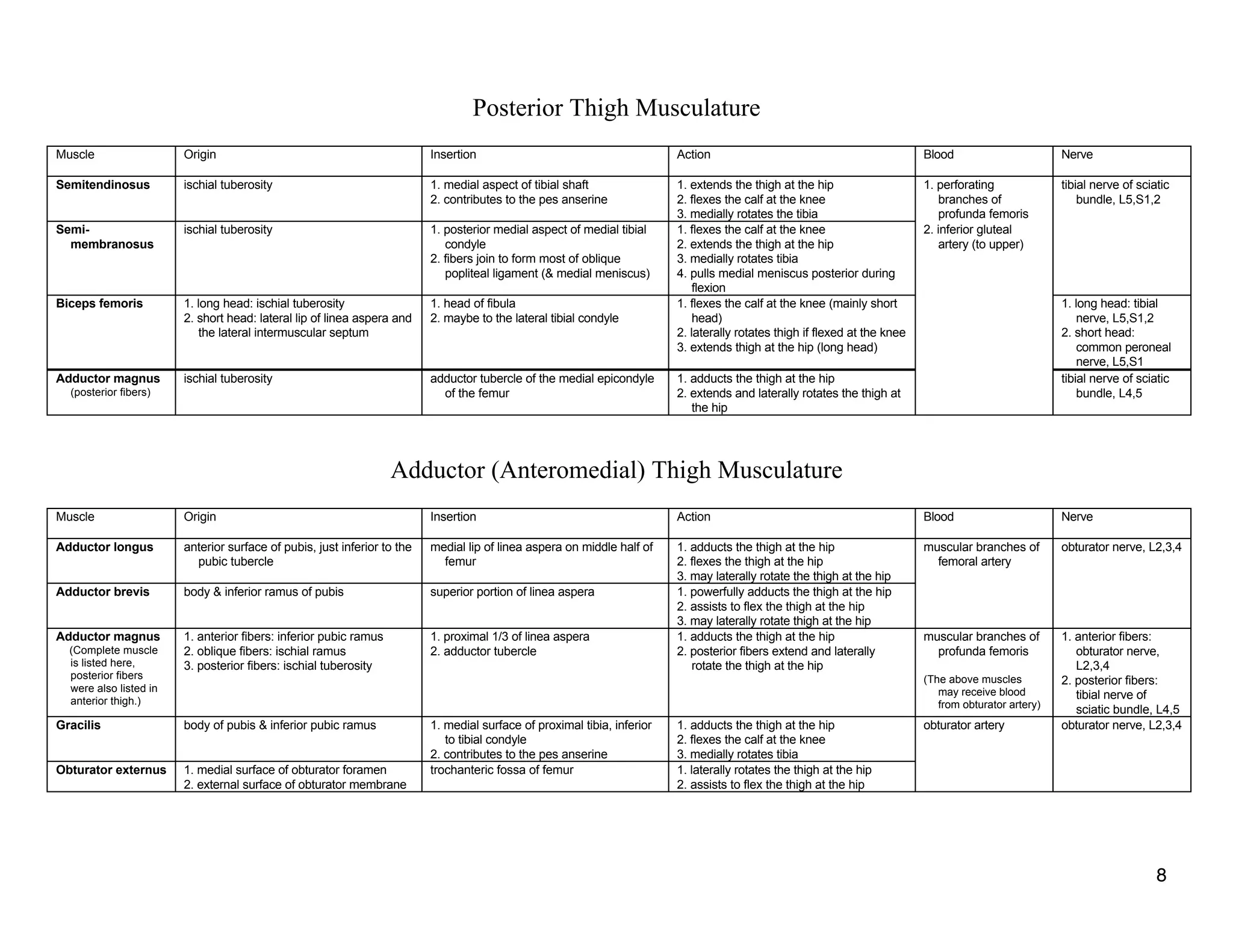
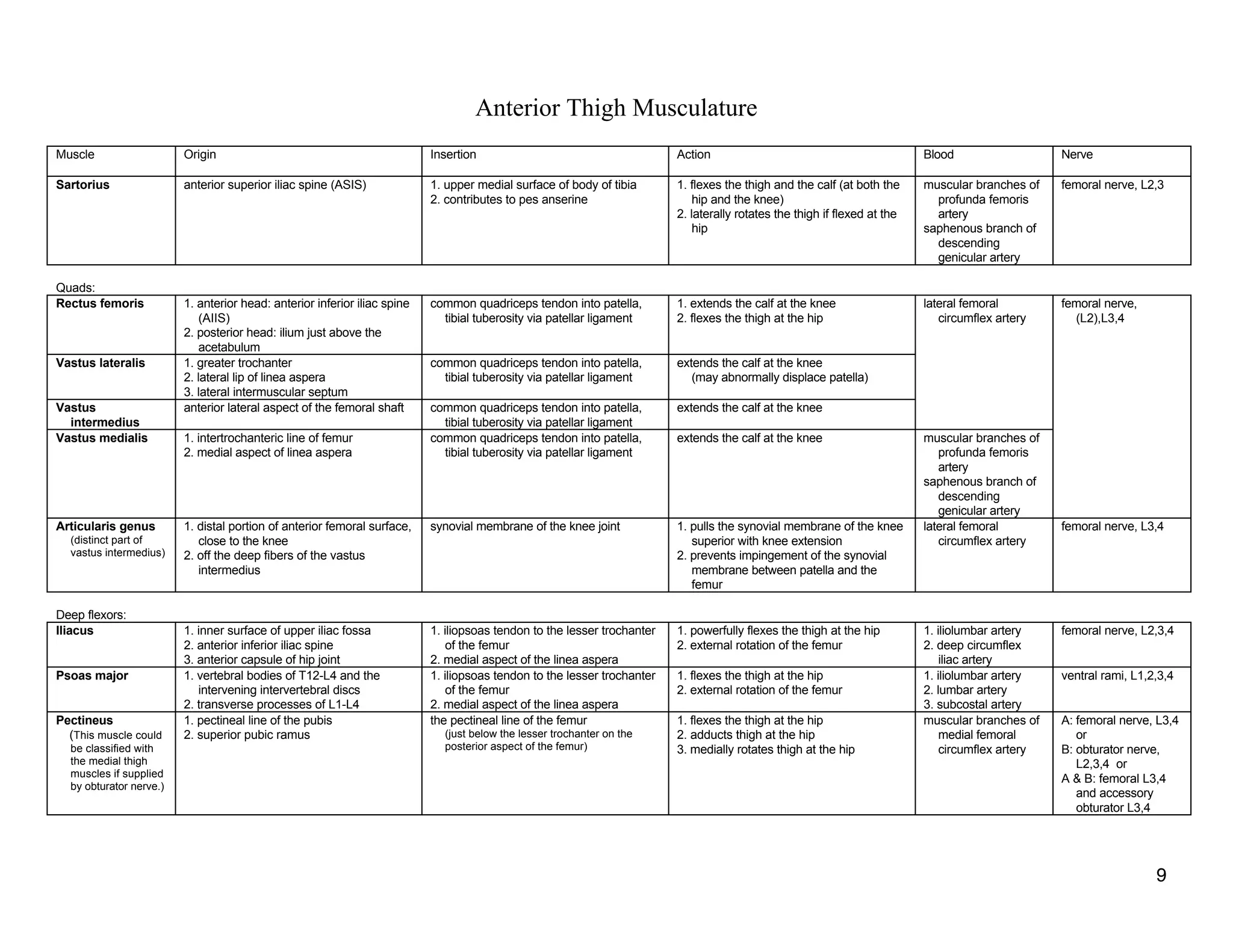
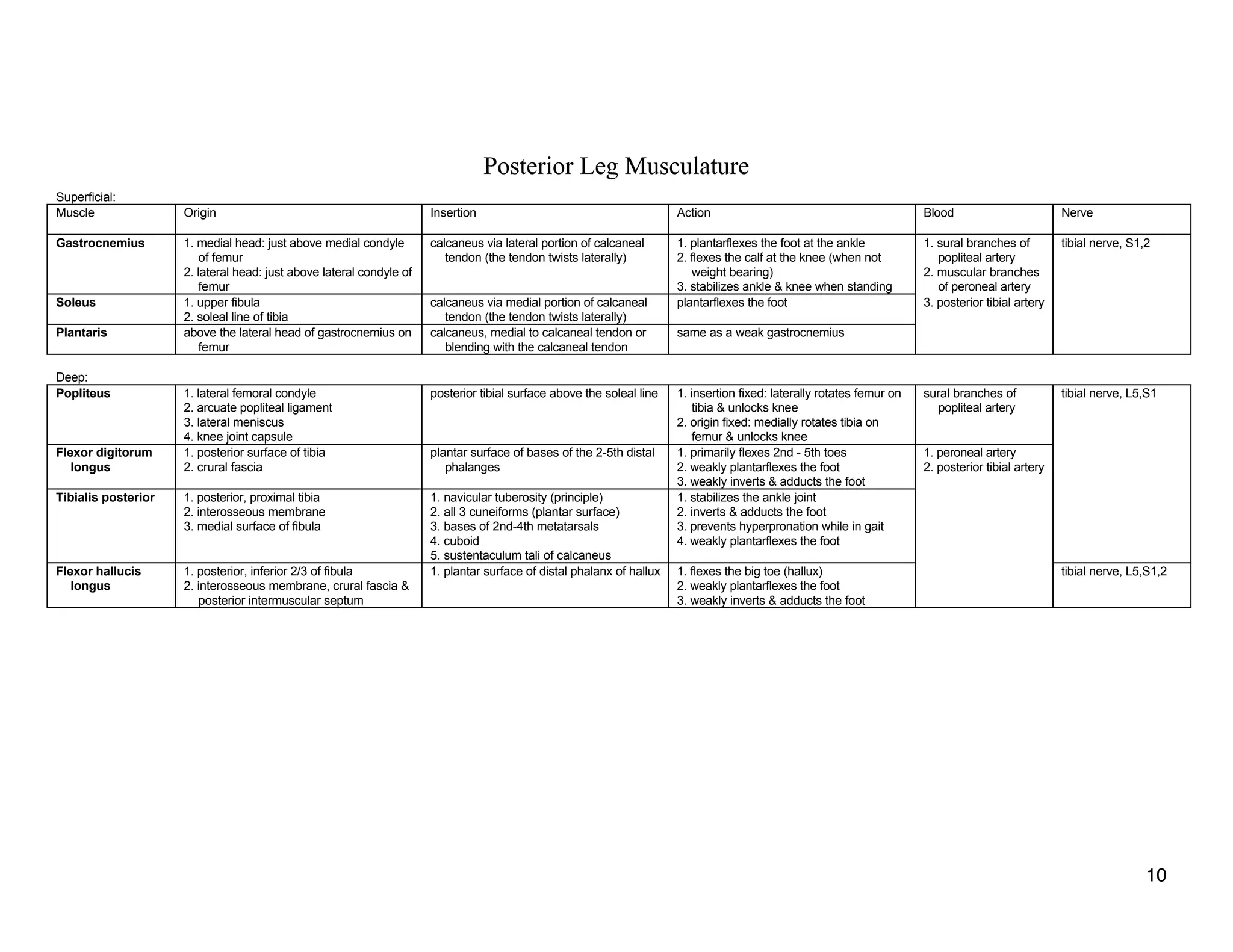
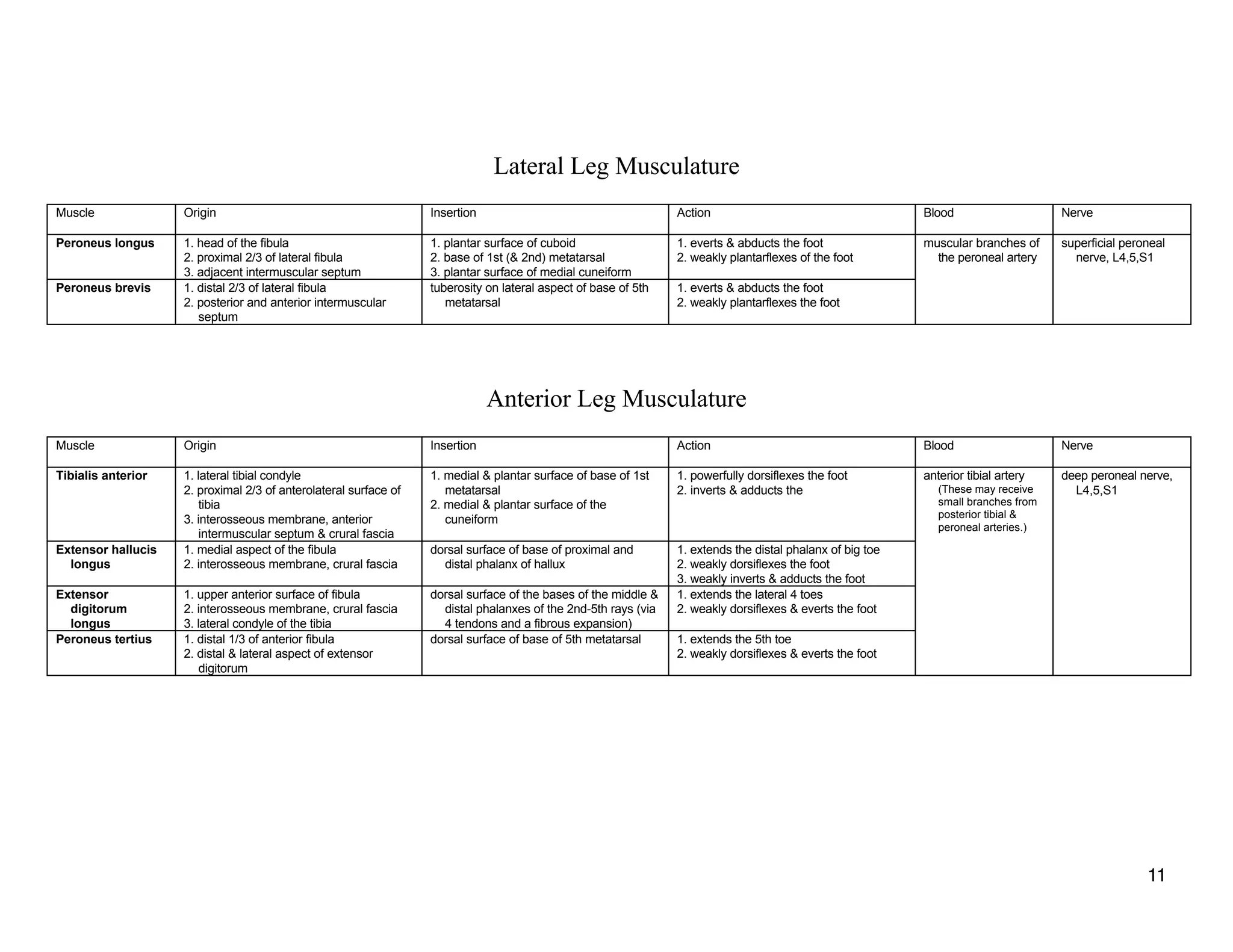
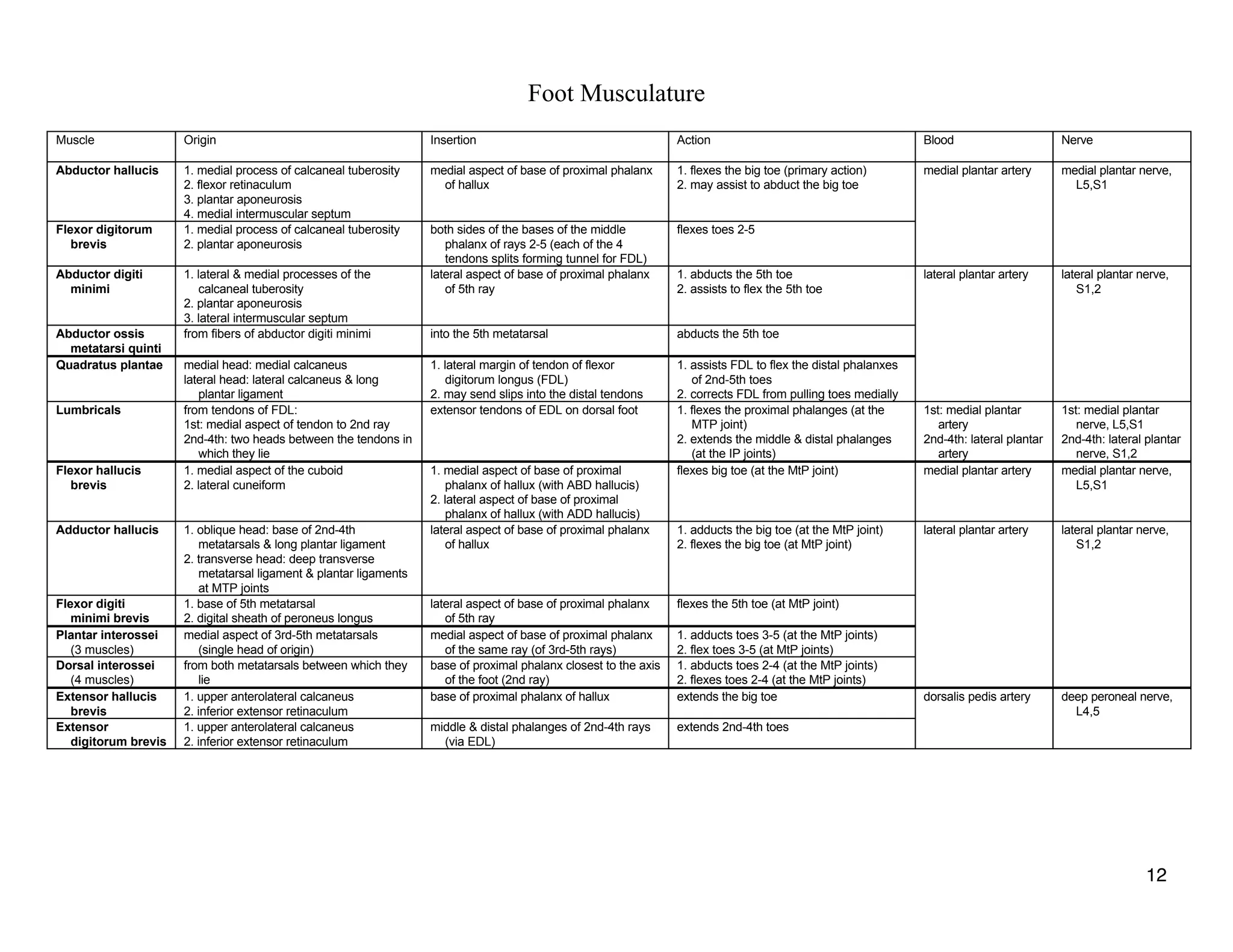
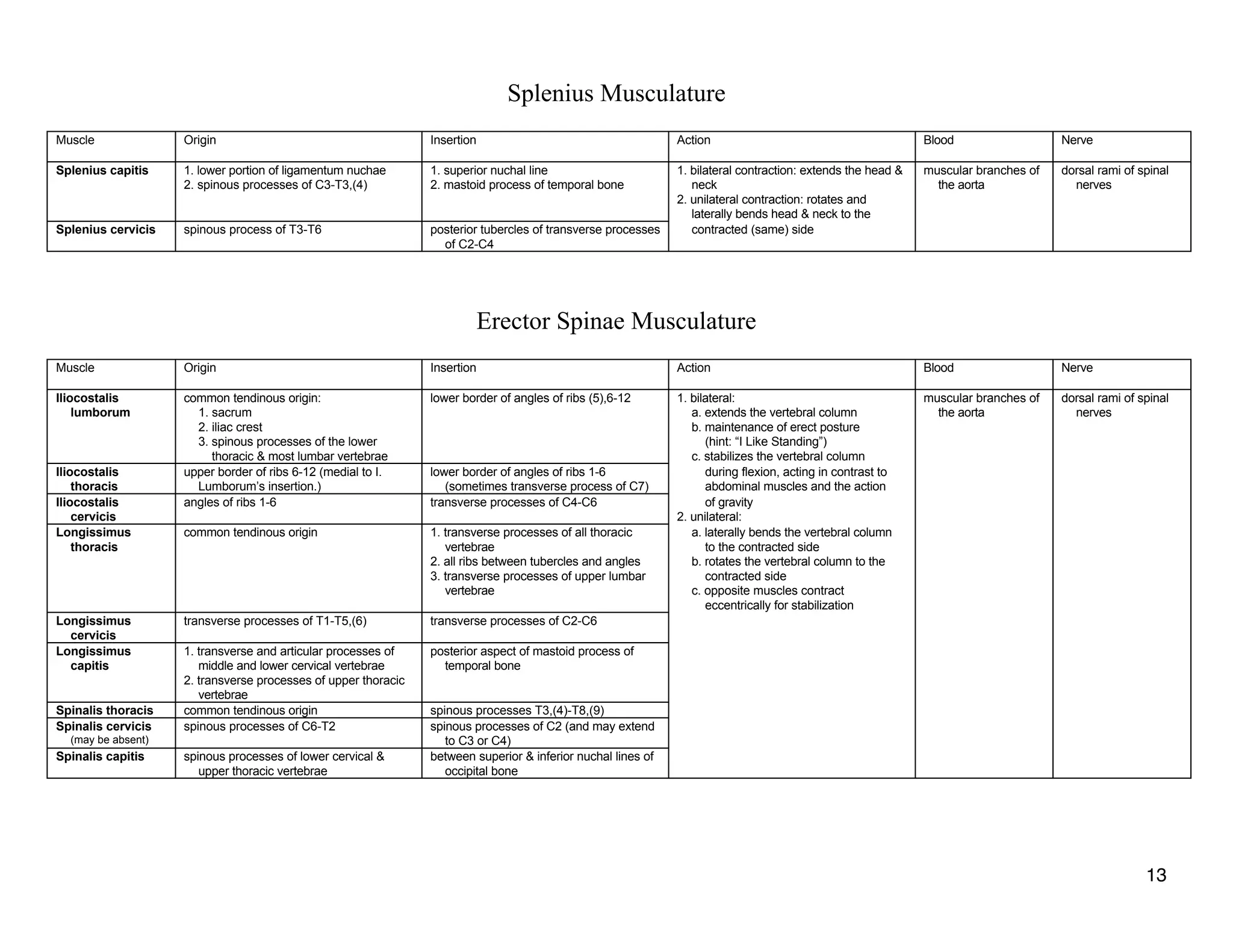
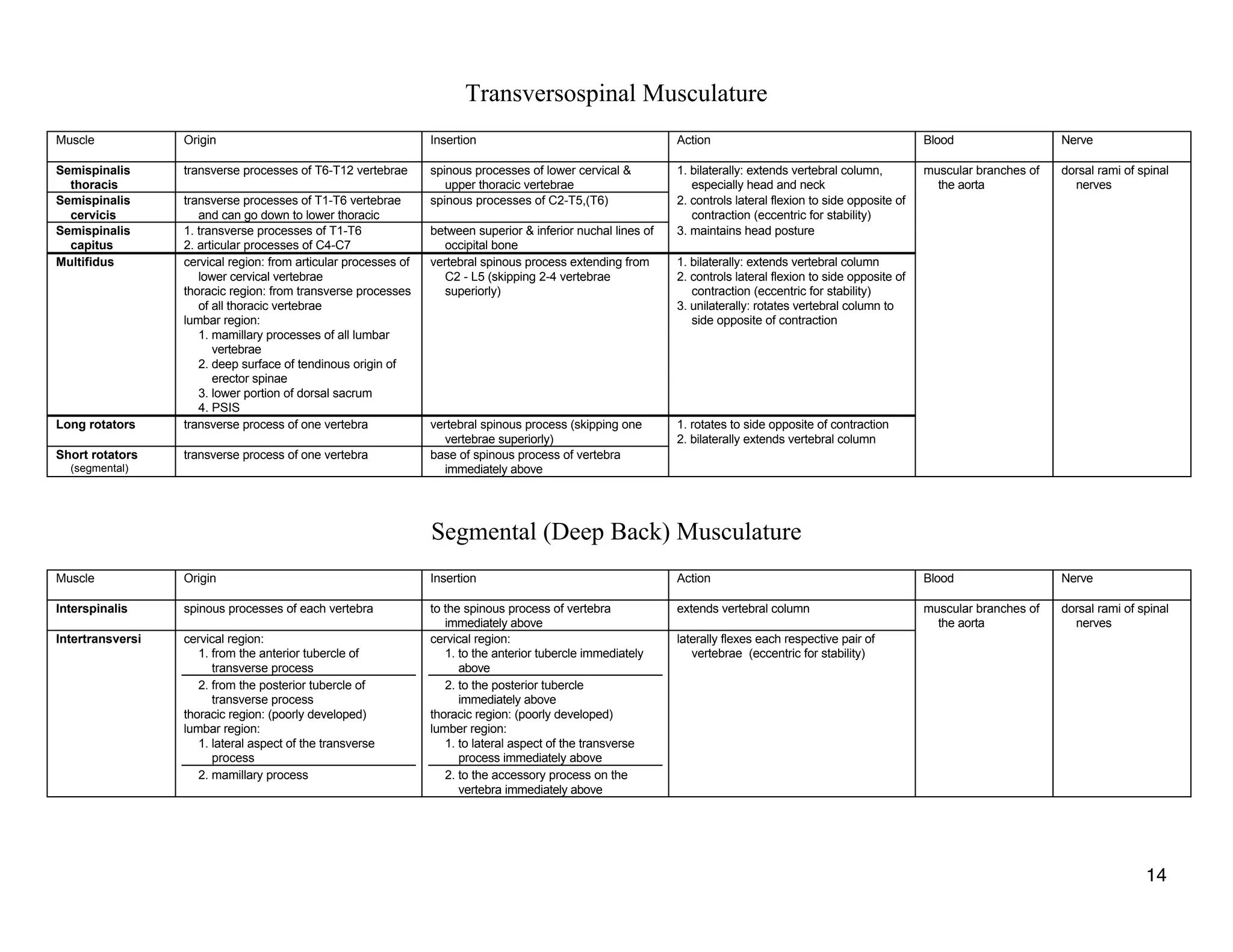
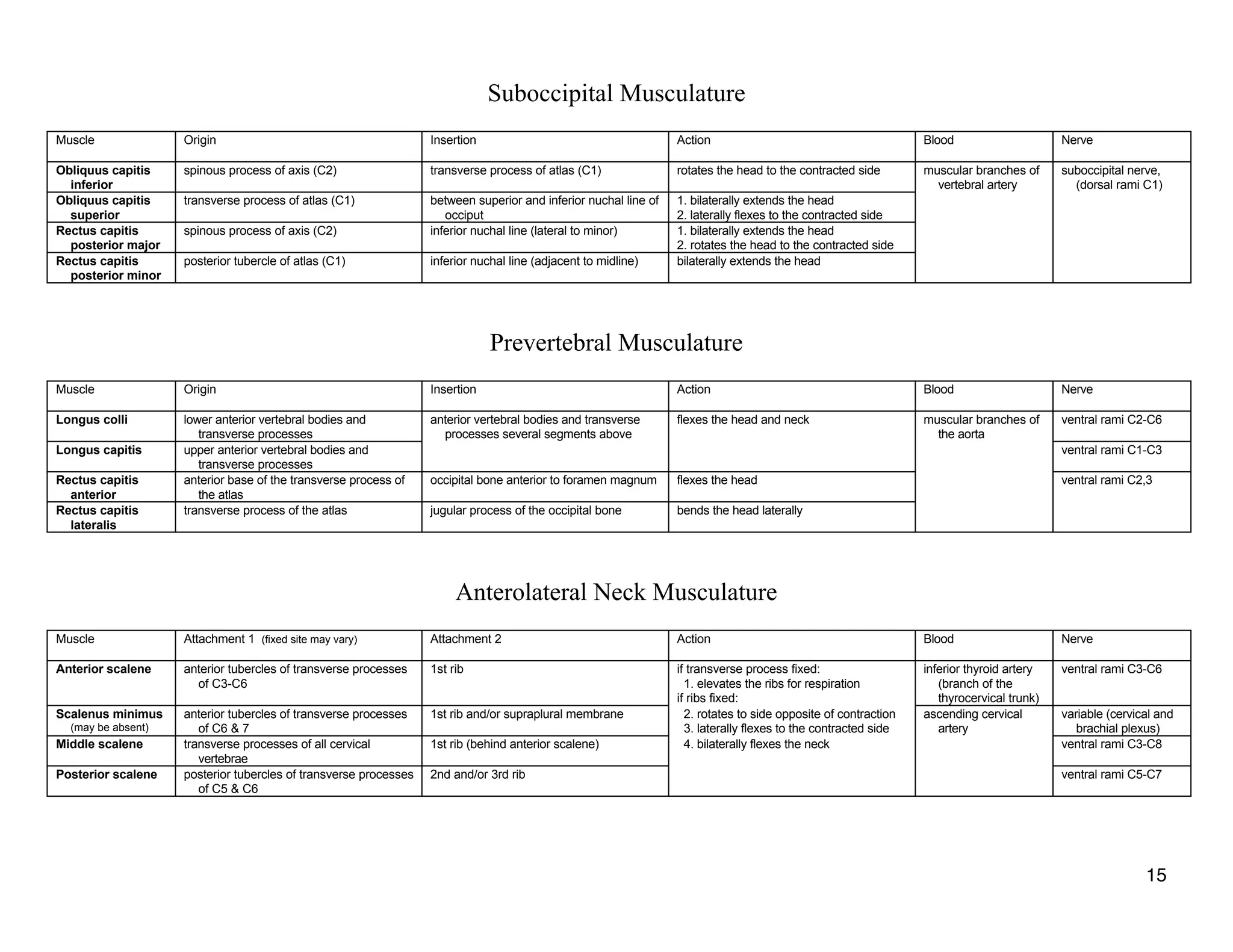
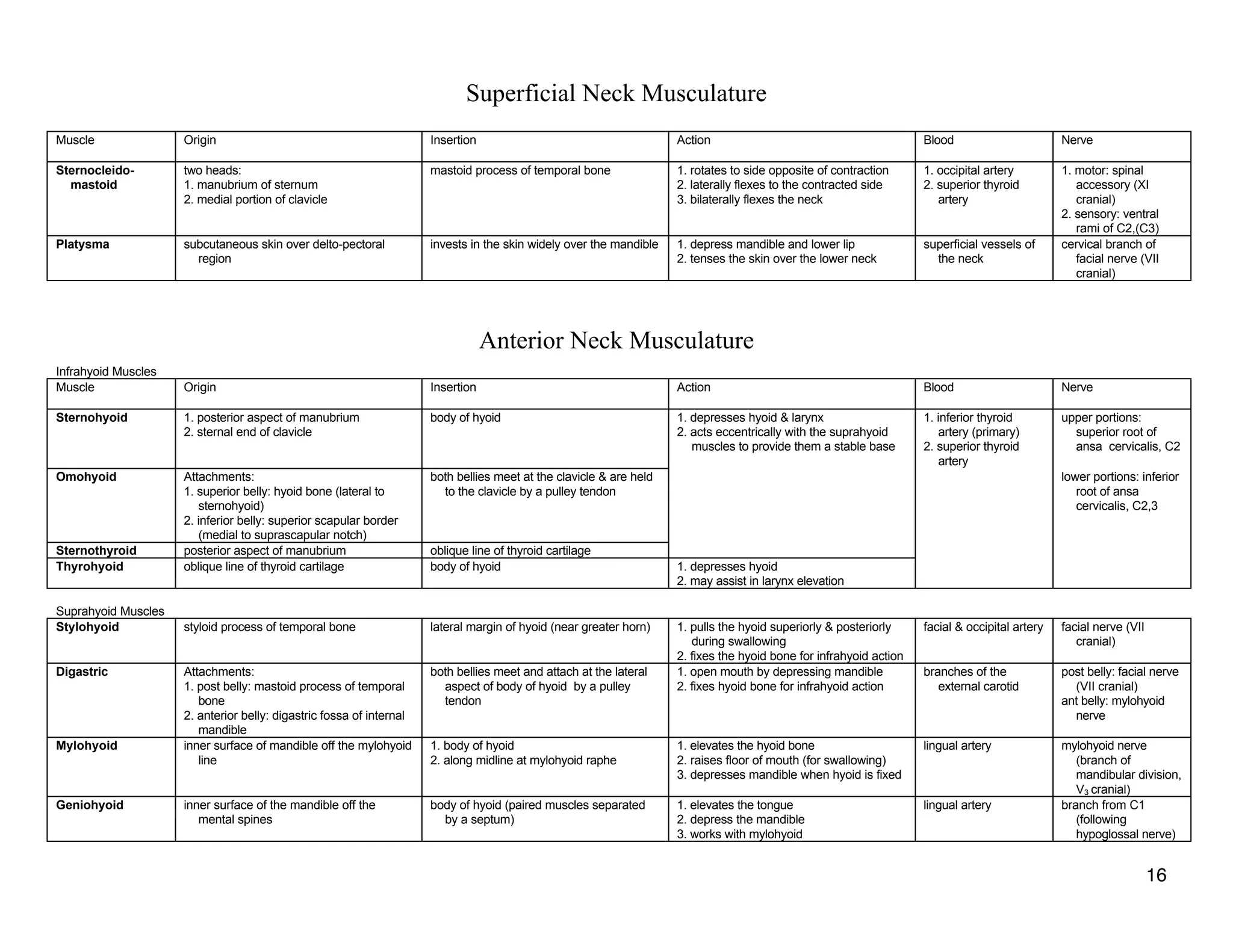
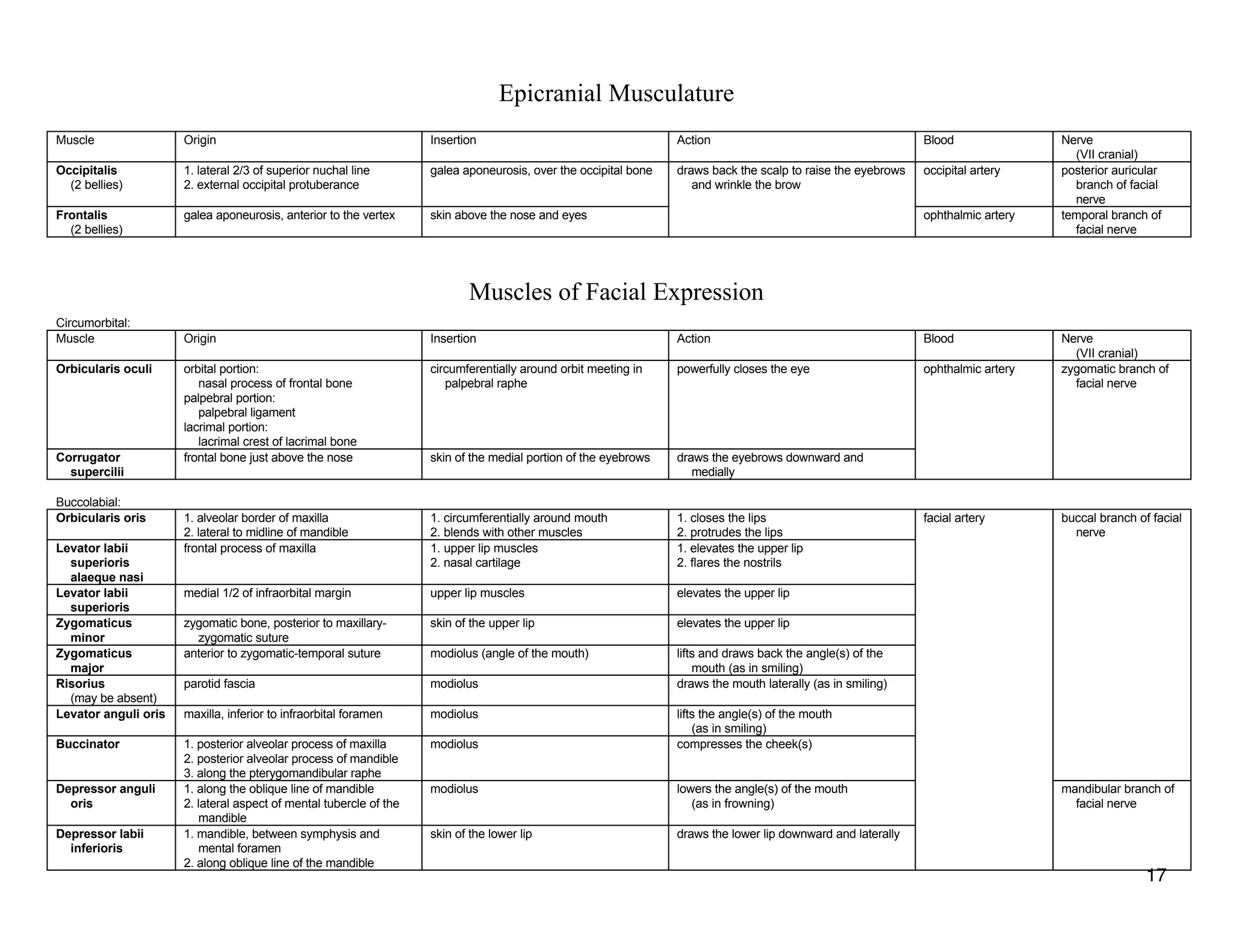
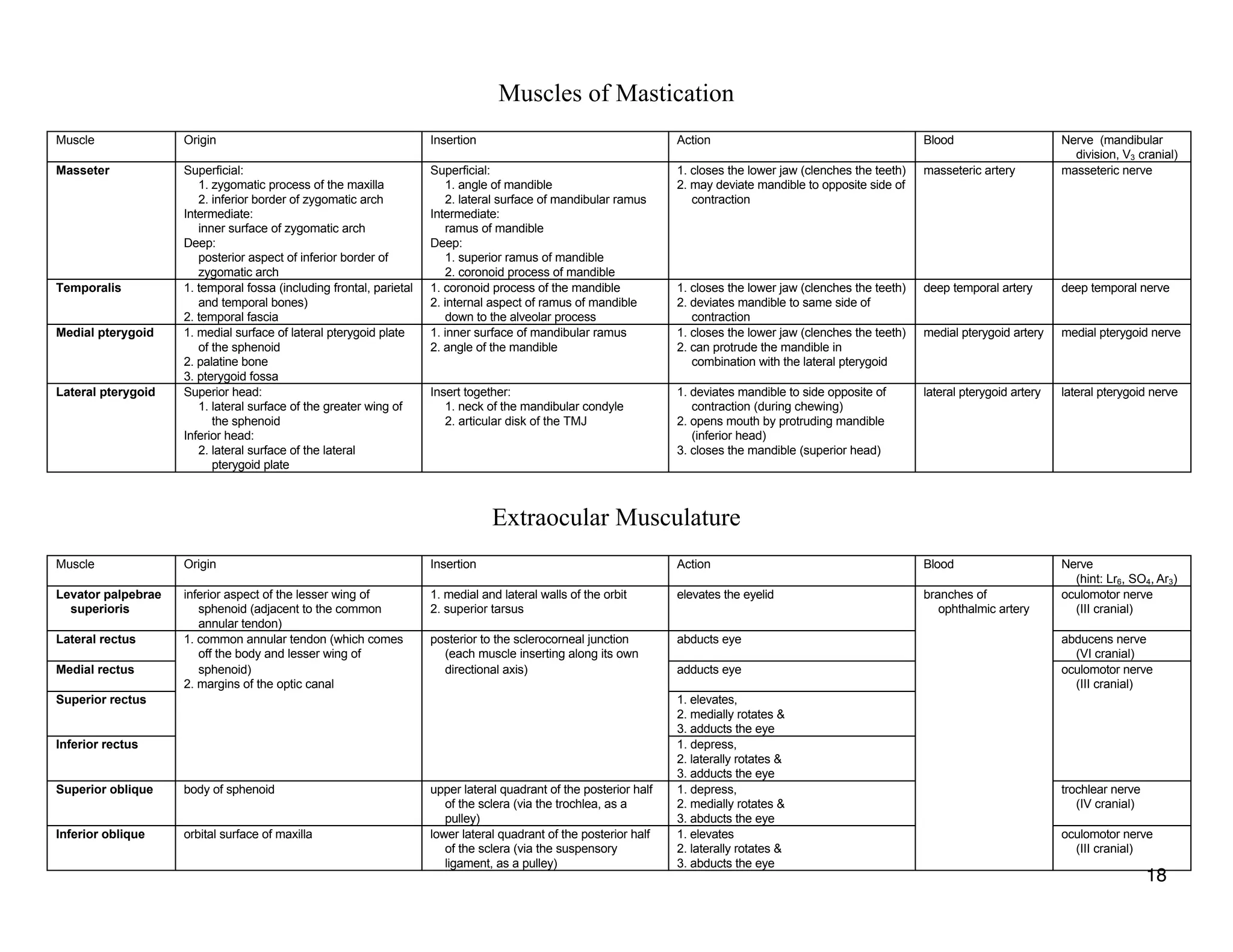
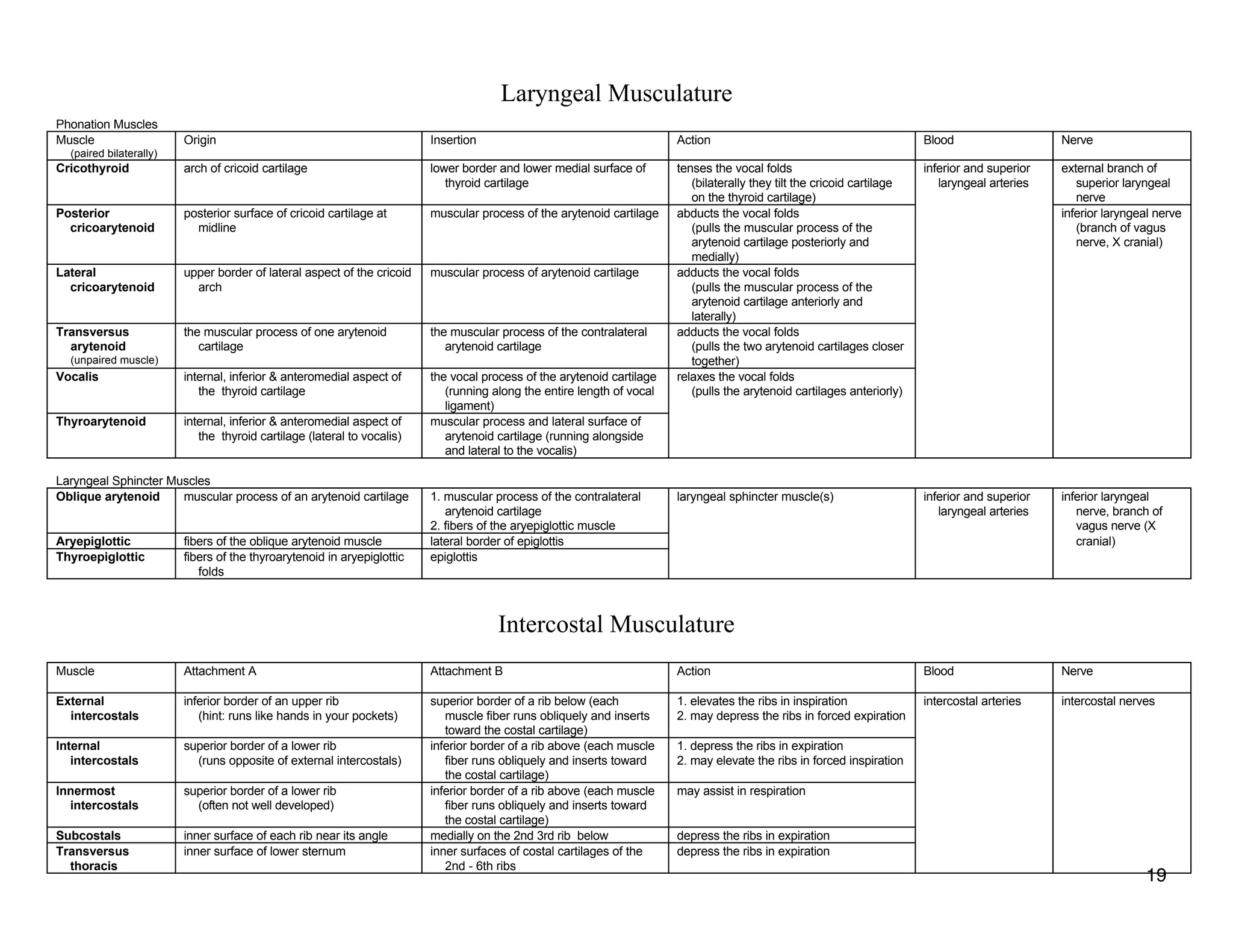
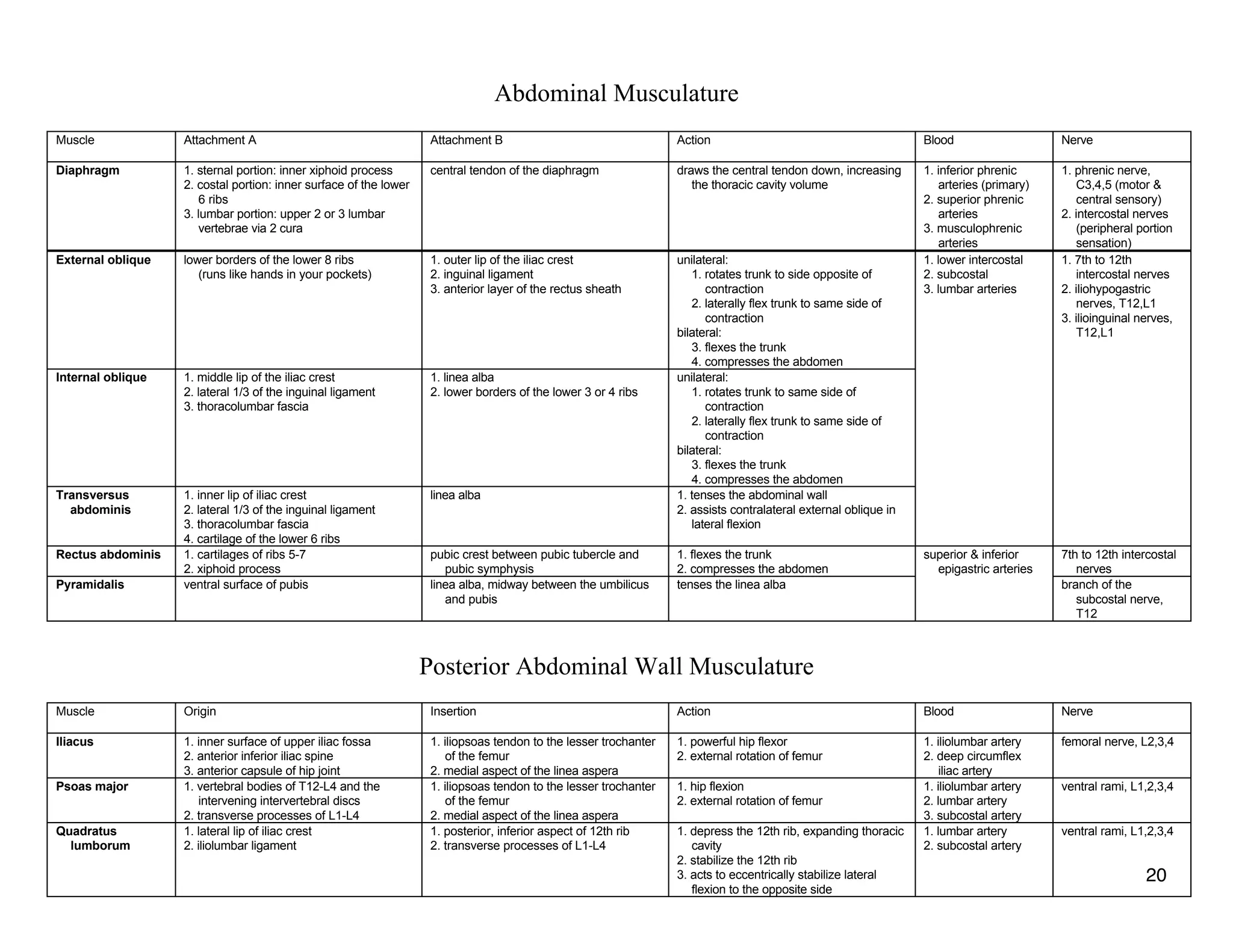
The document provides a table of contents listing various muscle groups of the human body, including the superficial back musculature, shoulder girdle musculature, pectoral musculature, brachium musculature, antebrachial flexor musculature, antebrachial extensor musculature, hand and wrist musculature, and others. It then provides details on the origin, insertion, action, blood supply, and nerve innervation of individual muscles within several of these groups, including descriptions of muscles like the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, deltoid, biceps brachii, and flexor digitorum profundus.