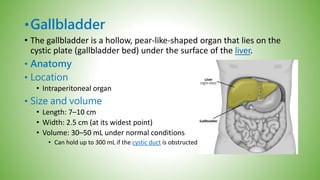
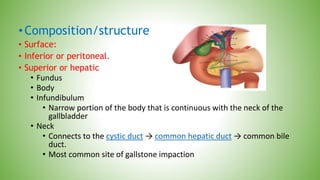
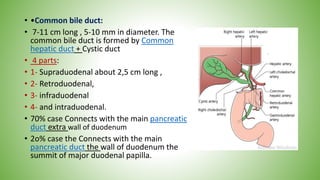
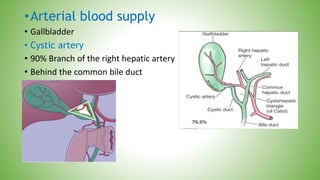
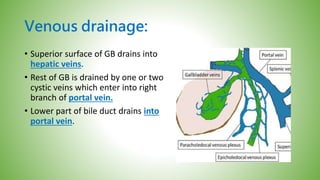
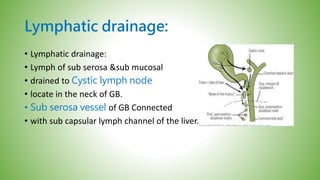
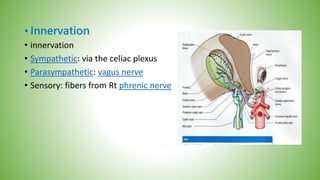
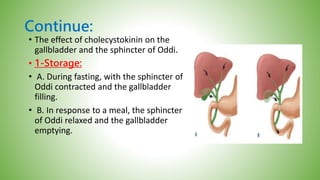
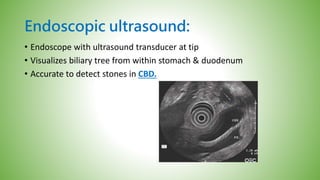
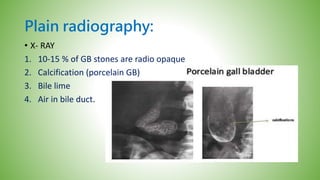
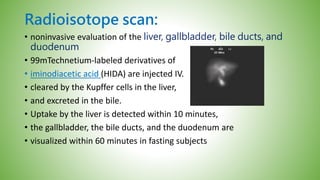
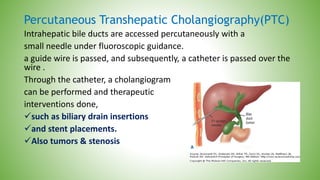
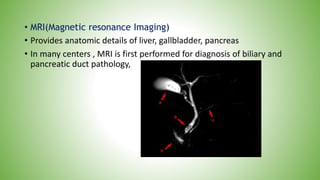
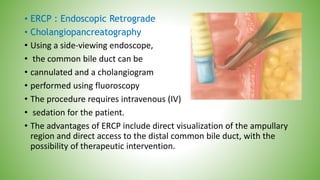
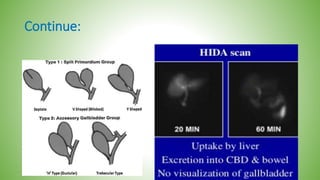
The gallbladder and bile ducts are described. The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ located under the liver that stores and concentrates bile produced by the liver. It has a fundus, body, neck and connects to the common bile duct via the cystic duct. The common hepatic duct forms from the right and left hepatic ducts and joins the cystic duct to form the common bile duct. Blood supply is from the cystic artery and drainage is into the portal vein and hepatic veins. Diagnostic tests for gallbladder and bile duct issues include blood tests, ultrasound, CT, MRI, HIDA scan, and ERCP which also allows for therapeutic interventions like sphincterotomy and stone extraction.