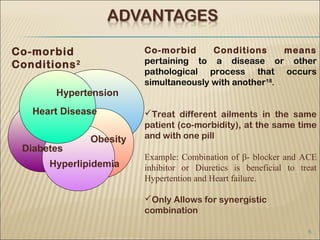
Bilayer tablets can avoid chemical incompatibilities between active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) through physical separation of layers, allowing different release profiles like immediate and extended release. Key advantages include combining incompatible drugs, reducing pill burden through additive drug effects, and addressing co-morbid conditions with a single tablet. Bilayer tablets are useful for APIs with short half-lives, instability at intestinal pH, or high first-pass metabolism. Practical challenges in developing bilayer tablets include layer separation, determining layer order and ratios, and cross-contamination between layers.