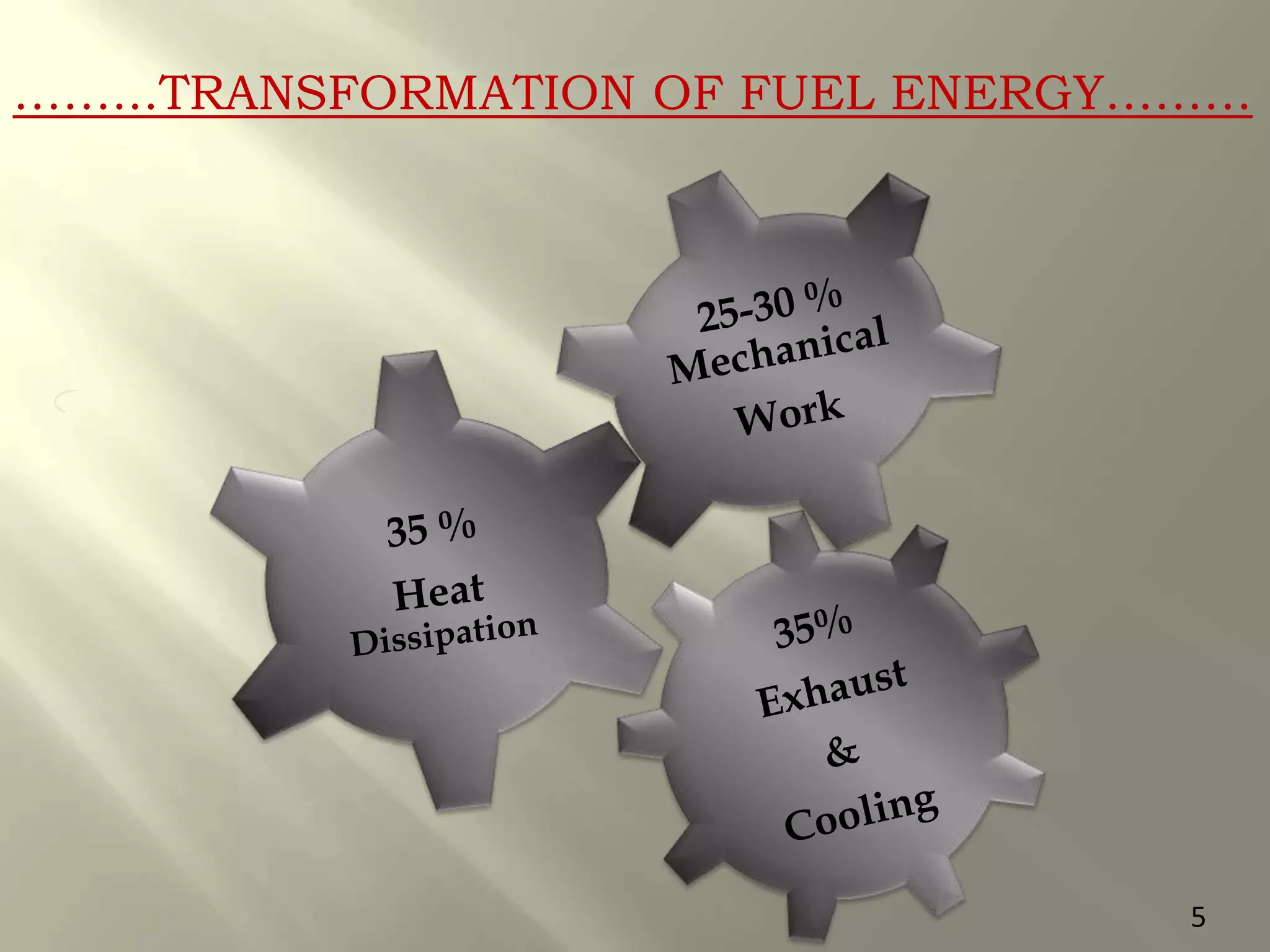
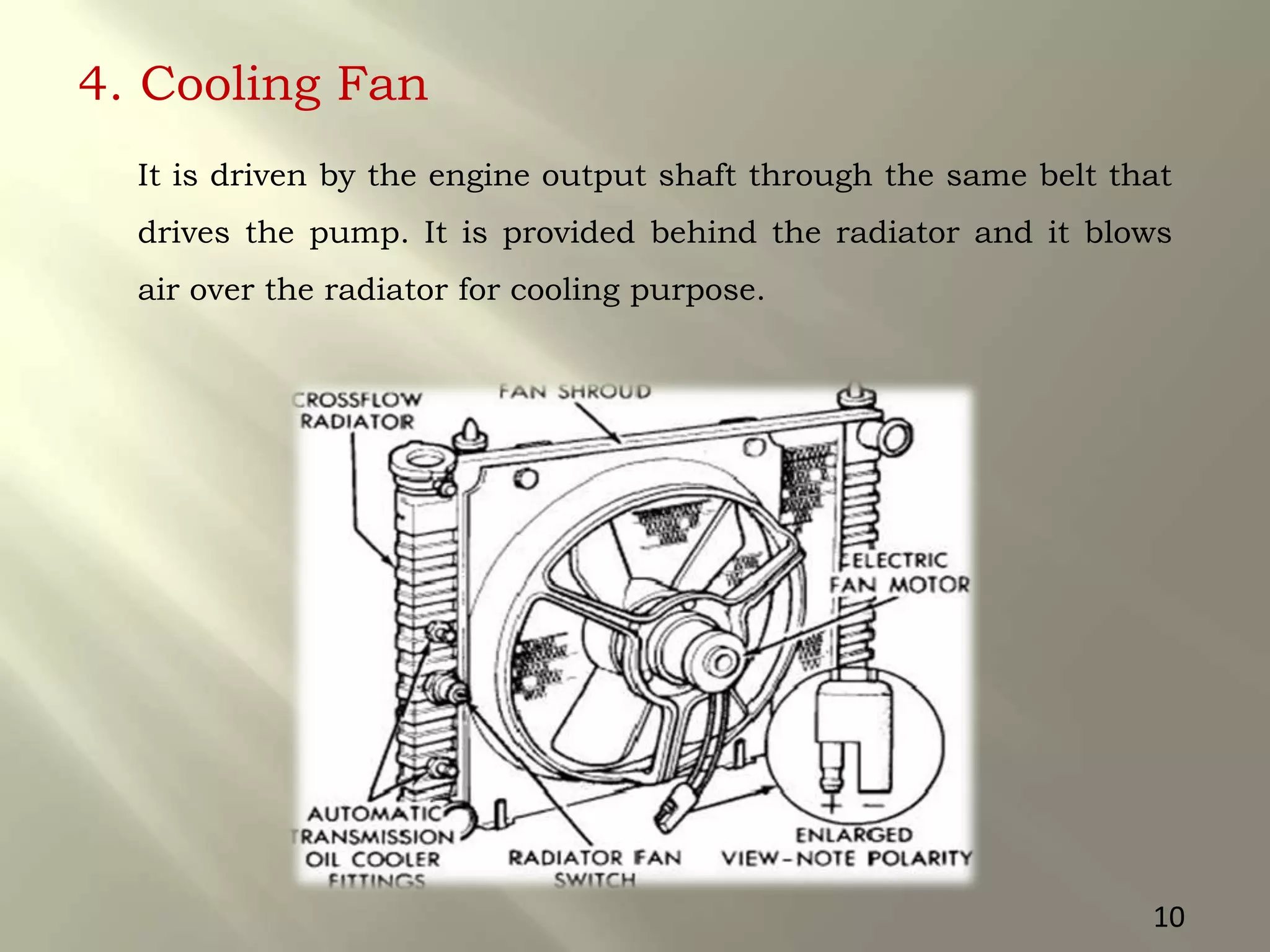
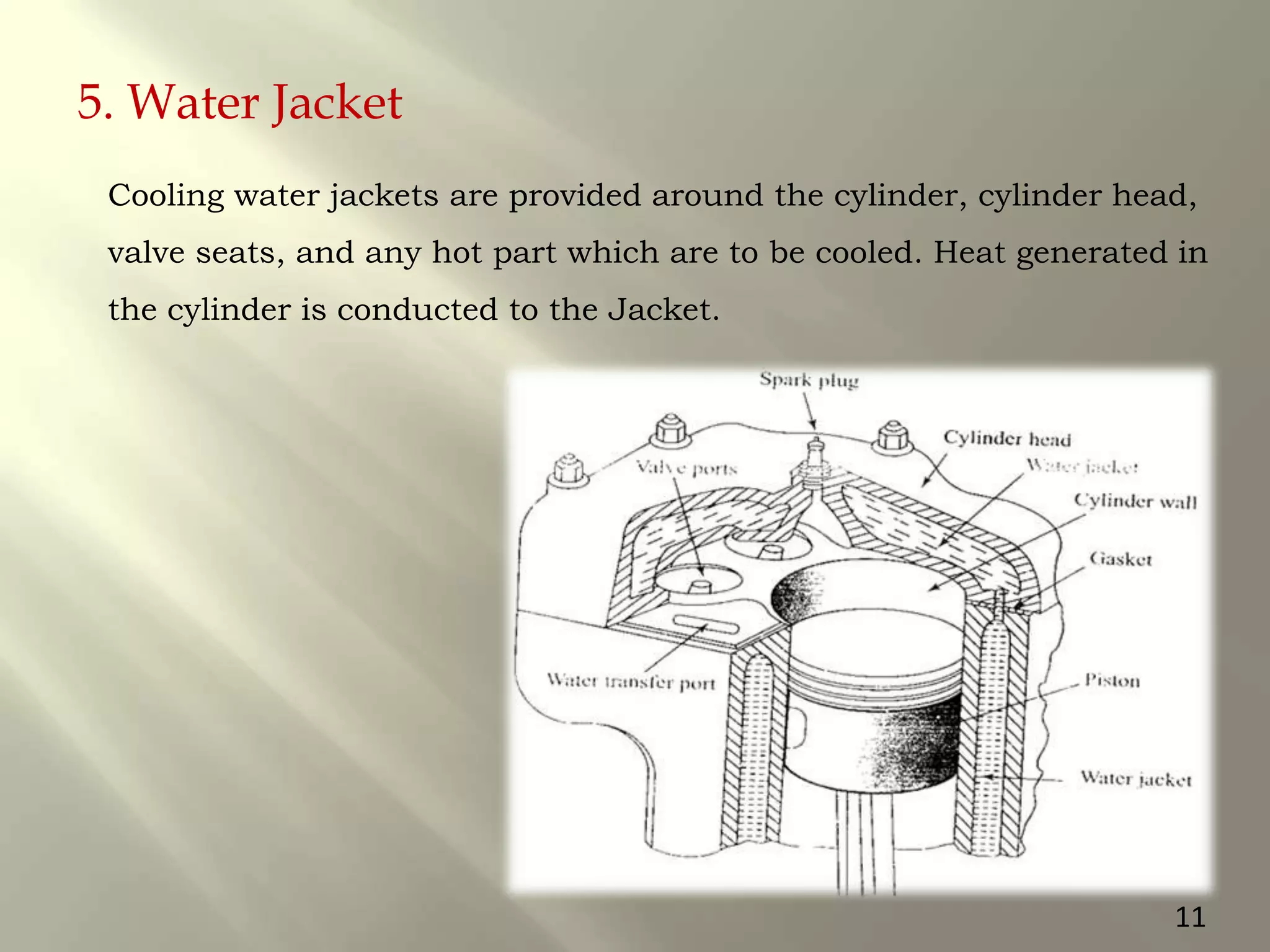
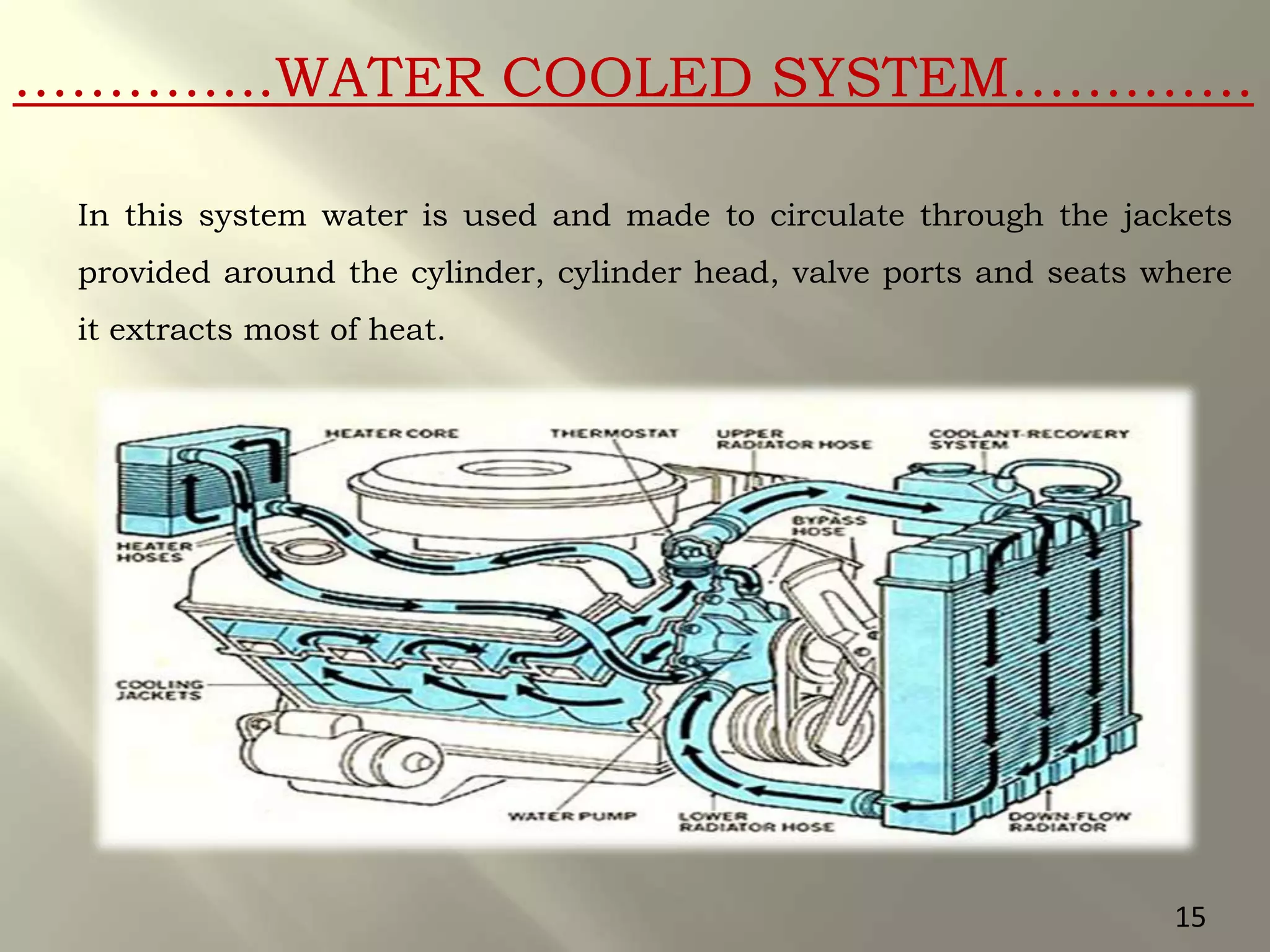
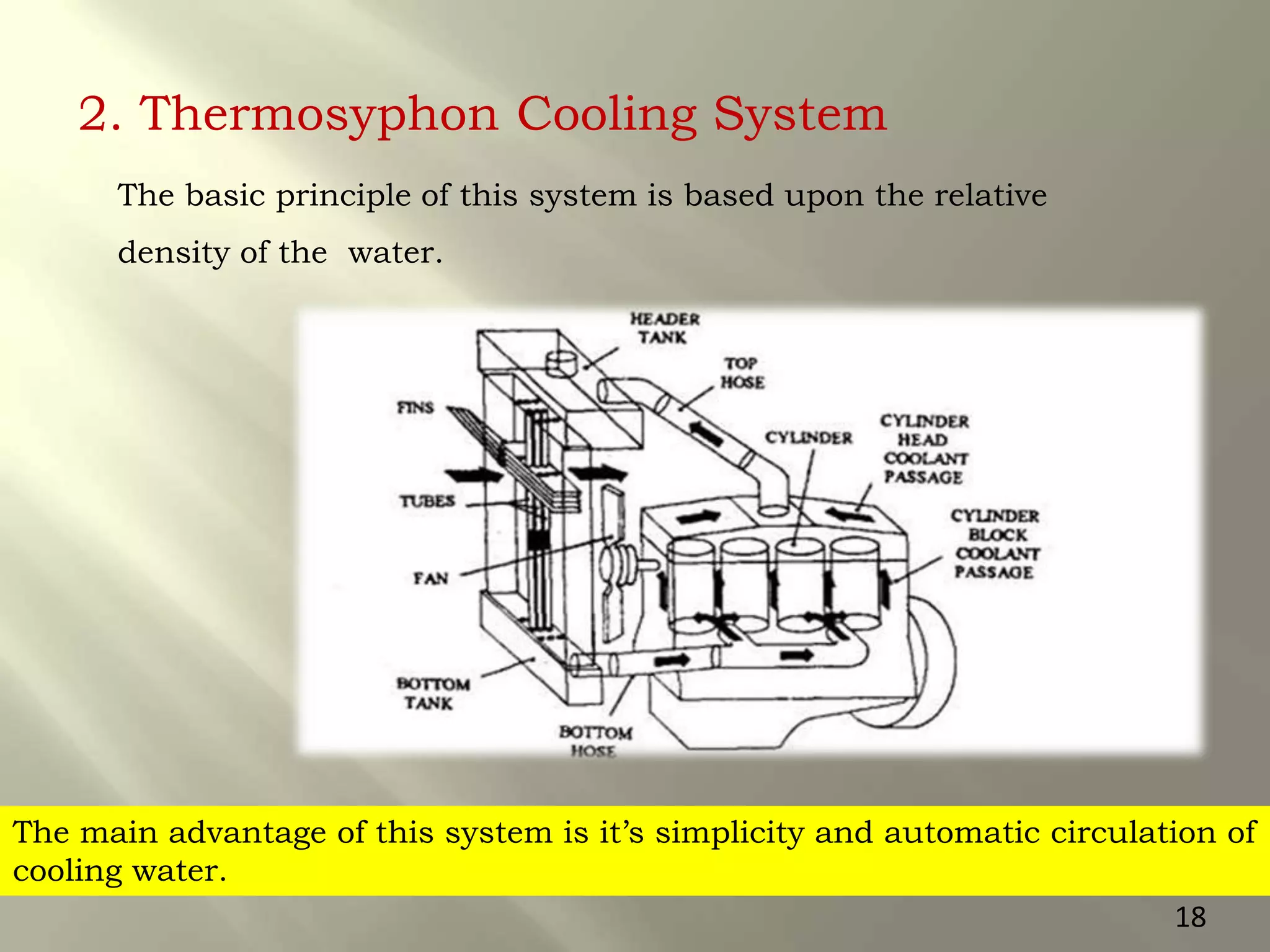
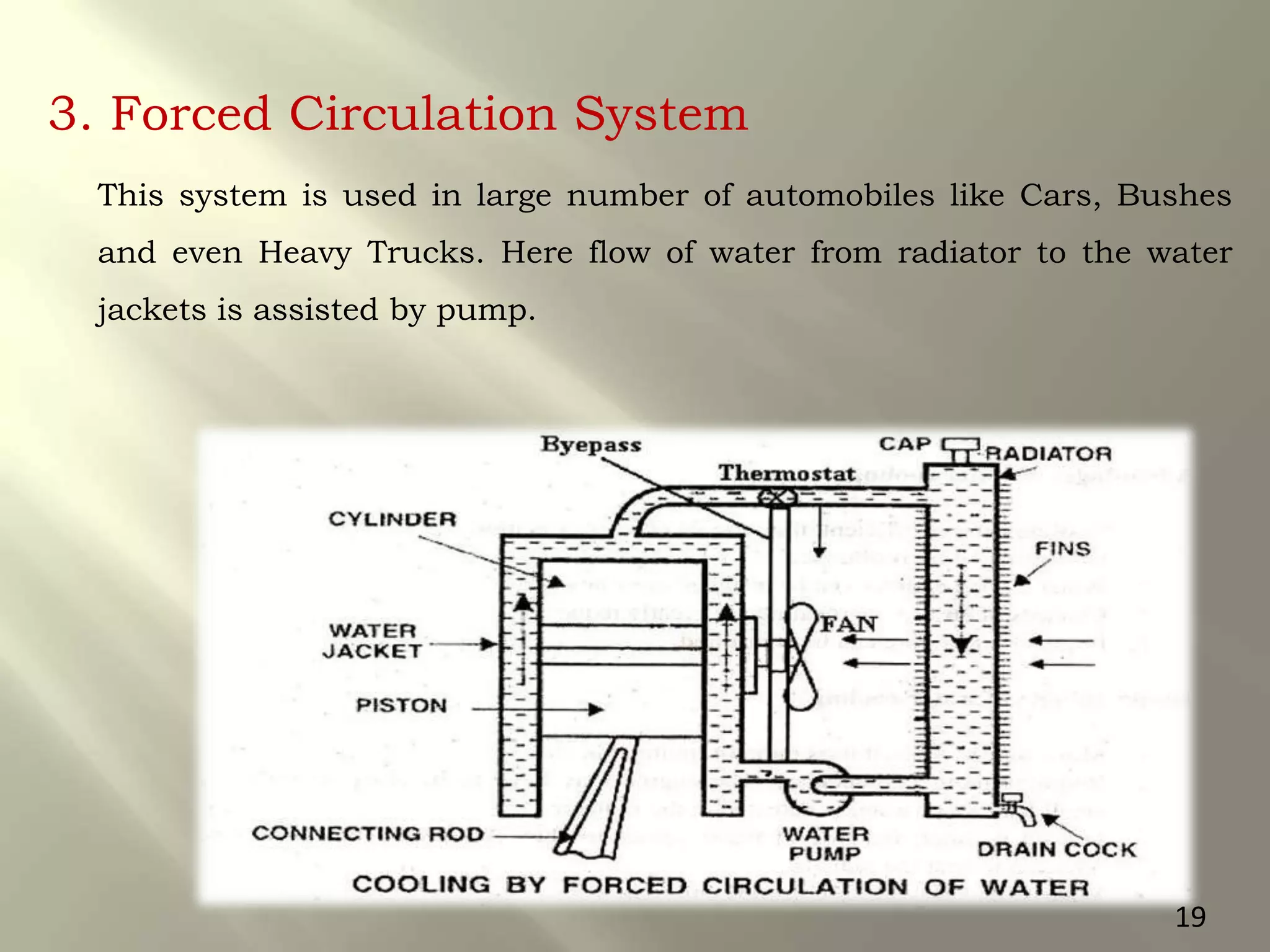
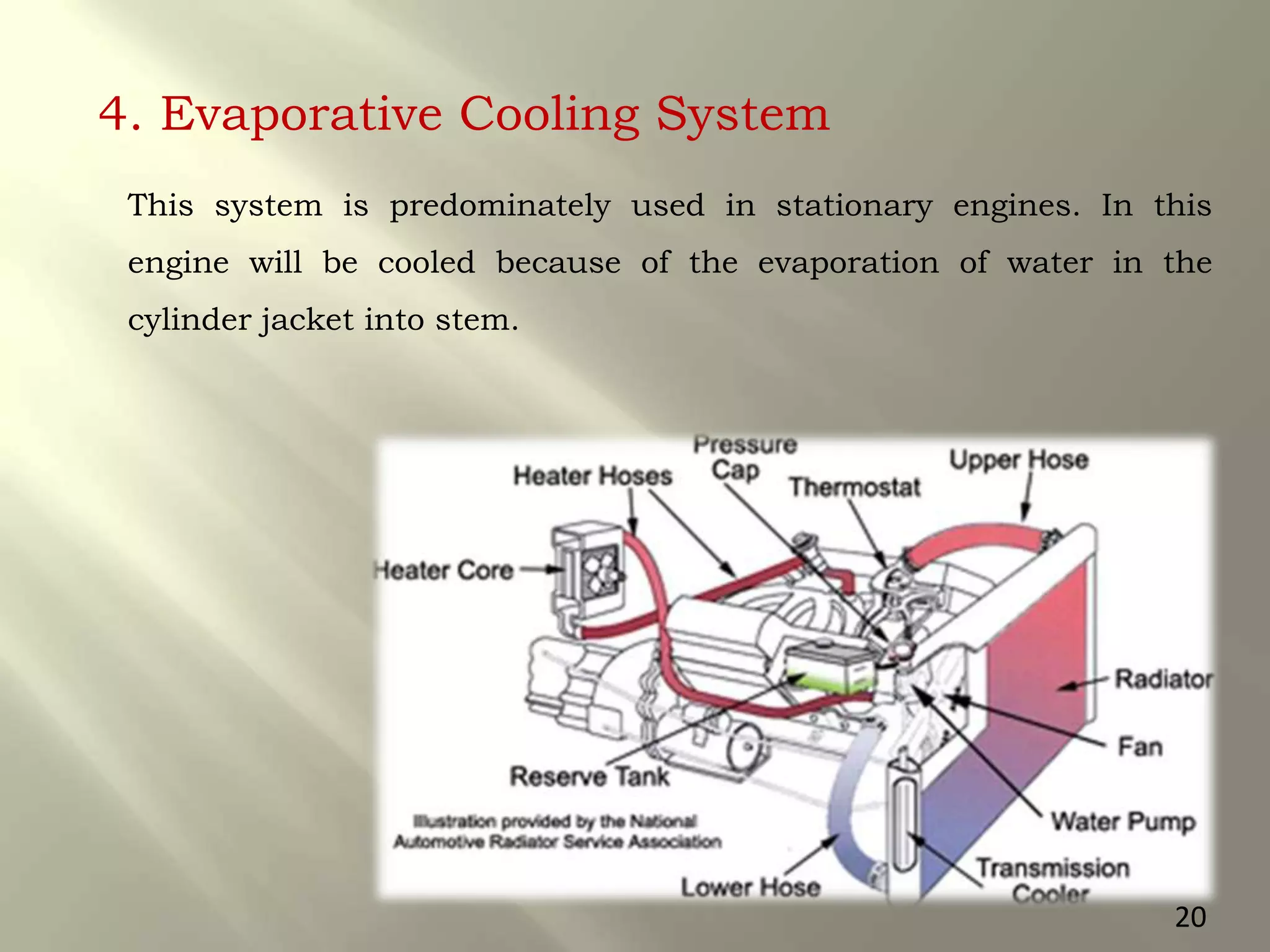
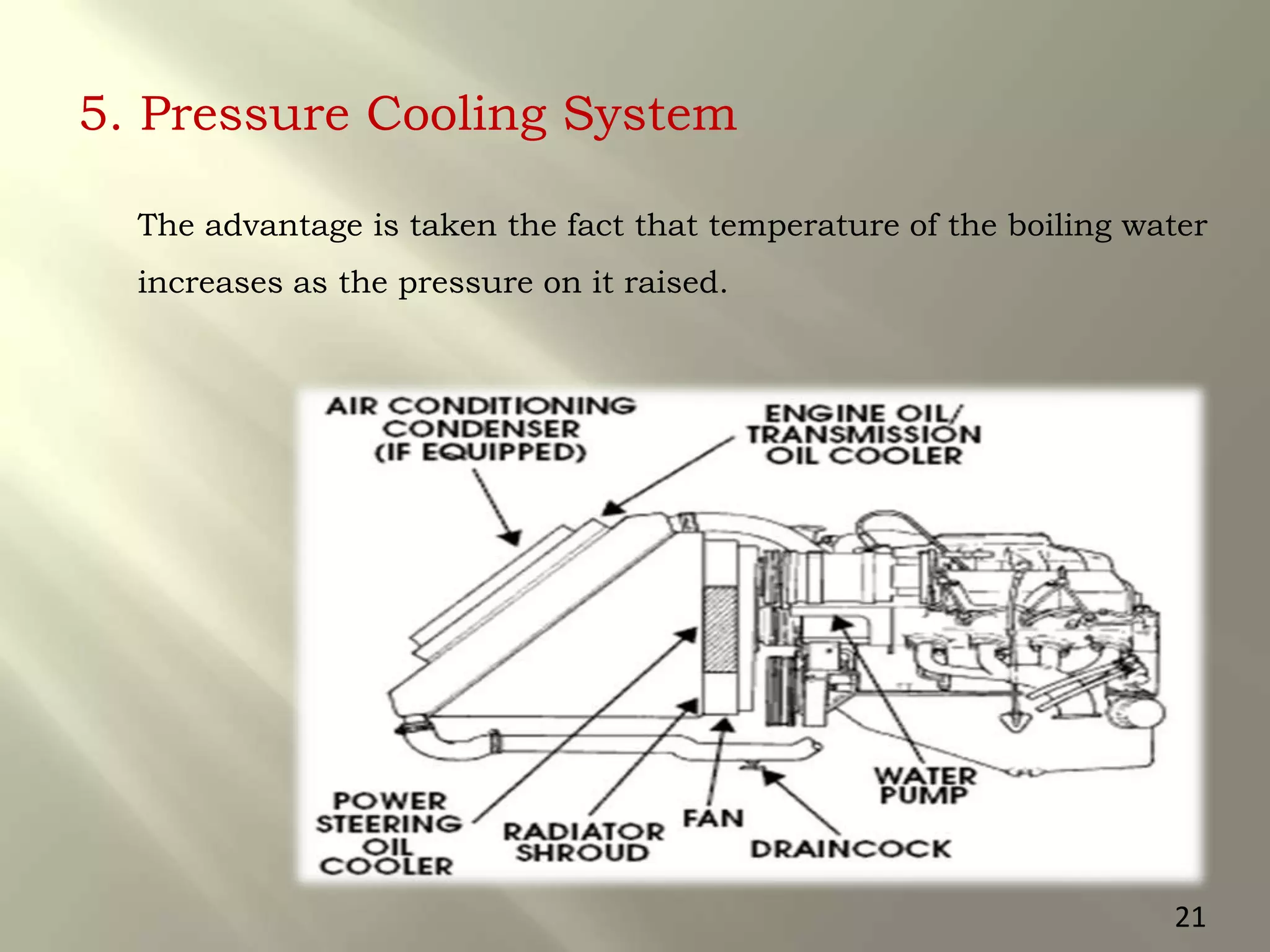
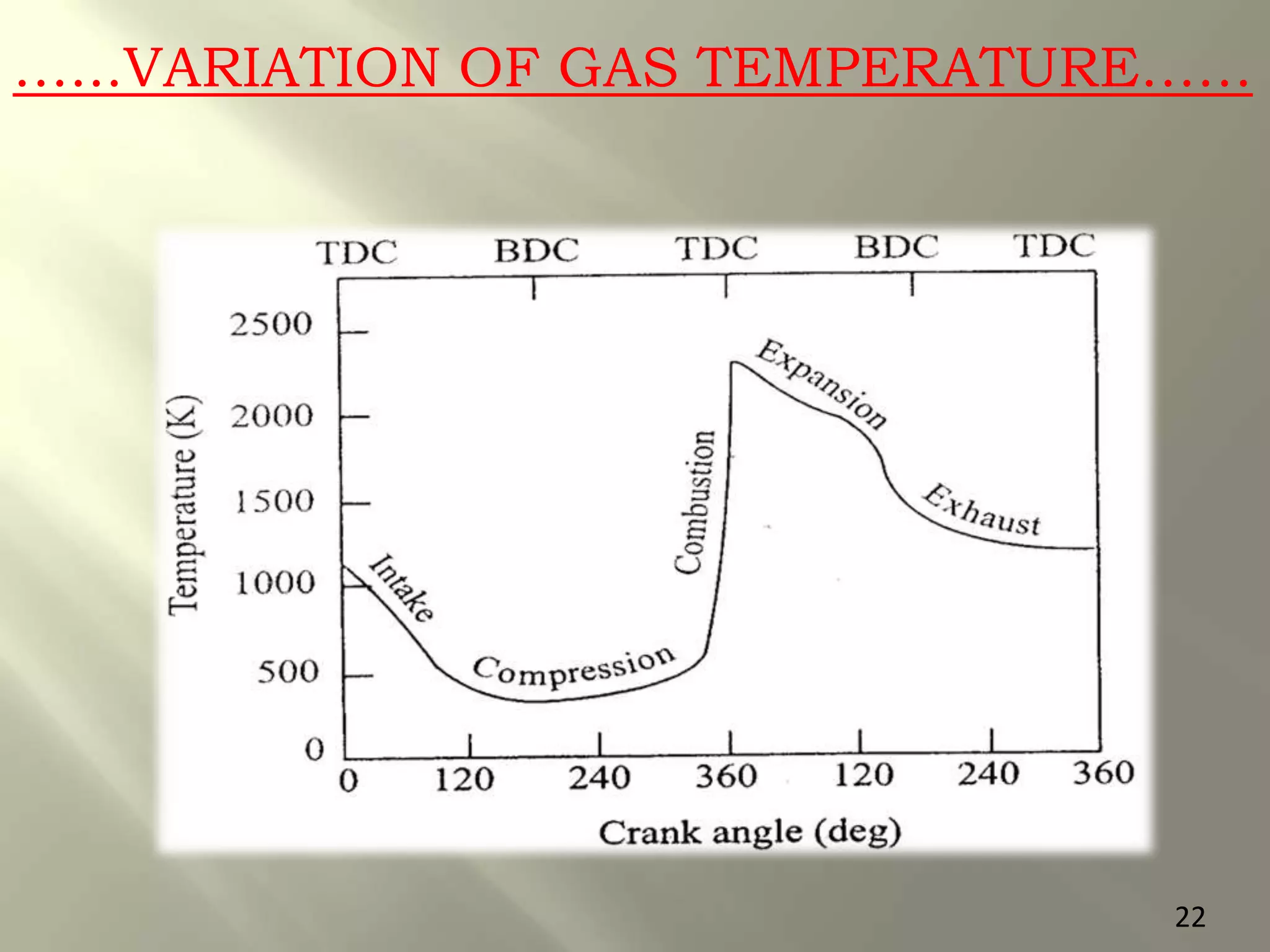
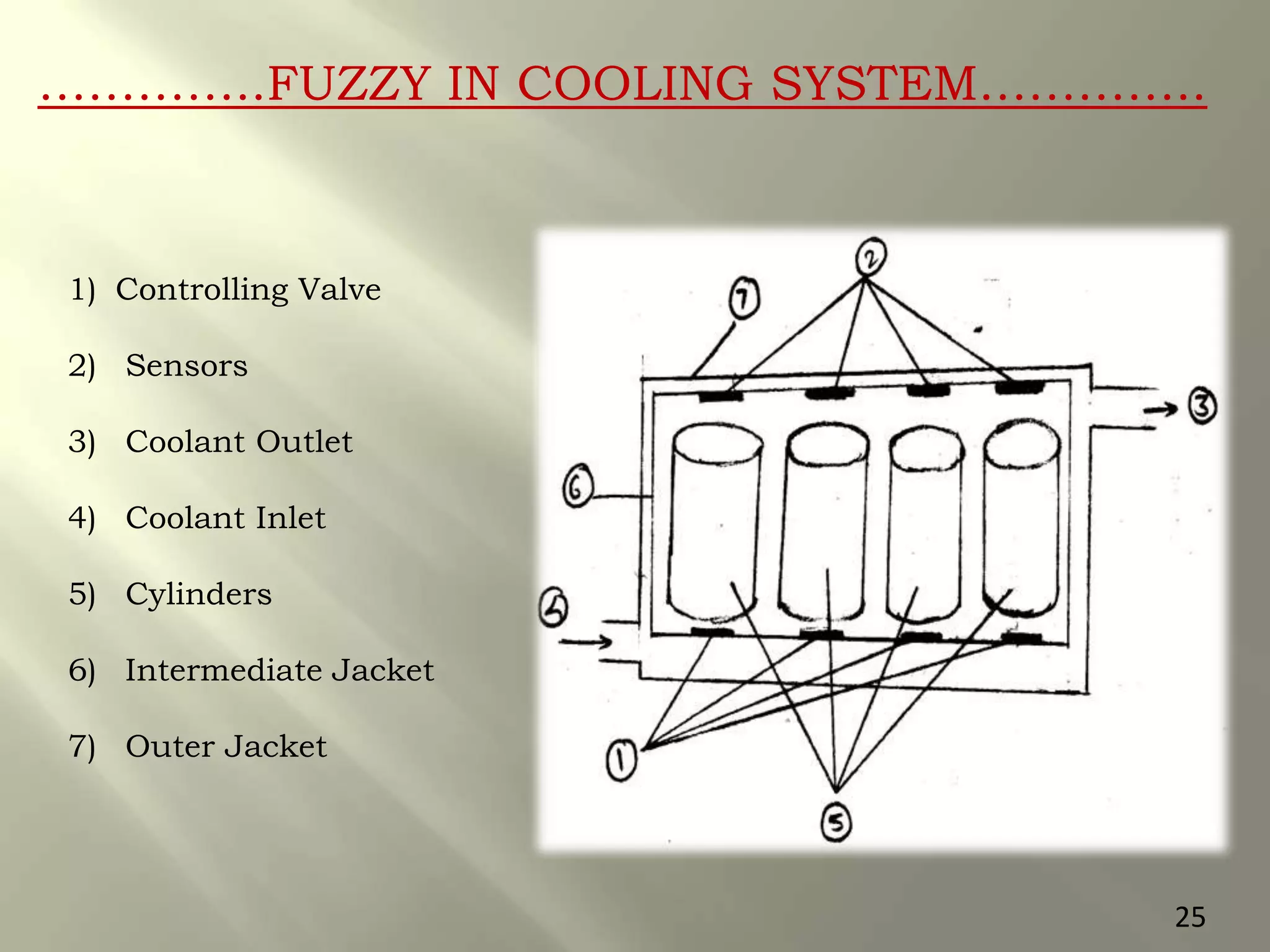
This document presents a seminar on an intelligent cooling system for engines that uses fuzzy logic. The key components of a typical cooling system are described, including the radiator, thermostat, water pump, cooling fan, and water jackets. Conventional cooling systems can cause overheating or excessive cooling, leading to issues like lubricant evaporation or corrosion. The intelligent cooling system aims to address these issues by using sensors to monitor cylinder temperature and control the flow of coolant via a valve implemented with fuzzy logic rules. This is expected to improve thermal efficiency while reducing maintenance needs.