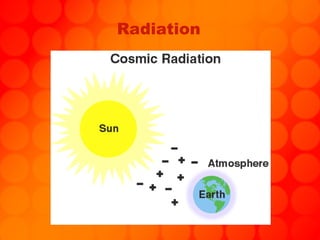
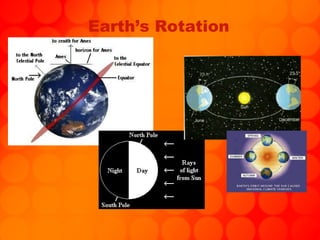
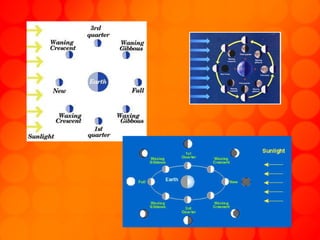
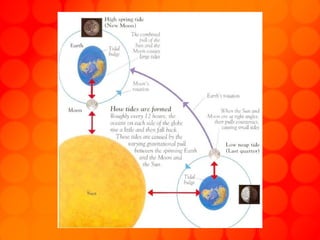
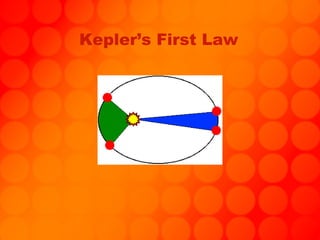
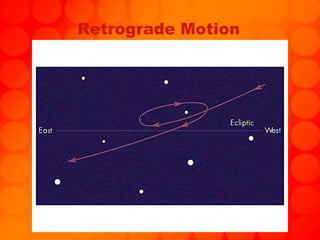
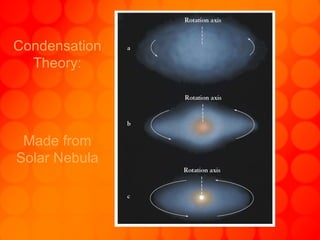
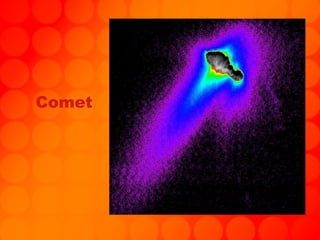
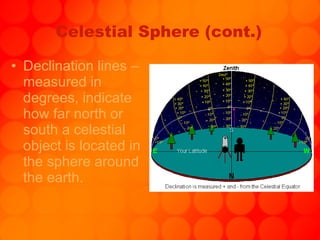
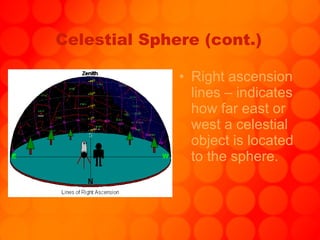
The document provides information about astronomy tools used to study space such as telescopes, satellites, probes, and spacecraft. It then summarizes key facts about the moon such as its composition, formation, phases and eclipses. Finally, it outlines a student project where each student is assigned a planet to research and create a children's book about.