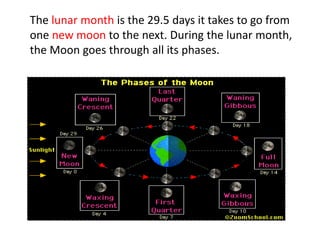
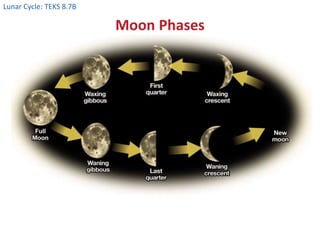
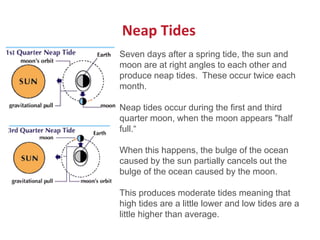
The Moon orbits Earth and reflects sunlight, which causes its phases to appear to change over the course of a lunar month as the illuminated portion changes from new to full and back to new. The Moon's gravitational pull, combined with the Sun's, causes two high and two low ocean tides each day. The greatest difference between high and low tides occurs during full Moons and new Moons, when their combined gravitational pulls reinforce each other.