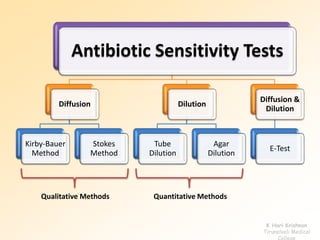
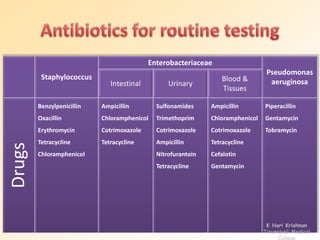
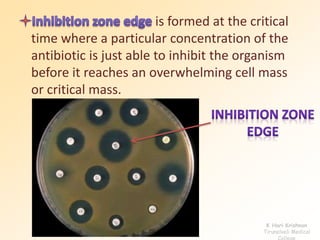
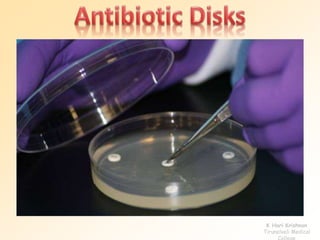
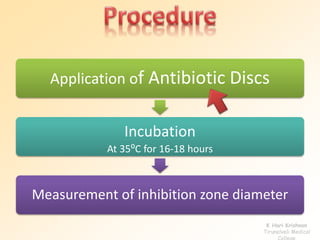
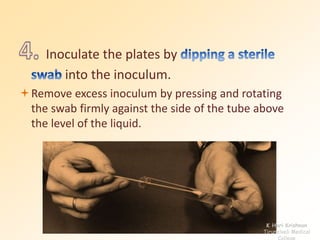
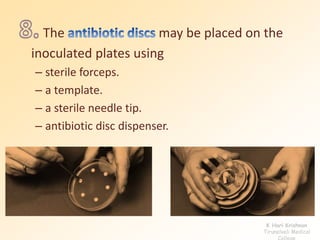
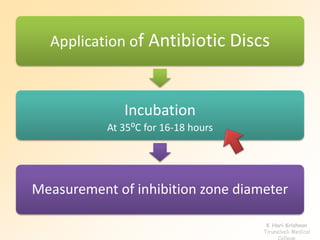
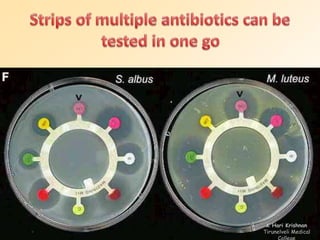
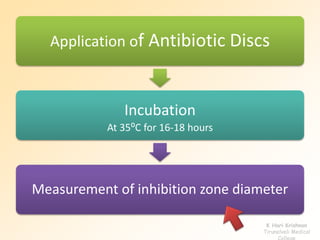
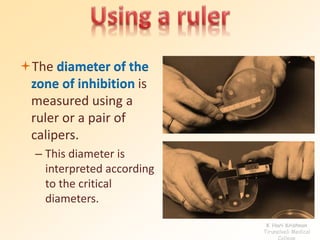
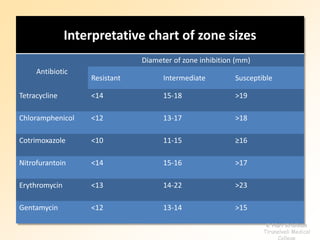
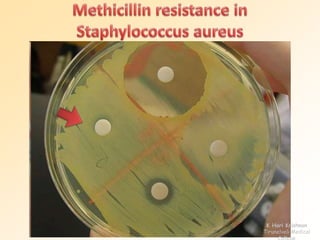
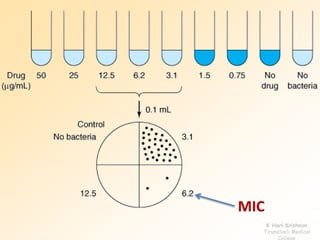
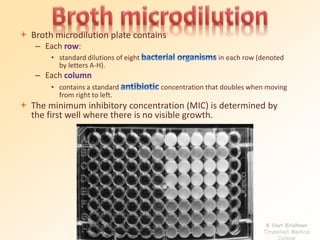
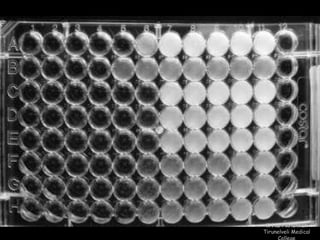
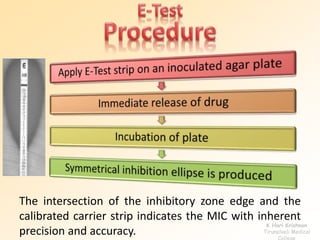
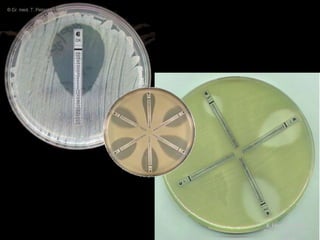
This document discusses antibiotic sensitivity testing (AST), which determines how effective antibiotics are against bacteria in vitro. AST is important for selecting the best antibiotic treatment for patients, monitoring antibiotic resistance trends, and accumulating epidemiological data. The Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method is described, which uses antibiotic-impregnated disks placed on agar plates inoculated with bacteria. The diameter of inhibition zones around the disks after incubation indicates antibiotic sensitivity. Interpretive criteria classify results as sensitive, intermediate, or resistant. AST provides guidance for clinicians in choosing effective antibiotic therapy.