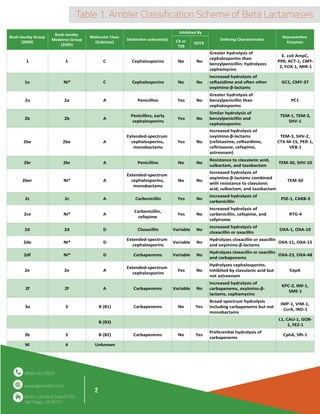
Beta-lactamase is an enzyme produced by bacteria that provides resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics like penicillin. It does this by hydrolyzing the beta-lactam ring structure in these antibiotics, rendering them ineffective. The document discusses the classification, mechanism of action, and applications of beta-lactamase. It describes how beta-lactamase is used to inactivate beta-lactam antibiotics in blood cultures and antibiotic assays to prevent false negative results. Protocols are provided for using beta-lactamase in blood cultures and aminoglycoside antibiotic assays.






![REFERENCES CONTINUED
8
www.agscientific.com
(858) 452-9925
6450 Lusk Blvd. Suite E102,
San Diego, CA 92121
Your Loyal Companion in ScienceTM
12. Neu HC. Effect of Beta-Lactamase Loca�on in Escherichia Coli on Penicillin Synergy. Appl Microbiol.
1969;17(6):783–6. PMC 377810.PMID4894721
13. Ambler RP. The Structure of Beta-Lactamases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci.
1980;289(1036): 321–31. doi:10.1098/rstb.1980.0049.
14. Genzyme Diagnos�cs. Penicillinase and β-Lactamase [PDF]. Charlo�etown, Canada: Genzyme
Diagnos�cs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/256e6ef2-5570-4ca4-a767-b9fe7282fa52-170216030215/85/BLG_fin-9-320.jpg)