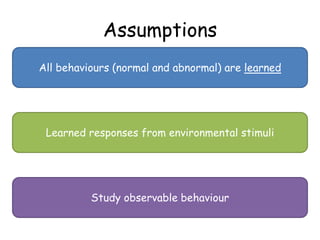
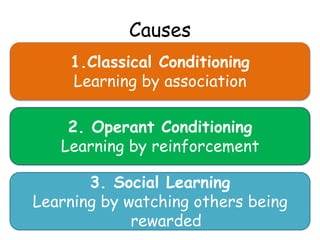
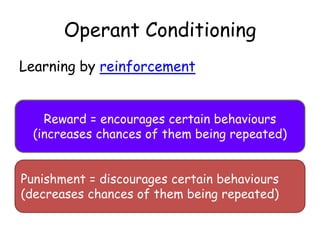
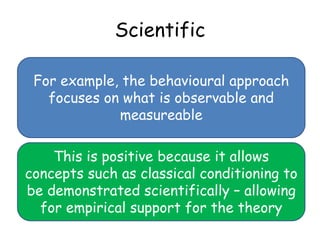
The behavioral approach views all behaviors as learned through environmental stimuli and interactions. It studies observable behaviors and focuses on three main learning processes: classical conditioning through association; operant conditioning through reinforcement and punishment; and social learning through observing others. A strength is its scientific study of concepts like classical conditioning, but it is also reductionist by oversimplifying complex issues. Using animal studies also poses issues with extrapolating findings to human behaviors.