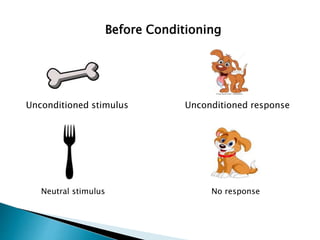
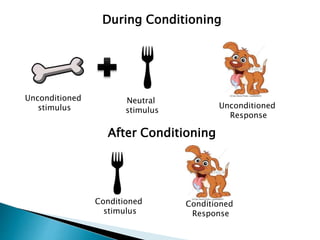
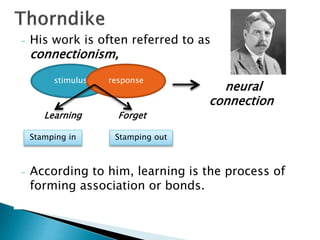
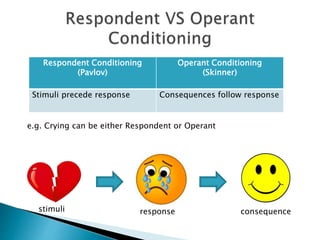
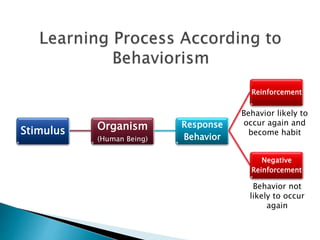
This document discusses behaviorism and its key figures and application in language learning. Behaviorism focuses on observable behaviors and views the mind as a "black box." Key figures include Pavlov who discovered classical conditioning through training a dog to salivate to a tone, and Skinner who developed operant conditioning through reinforcement of behaviors. In the 1950s-60s, behaviorism influenced the audiolingual method of language teaching, which used repetition, pattern drills, and reinforcement to build stimulus-response associations without explicit focus on meaning or cognition. Writing instruction focused on imitation and copying practiced sentences.