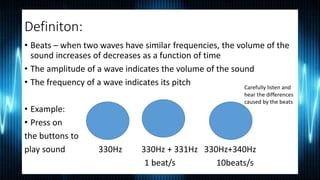
Beats occur when two sounds with similar frequencies are played together, causing the overall volume to increase and decrease over time. The frequency of a wave determines its pitch, while the amplitude determines volume. When two tones have a small frequency difference, such as 330Hz and 331Hz, beats will occur approximately once per second. But with a larger difference, like 200Hz vs 400Hz, beats are no longer present. Beats can be modeled mathematically using equations that describe the interaction of two wave amplitudes over time and position. Questions about beat frequency and number of beats in a time period can be solved using formulas involving the individual frequencies.