This document outlines key concepts related to data processing including:
- Data refers to facts and observations represented by symbols. Data processing manipulates data to transform it into useful information.
- Data processing activities include tools to convert data into information, from manual to electronic tools.
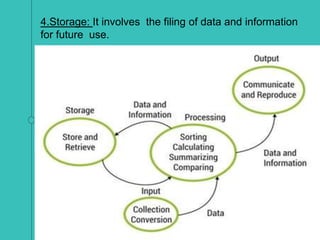
- The data processing cycle includes input, processing, output, and storage steps.
- Data hierarchy shows the arrangement of data from fields to records to files to databases.