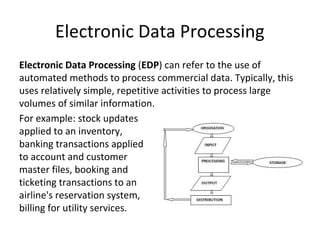
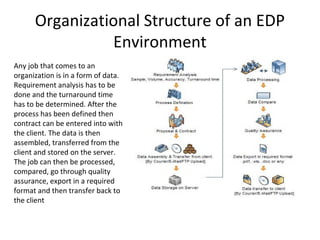
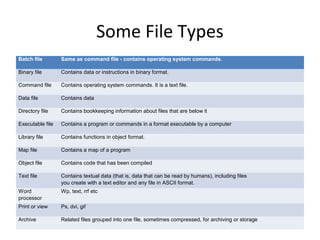
The document discusses key concepts related to electronic data processing (EDP) environments. It describes the organizational structure of an EDP environment and defines computer files and their elements. It explains different types of files like text, image, audio and video files. It also discusses various file organization methods like sequential, indexed-sequential and direct access. The document describes storage media devices, data processing activities, and vulnerabilities of files from improper input and software abuse.