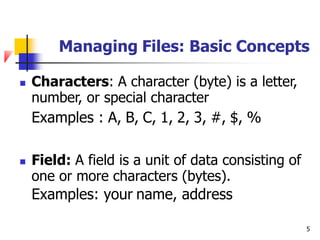
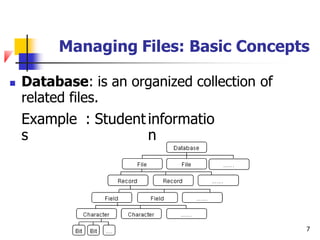
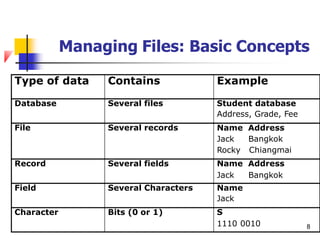
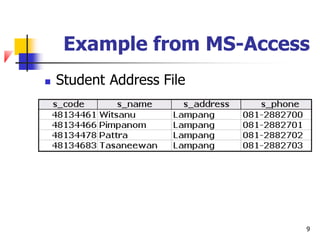
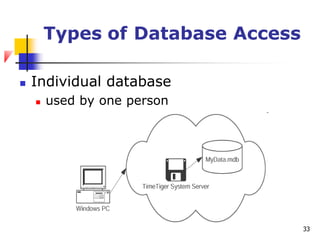
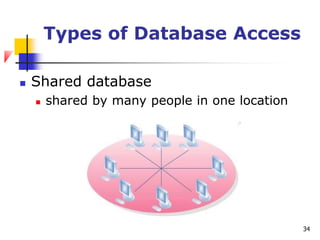
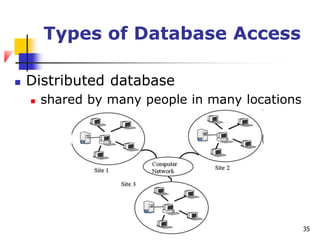
The document discusses basic concepts related to managing files and data storage in computers. It explains that data can be organized into hierarchical levels from bits to files and databases. It defines key terms like characters, fields, records, files and databases. It also describes different types of files like program files, data files, ASCII files, image files, audio files and web files. Additionally, it covers data access methods, online and offline storage, database management systems, and types of database access.