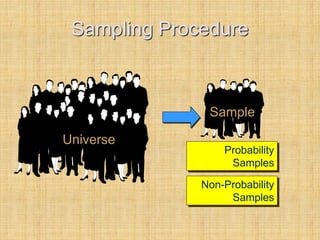
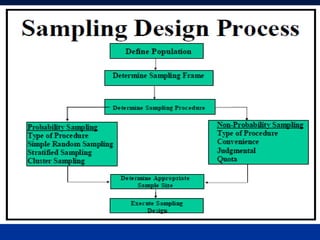
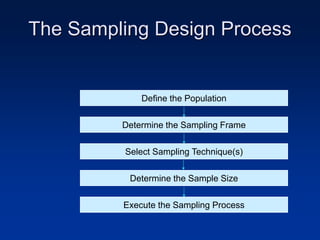
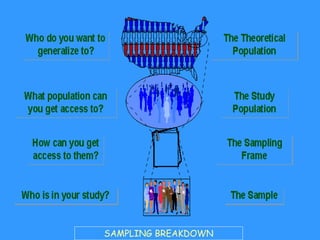
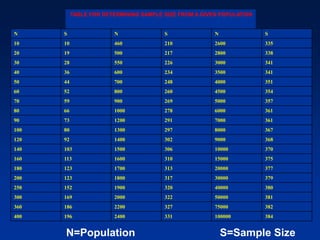
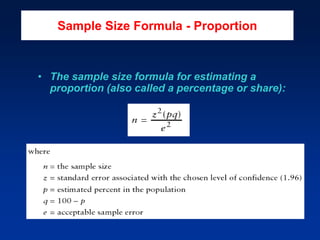
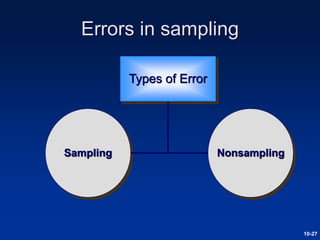
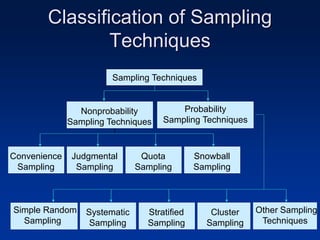
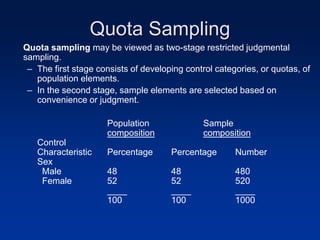
This document discusses sample design and the steps involved in determining an appropriate sample. It defines key terms like population, sample, sampling frame, and outlines different sampling techniques. It emphasizes the importance of sample size and how to calculate it using confidence intervals in order to achieve the desired level of accuracy and confidence in results. Sources of error like sampling error and non-sampling error are also explained.