Embed presentation
Downloaded 15 times



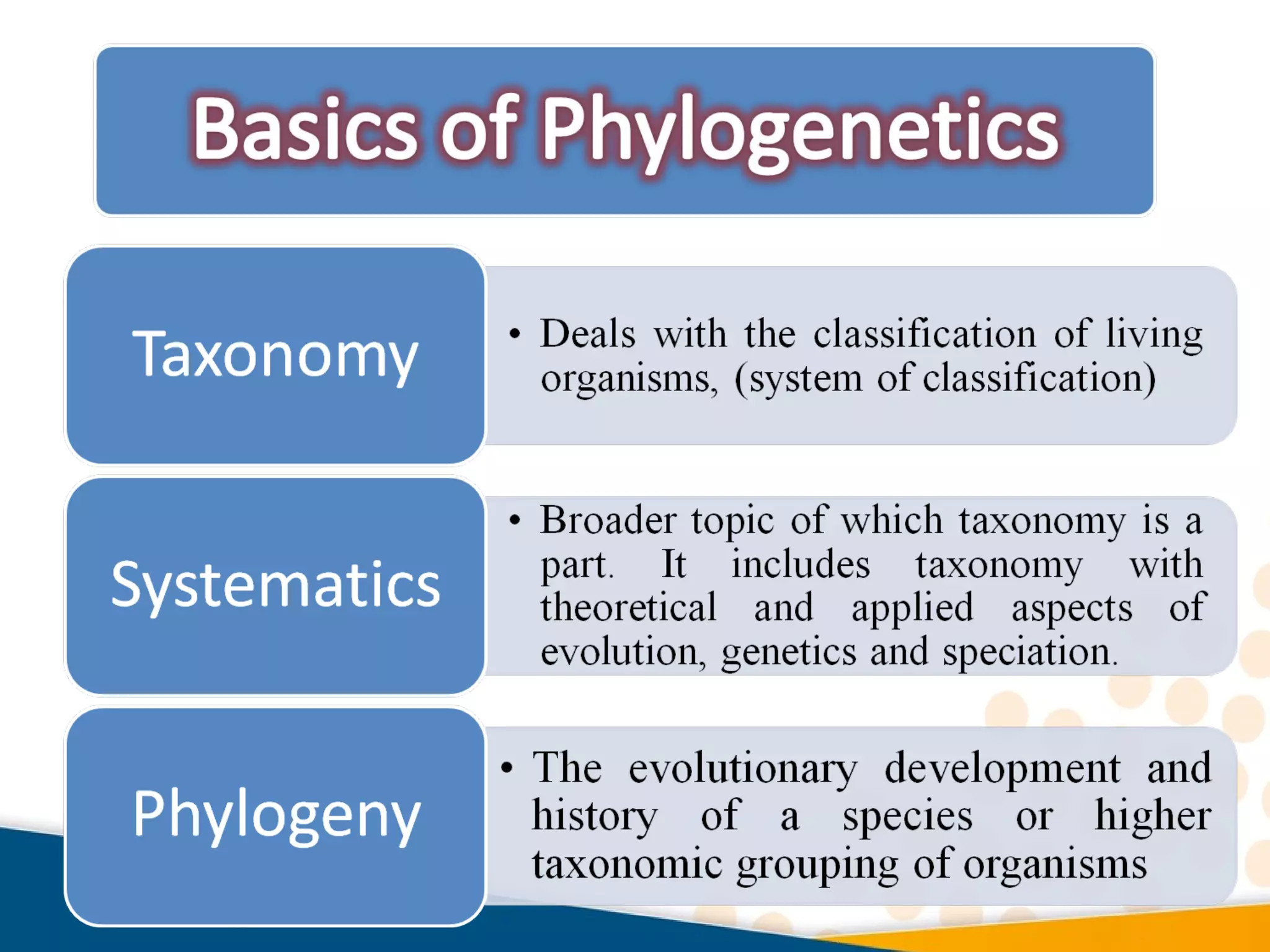
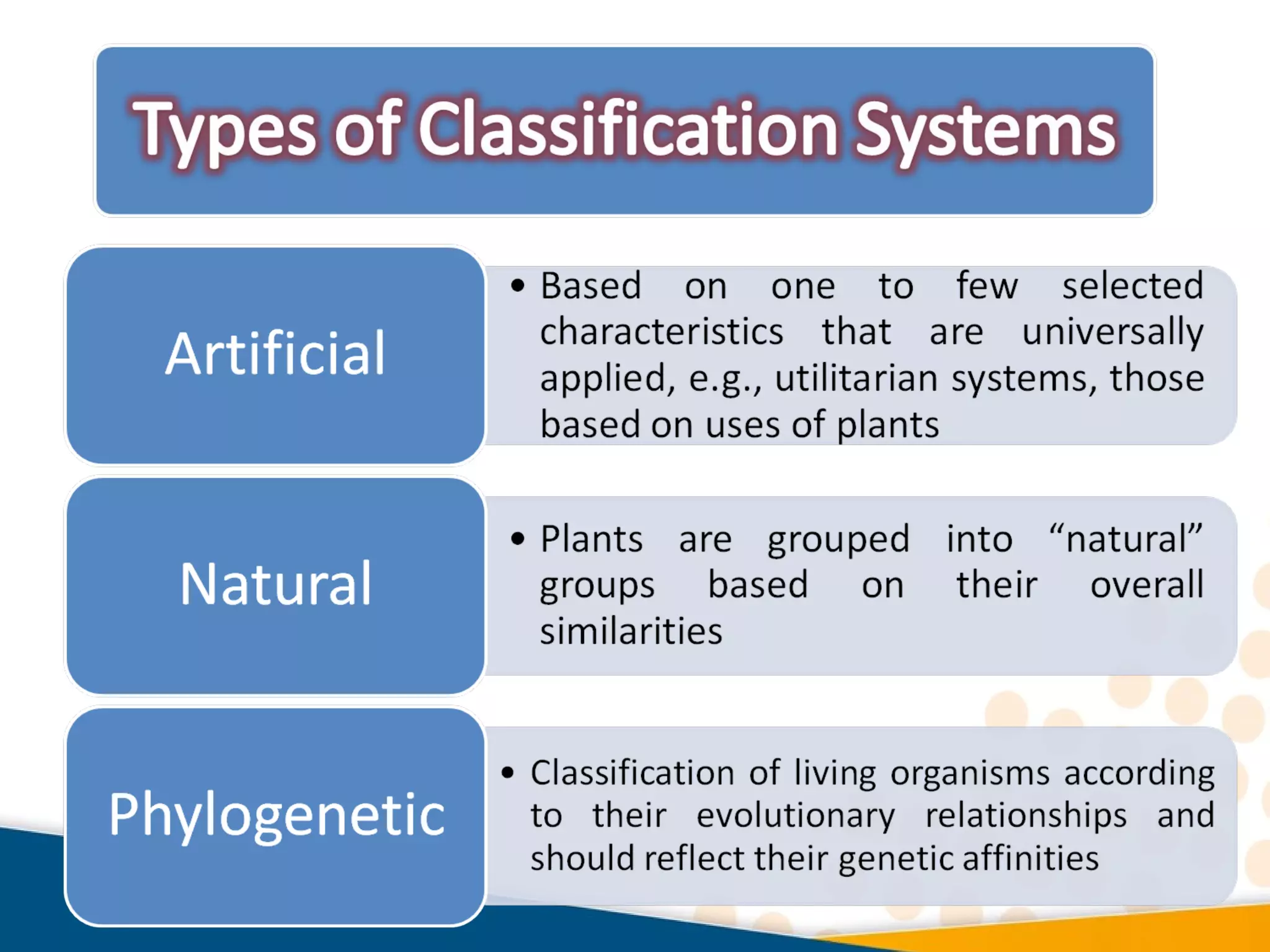
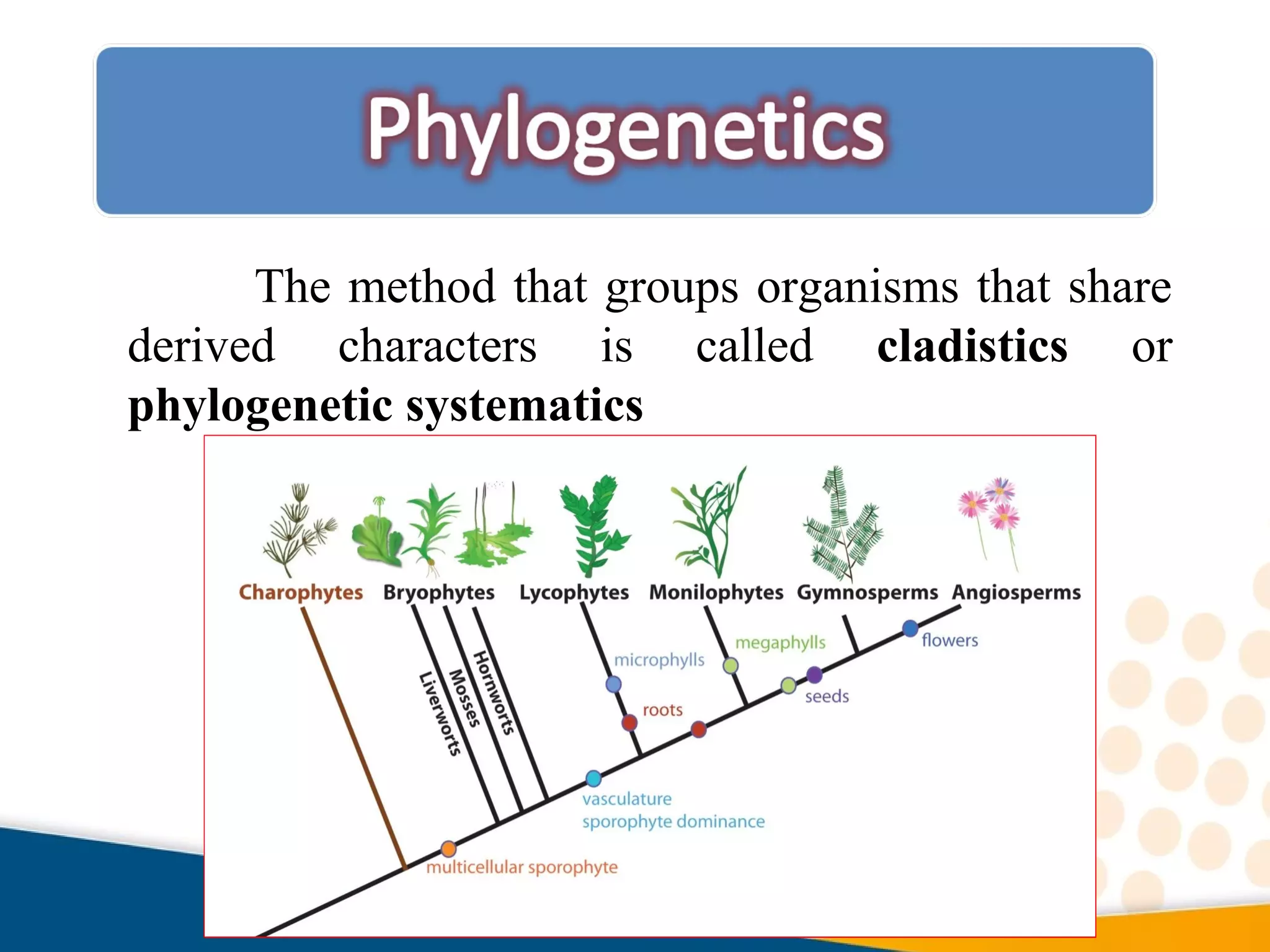
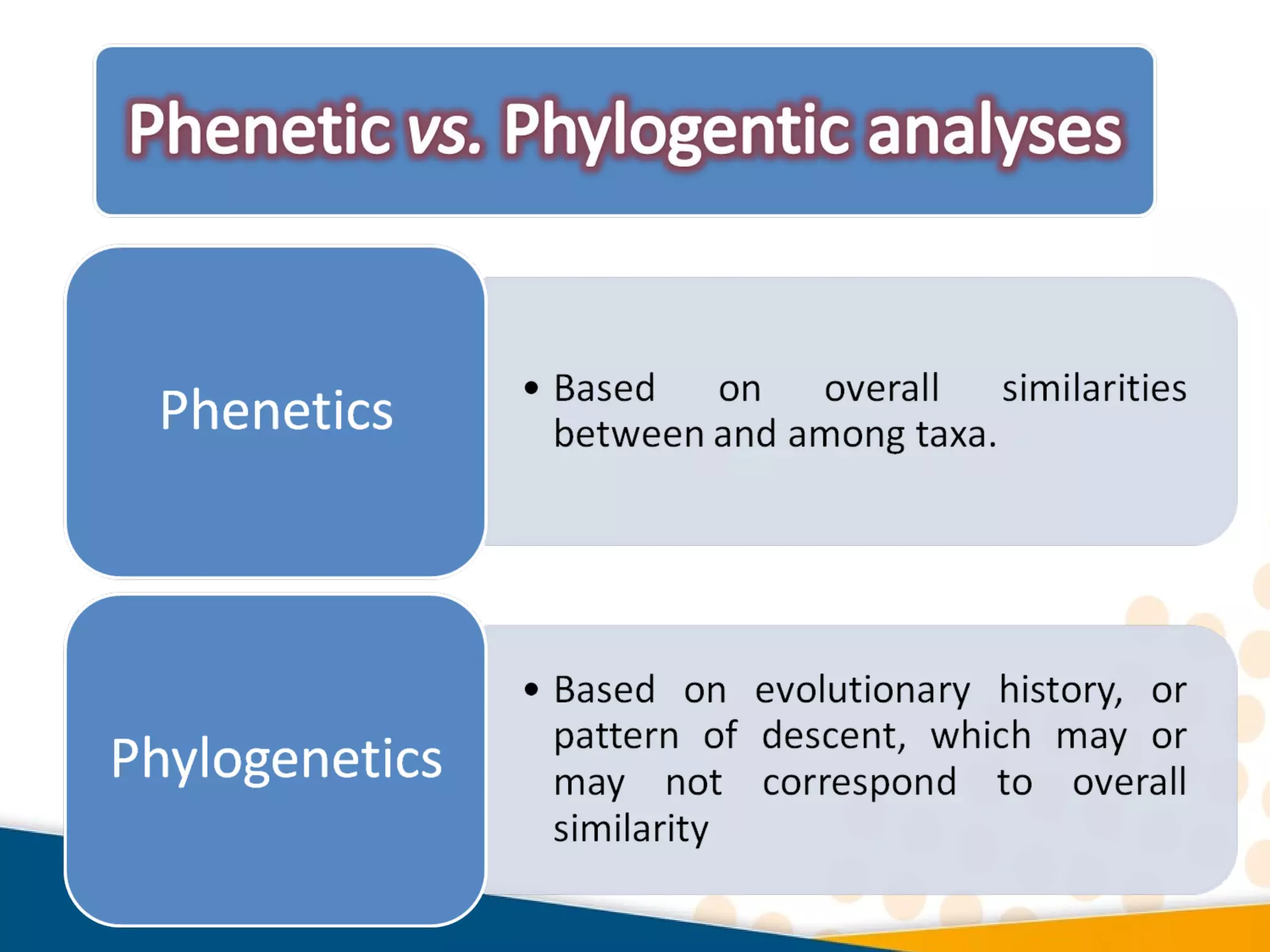
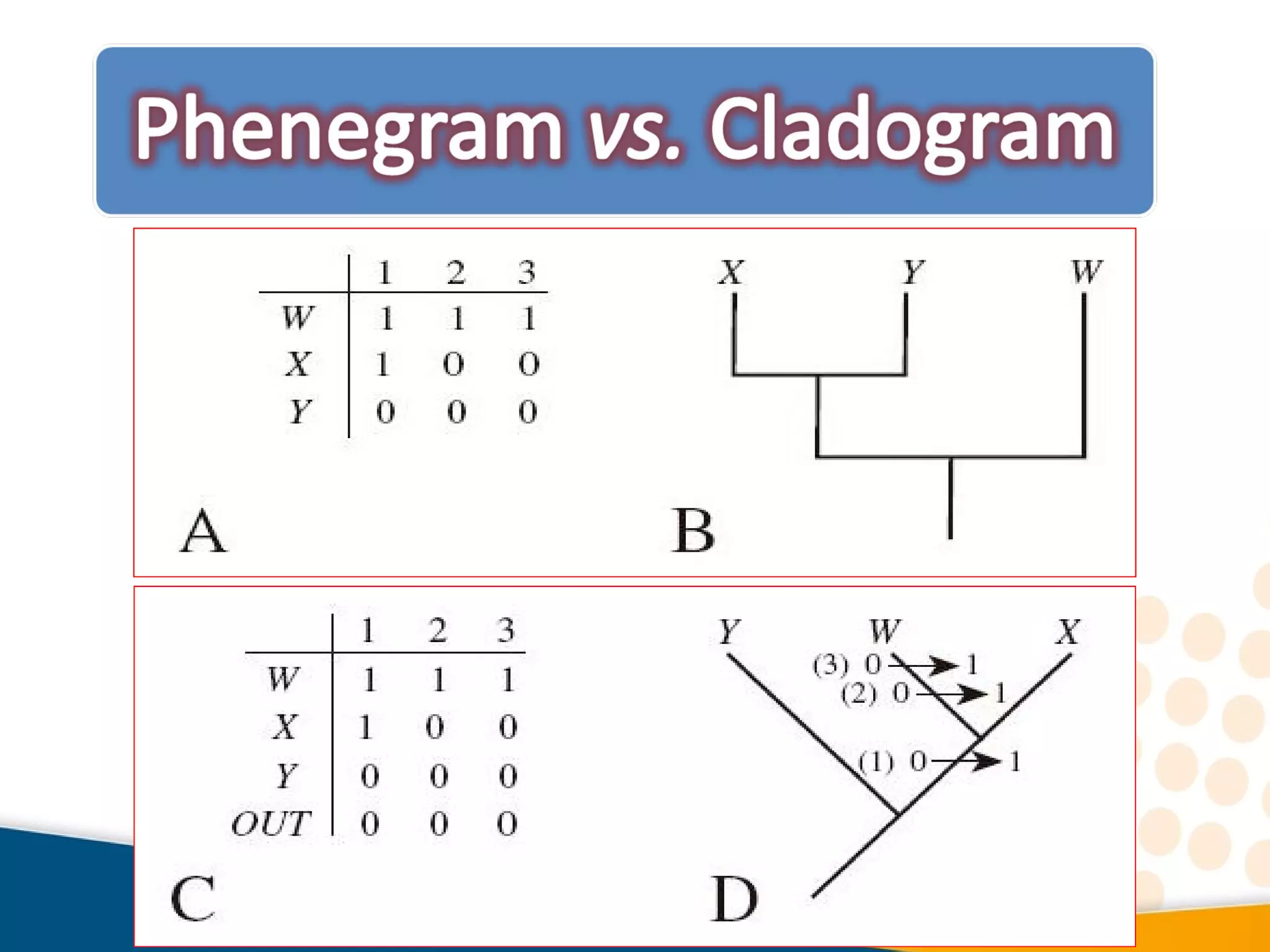
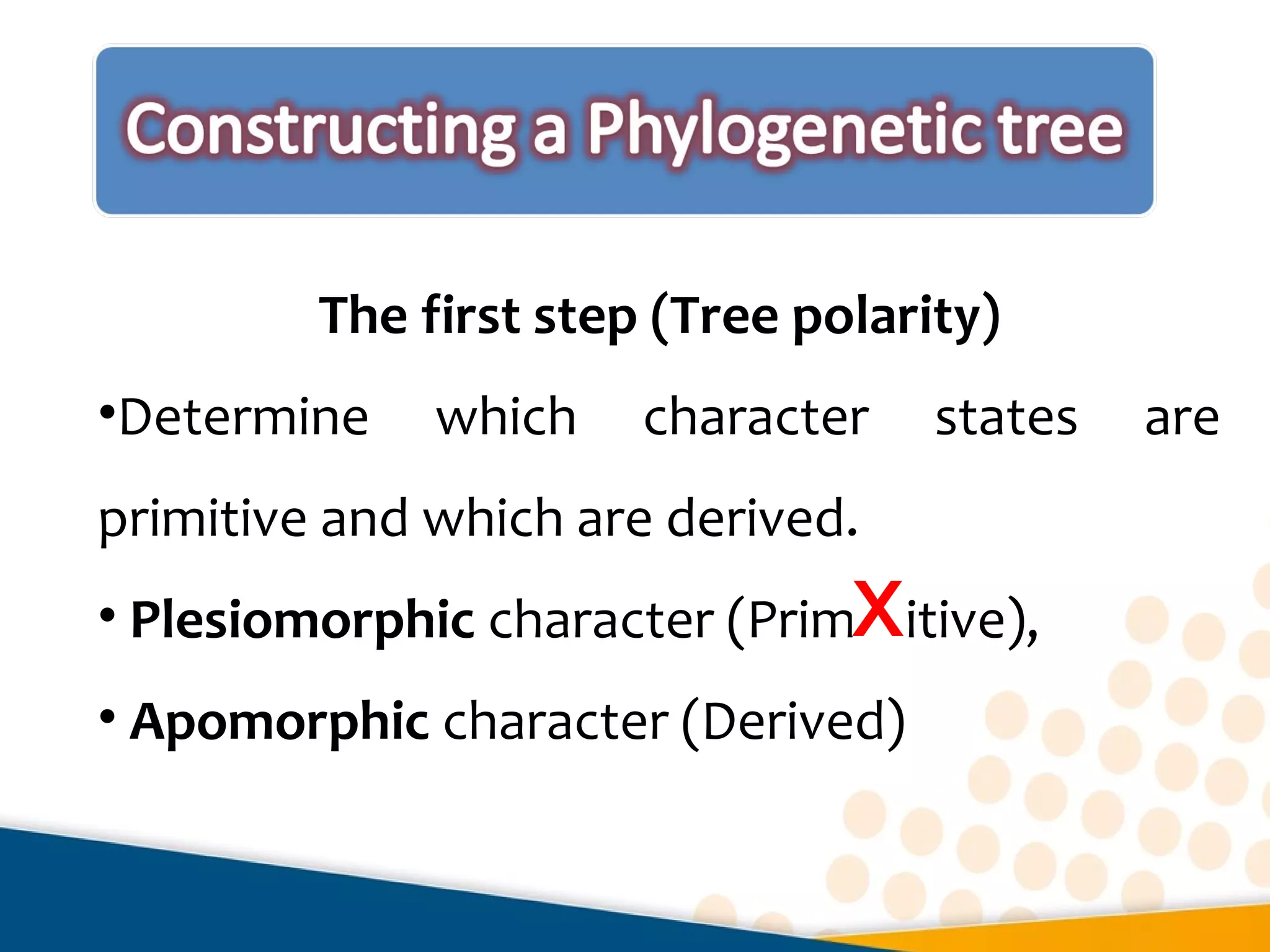

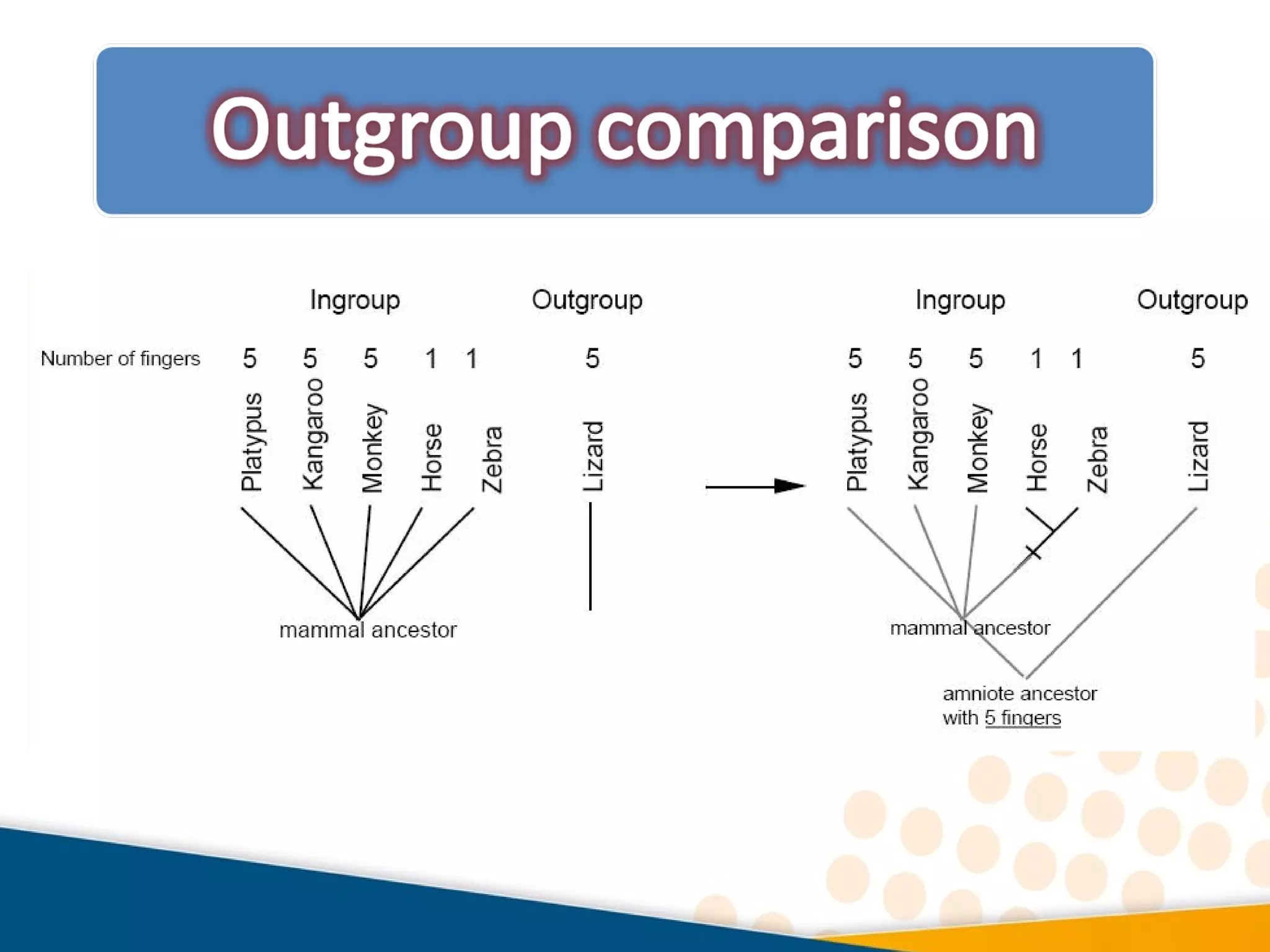
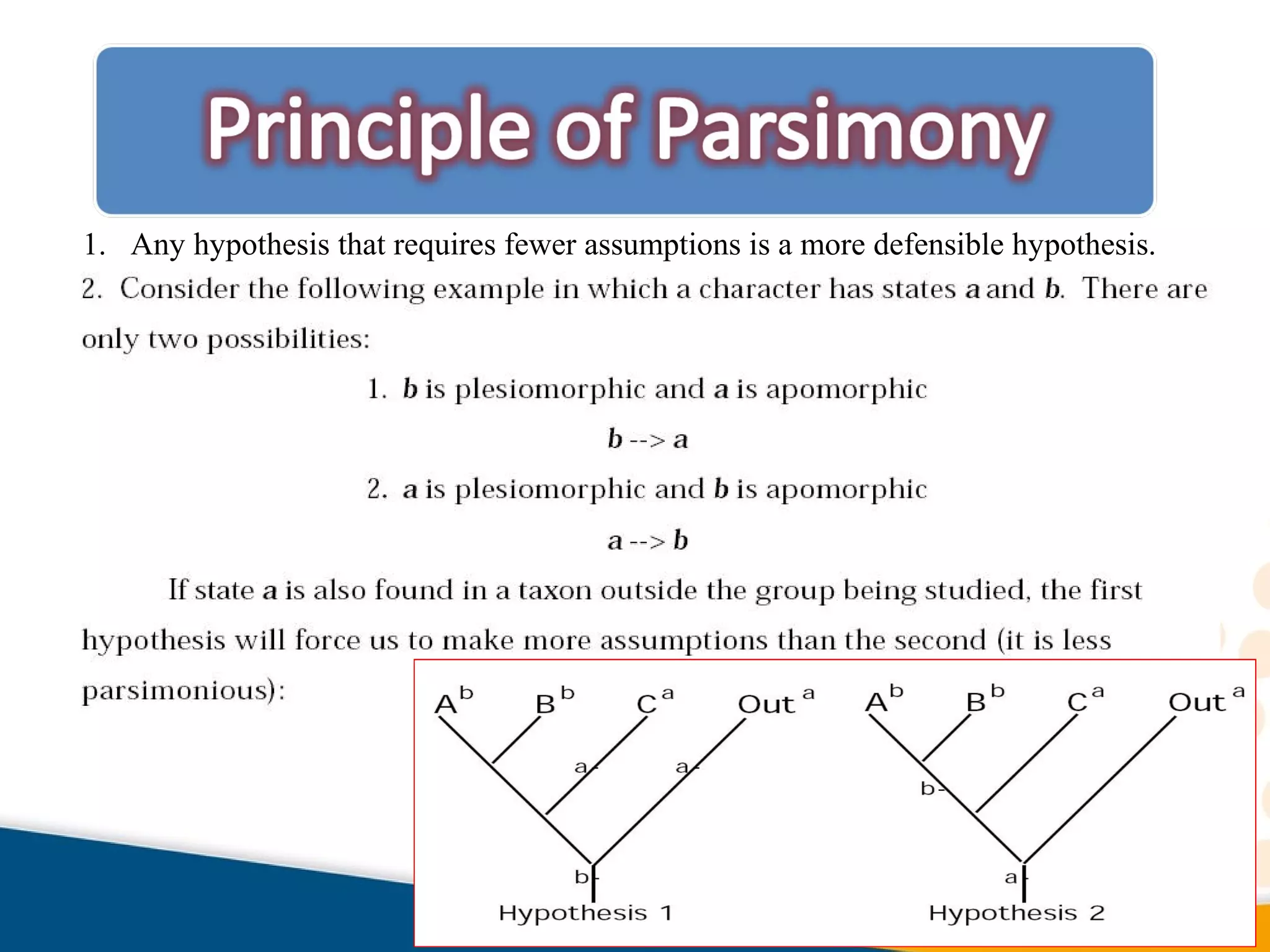

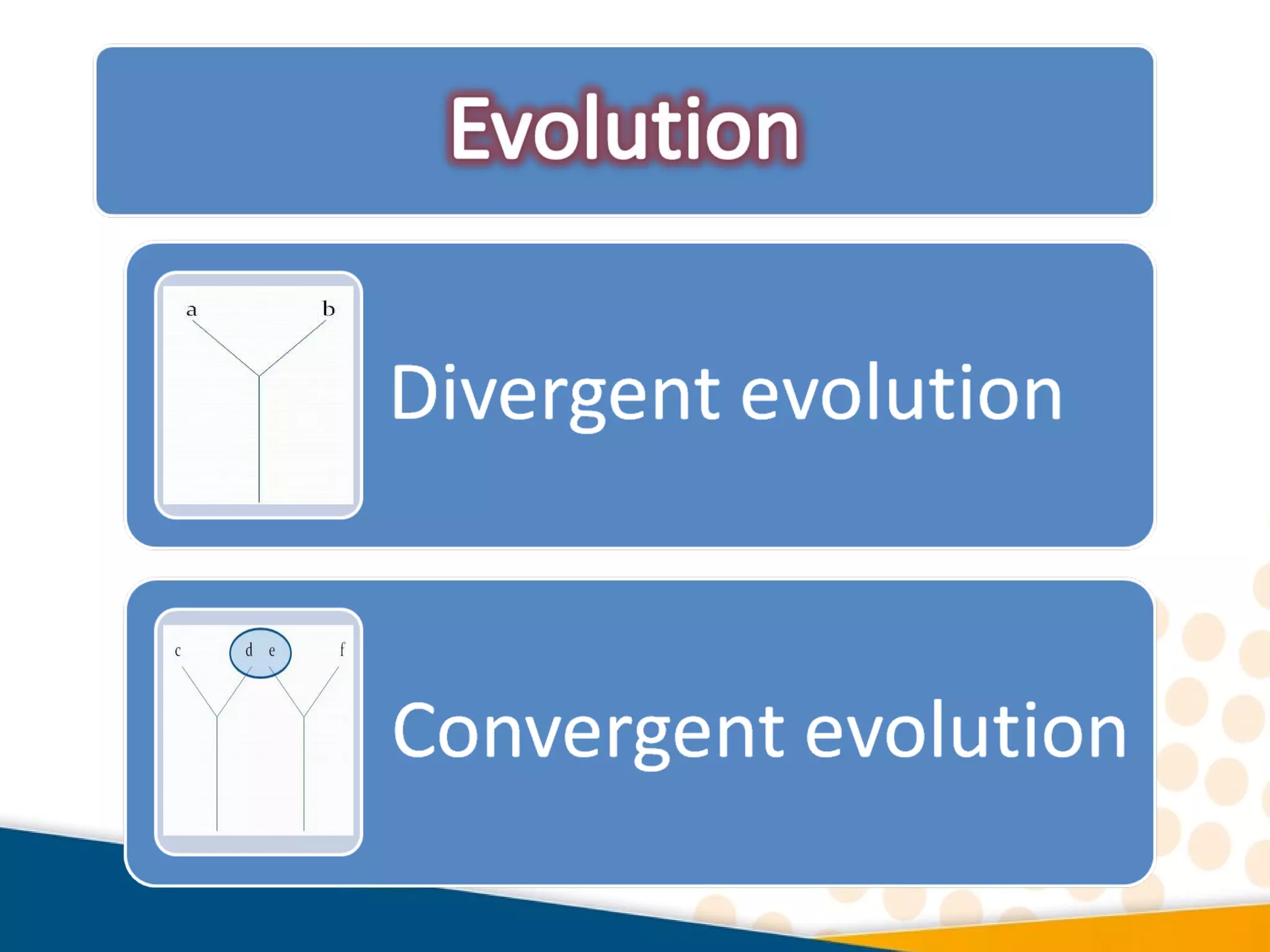
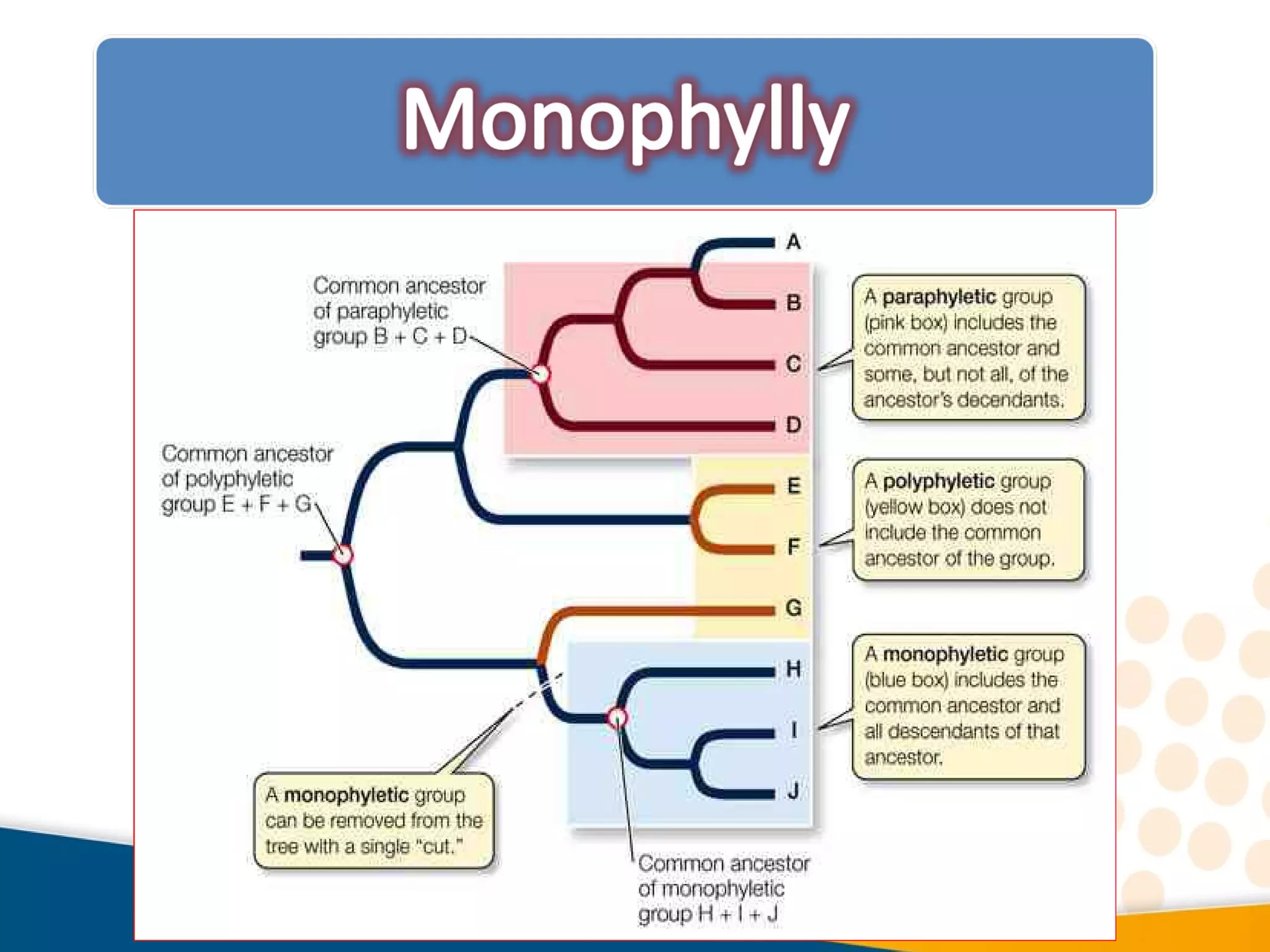
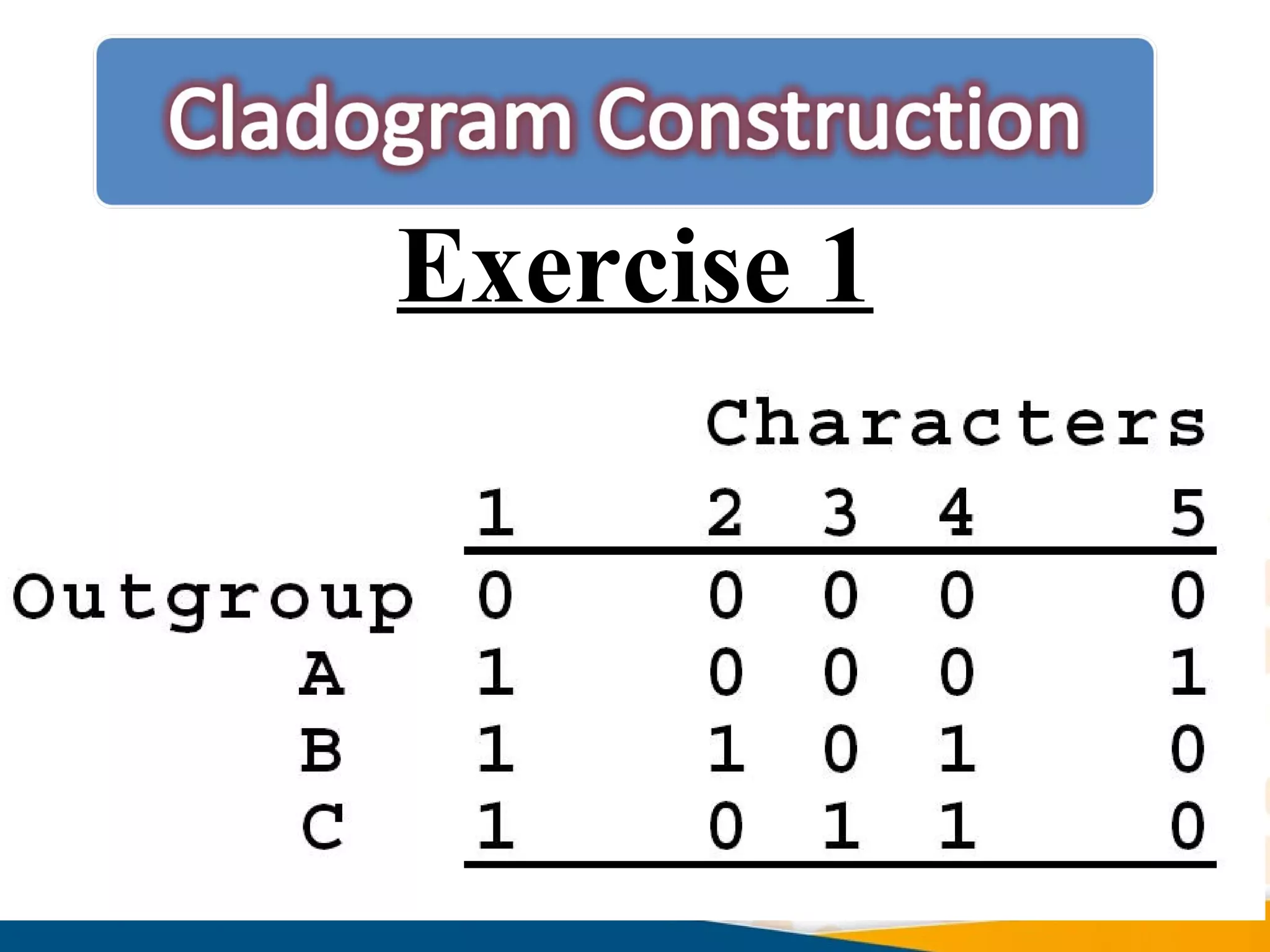
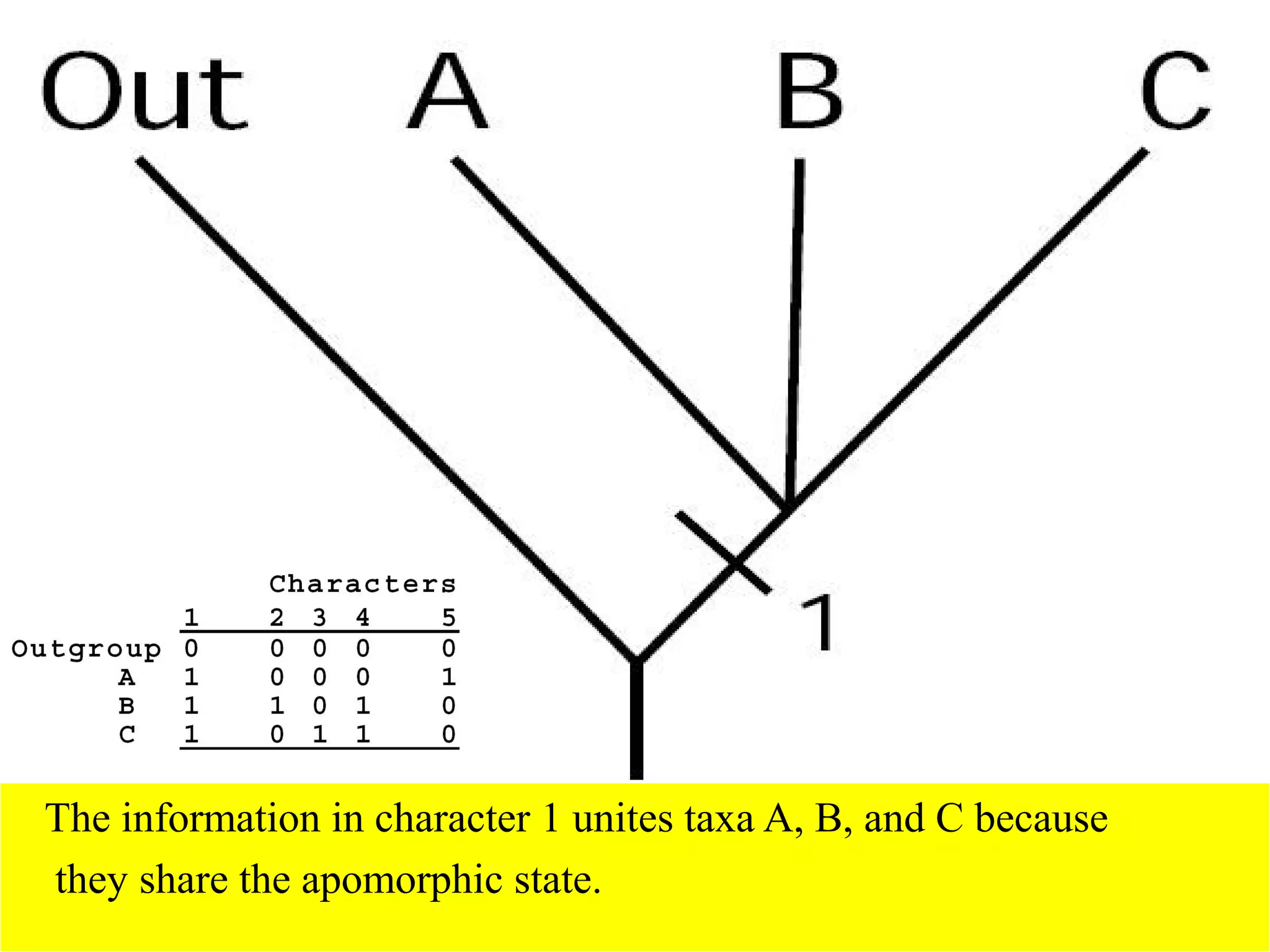
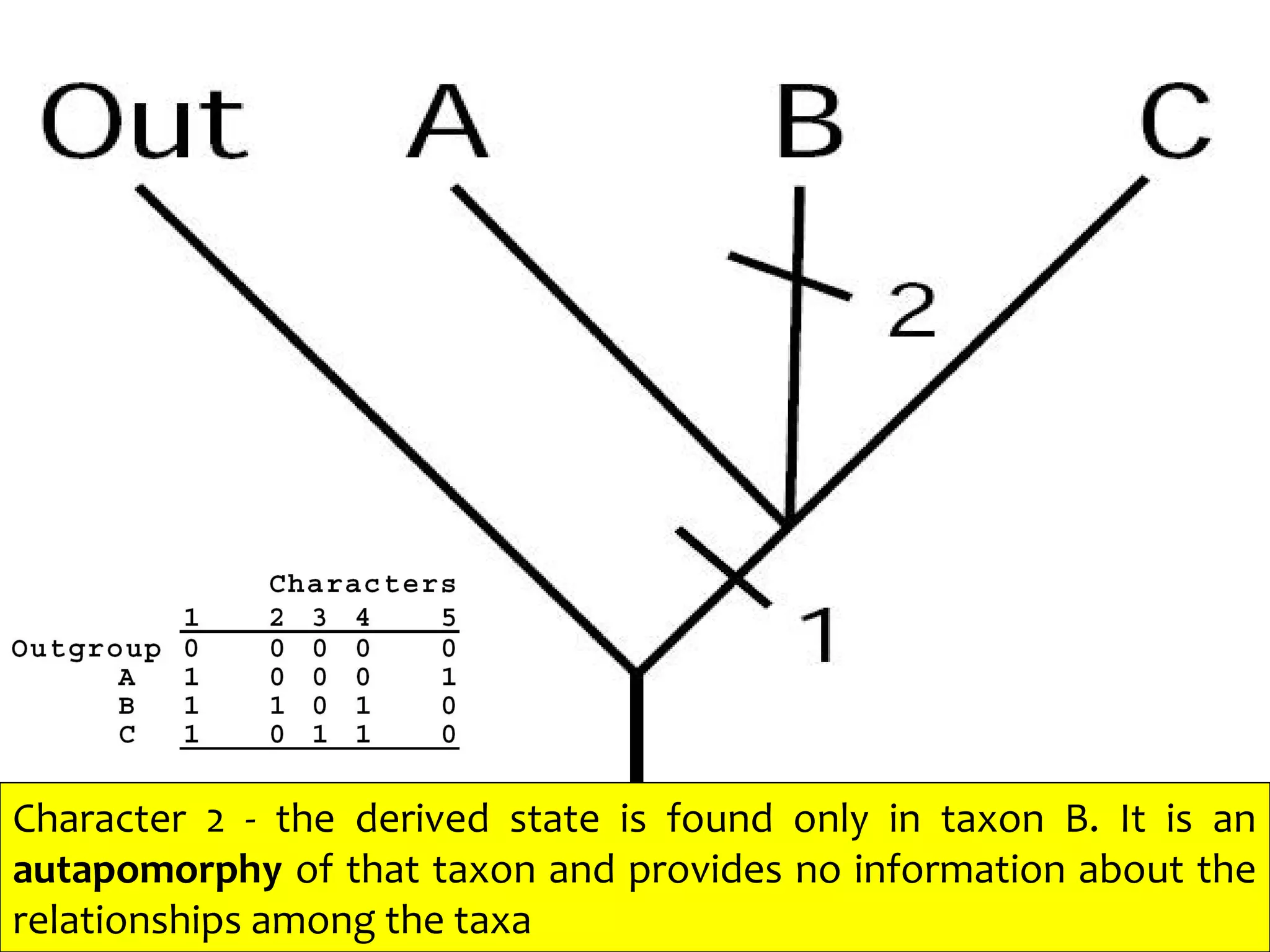
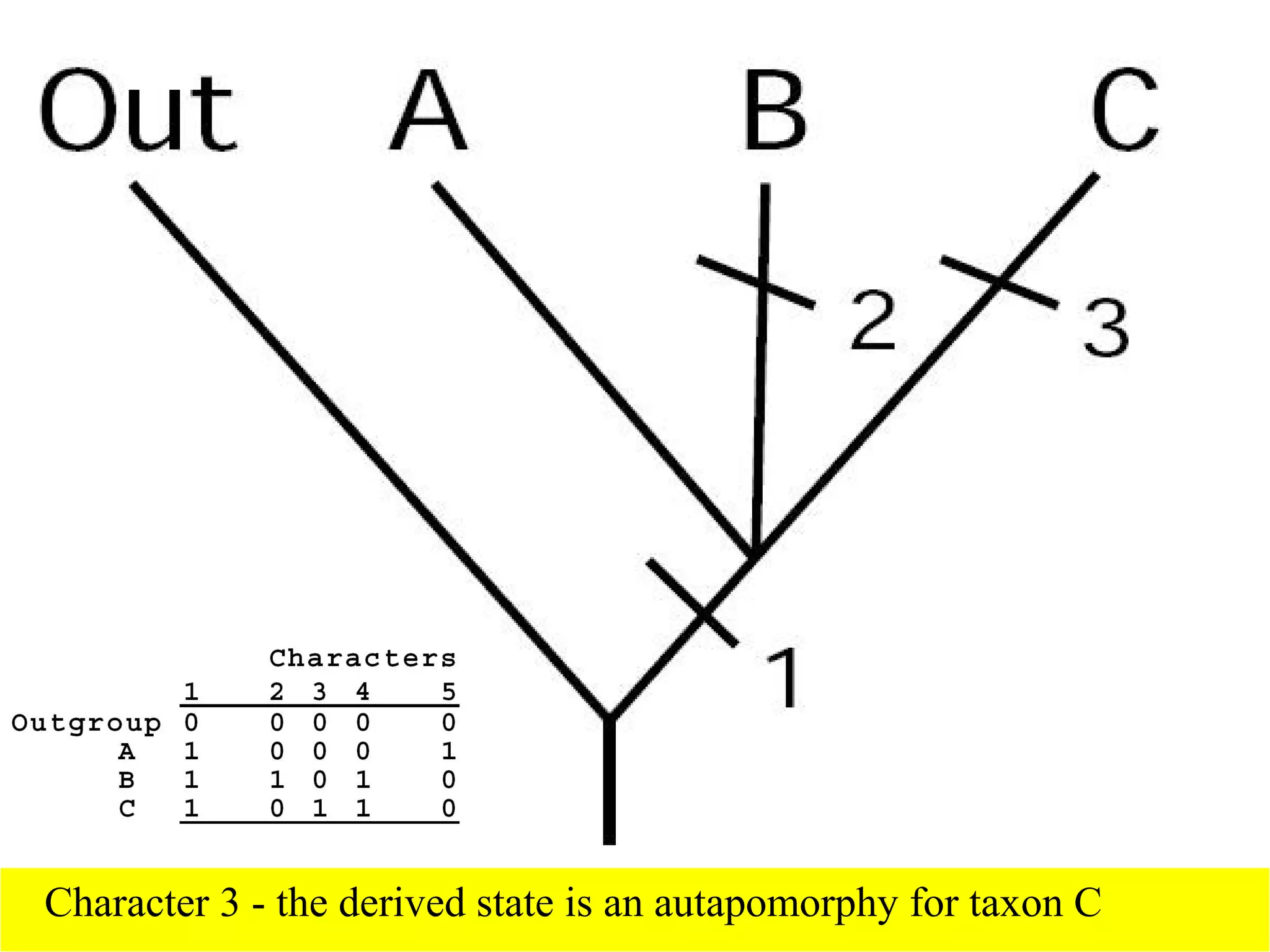
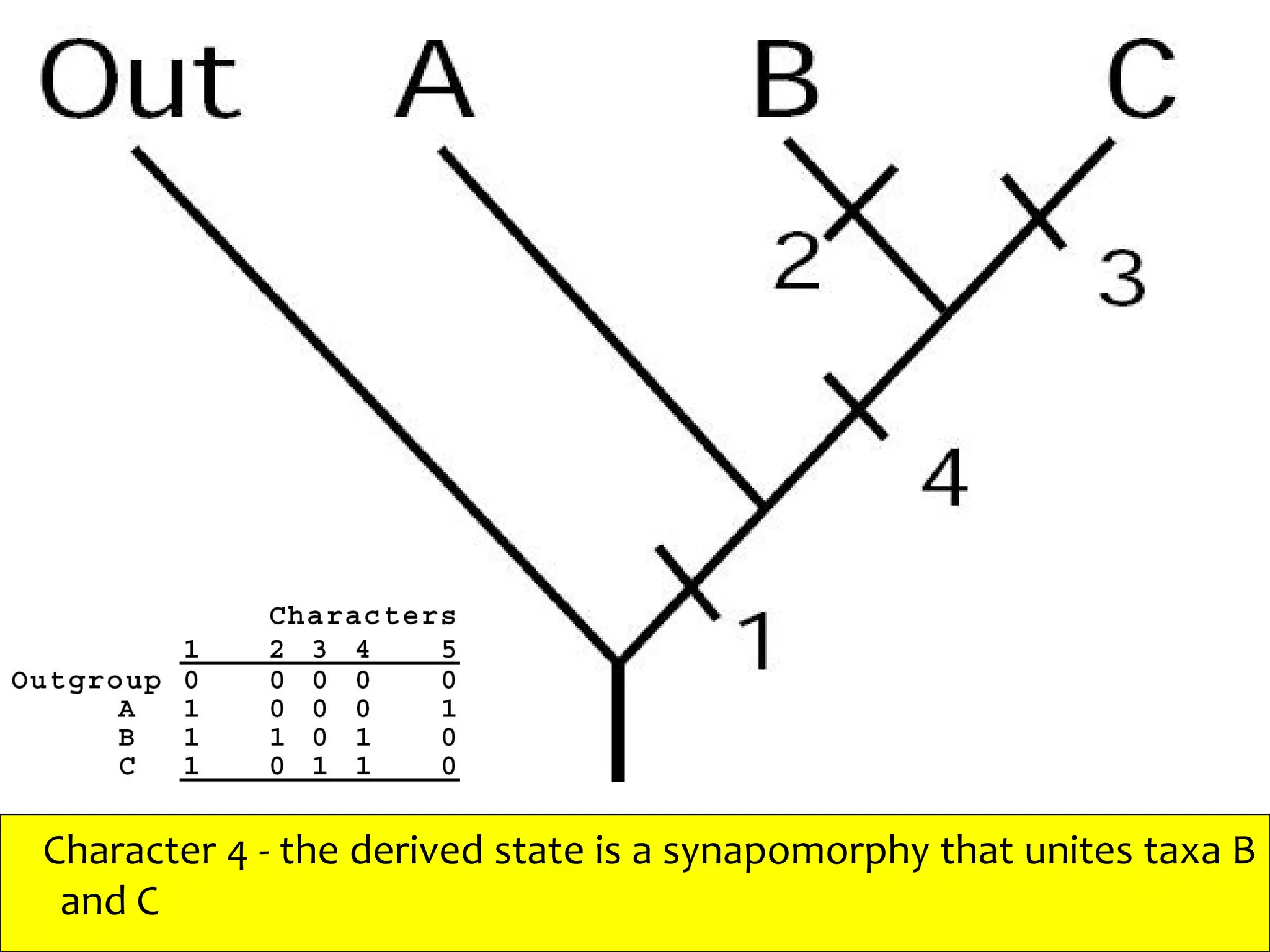
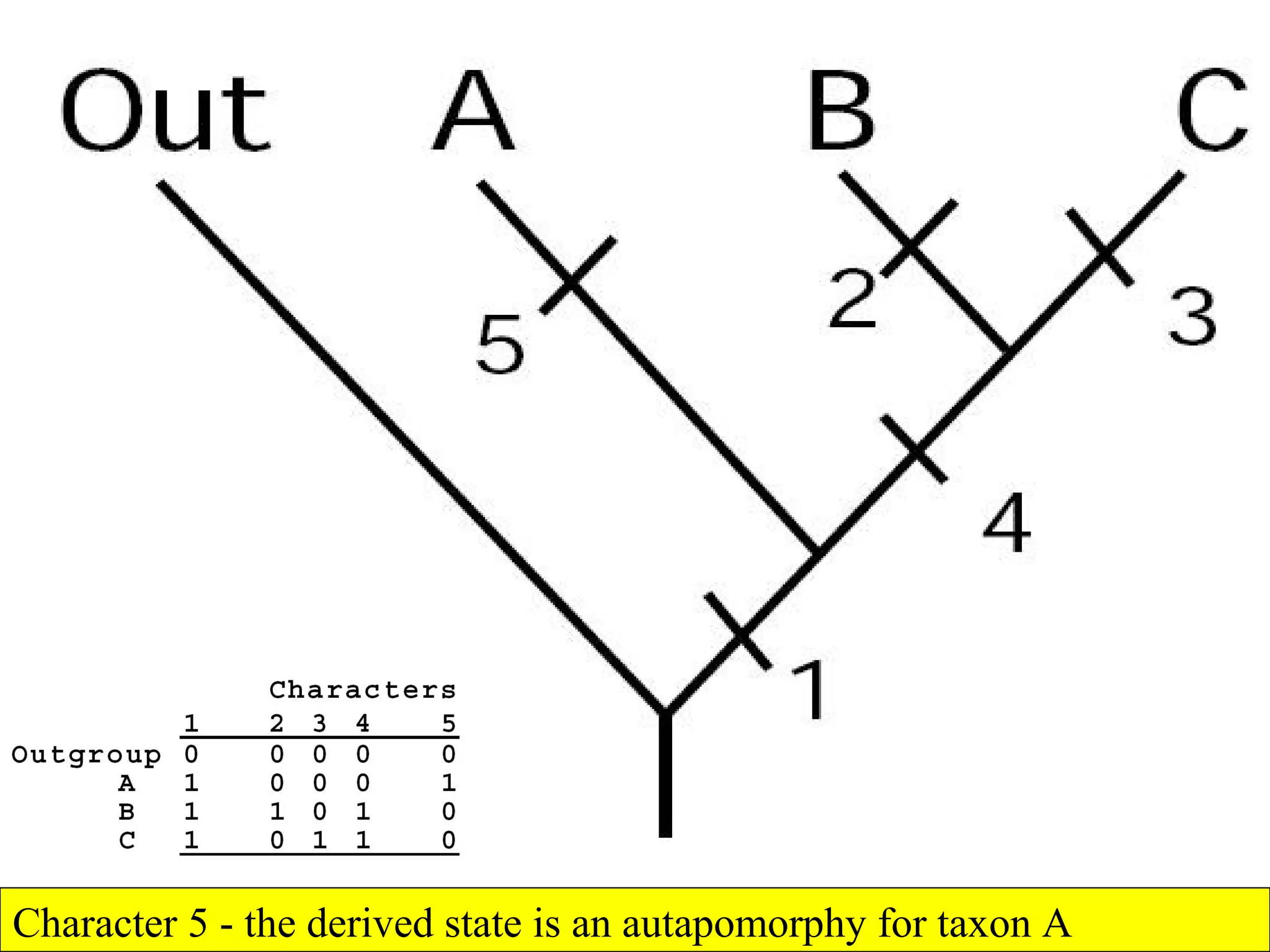
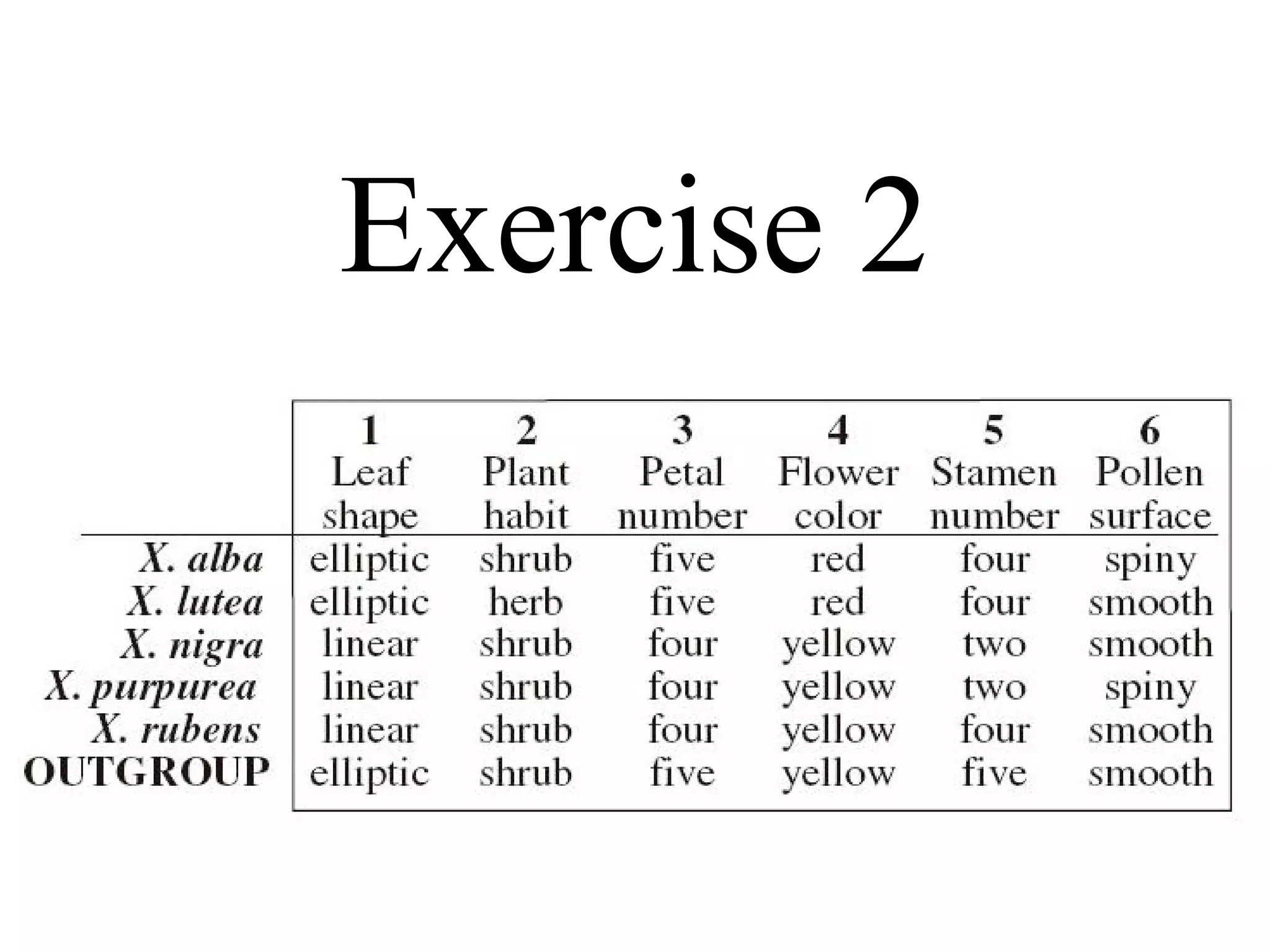
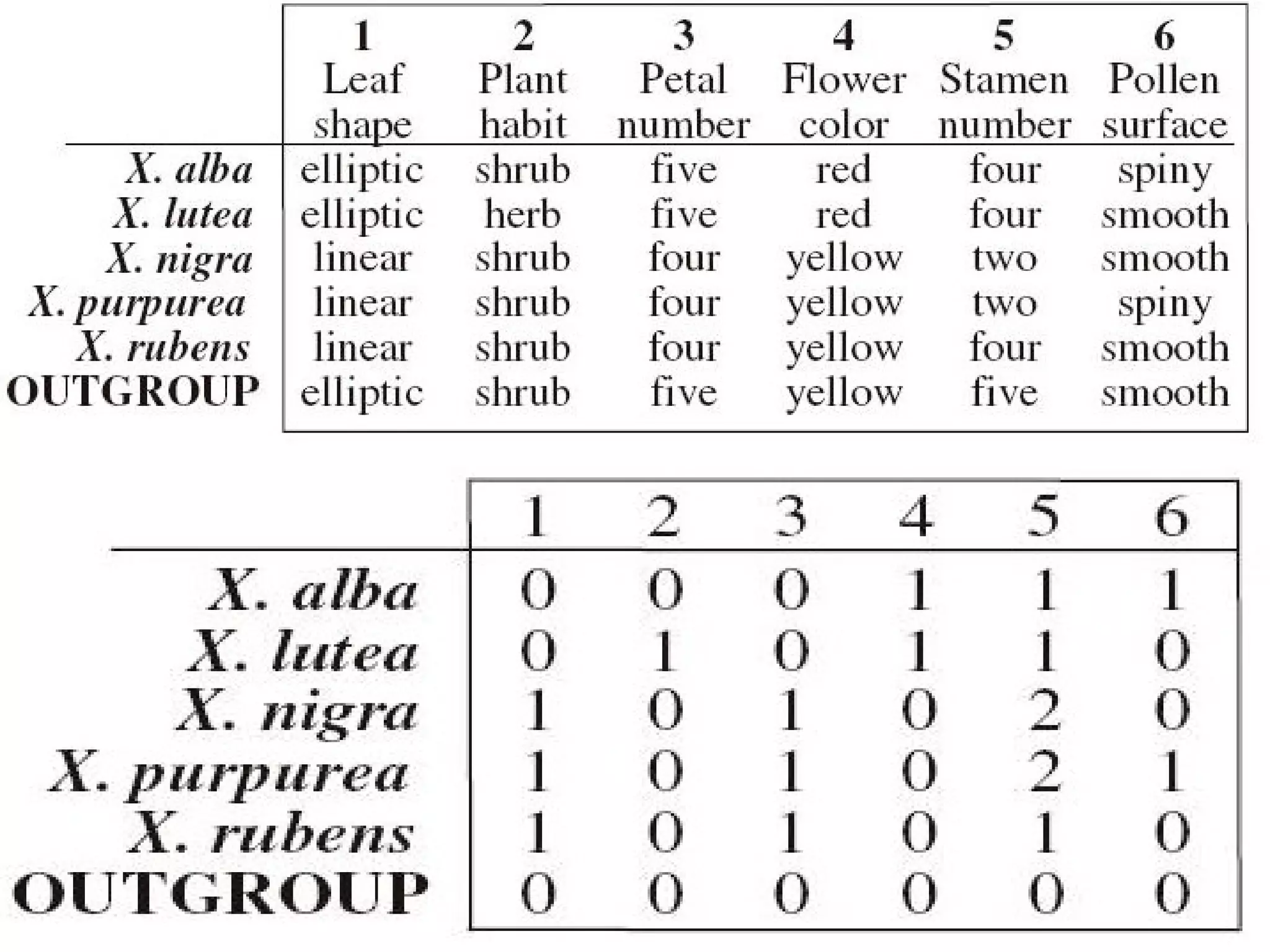
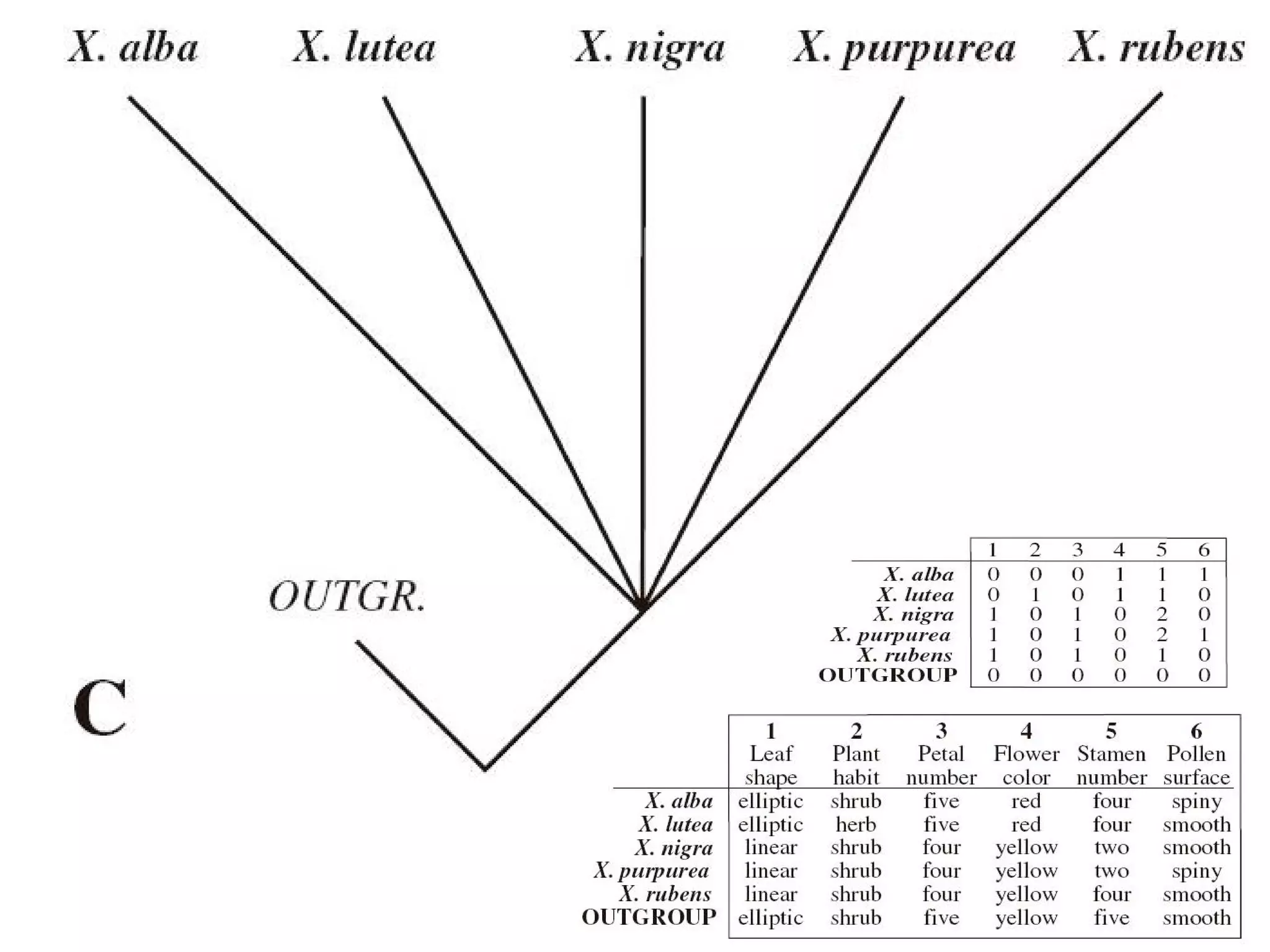
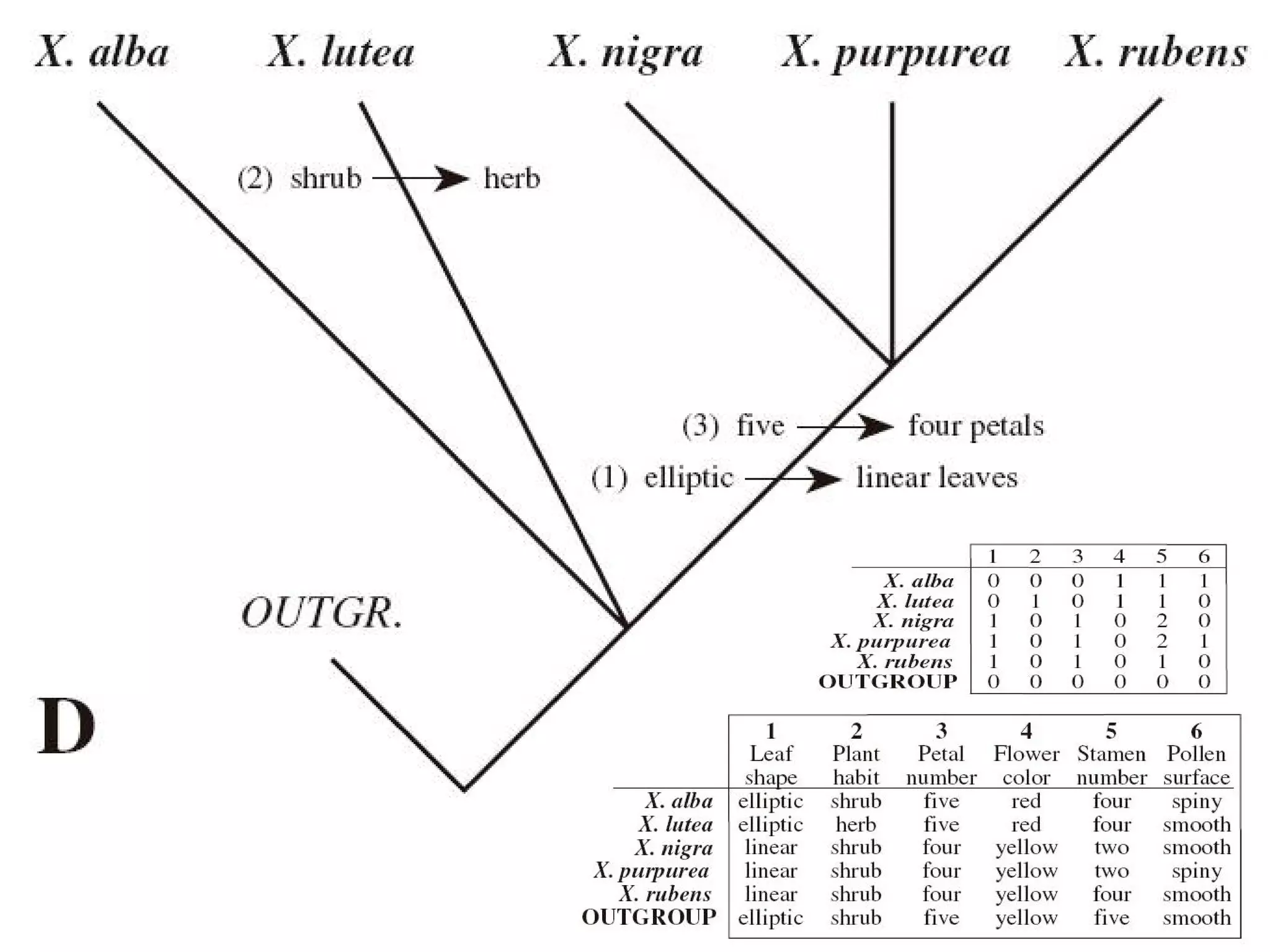
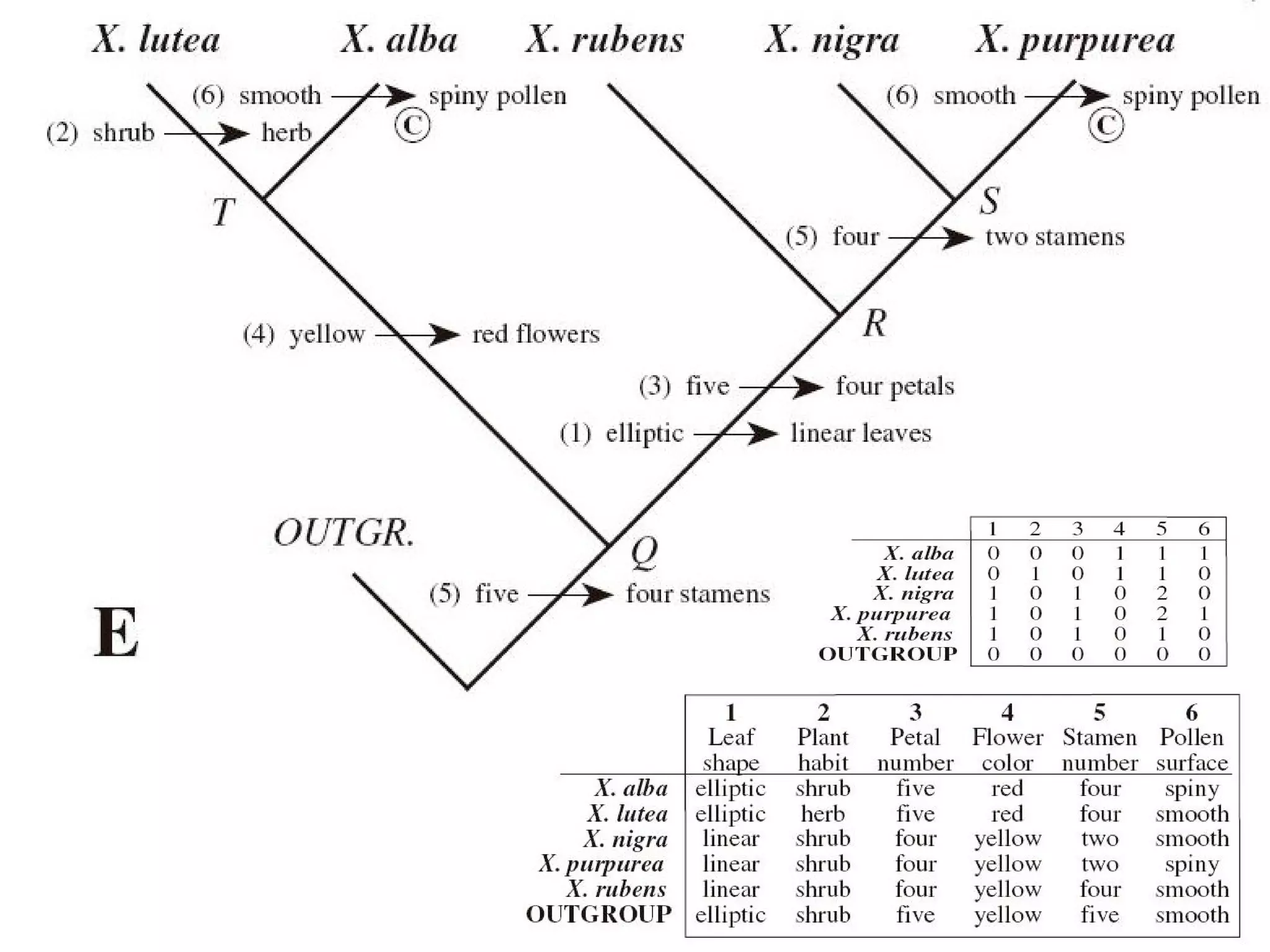
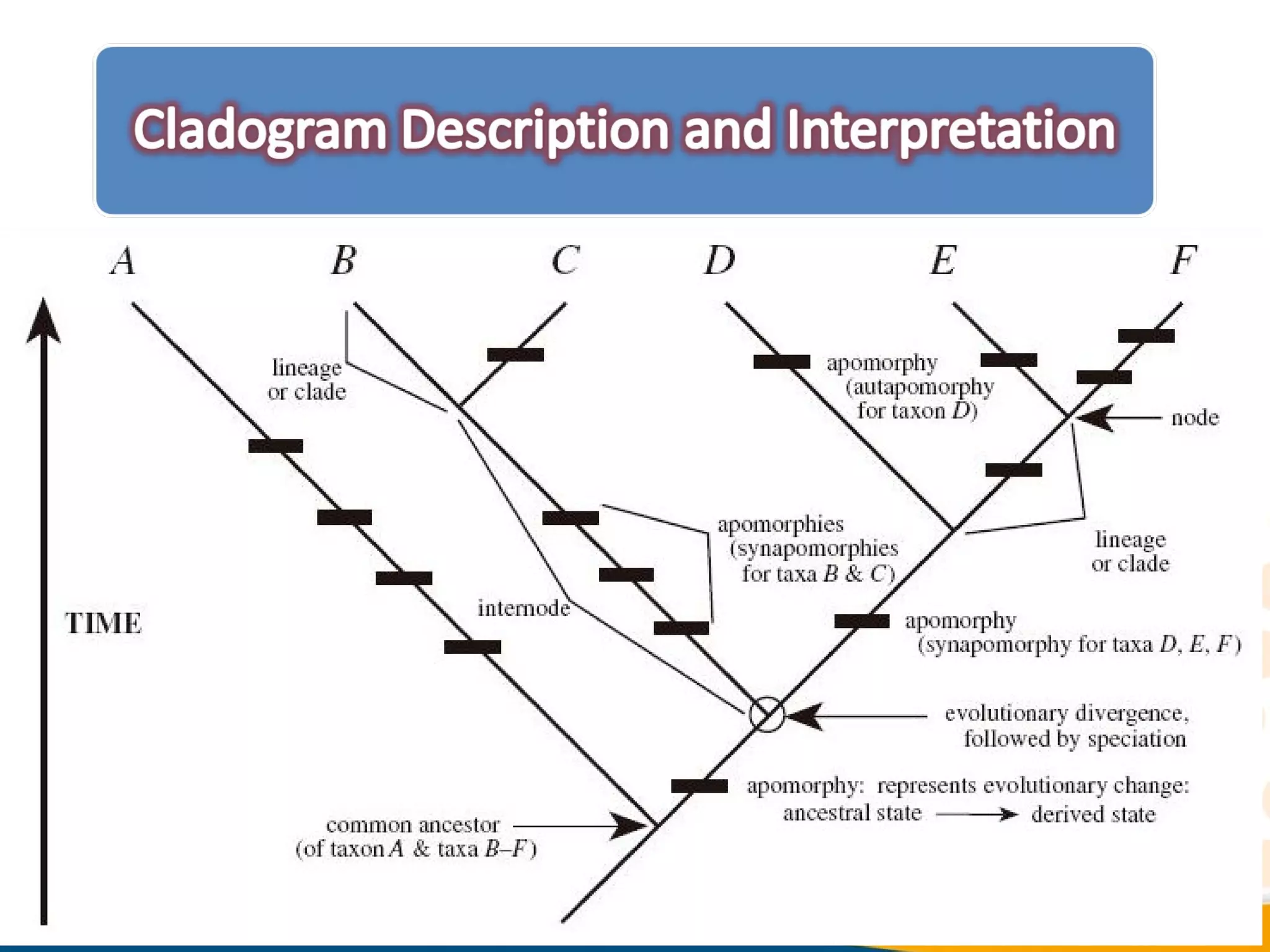
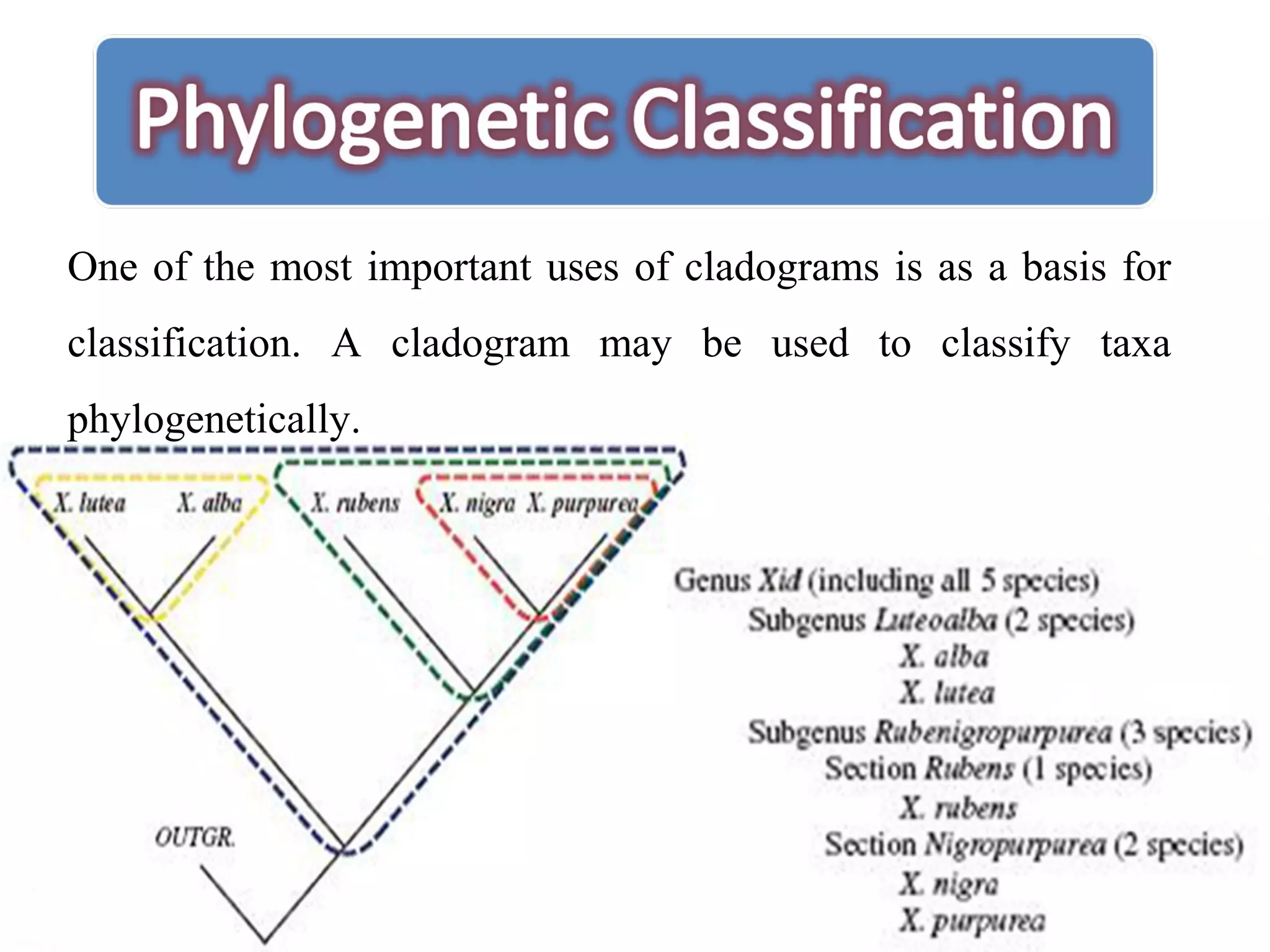

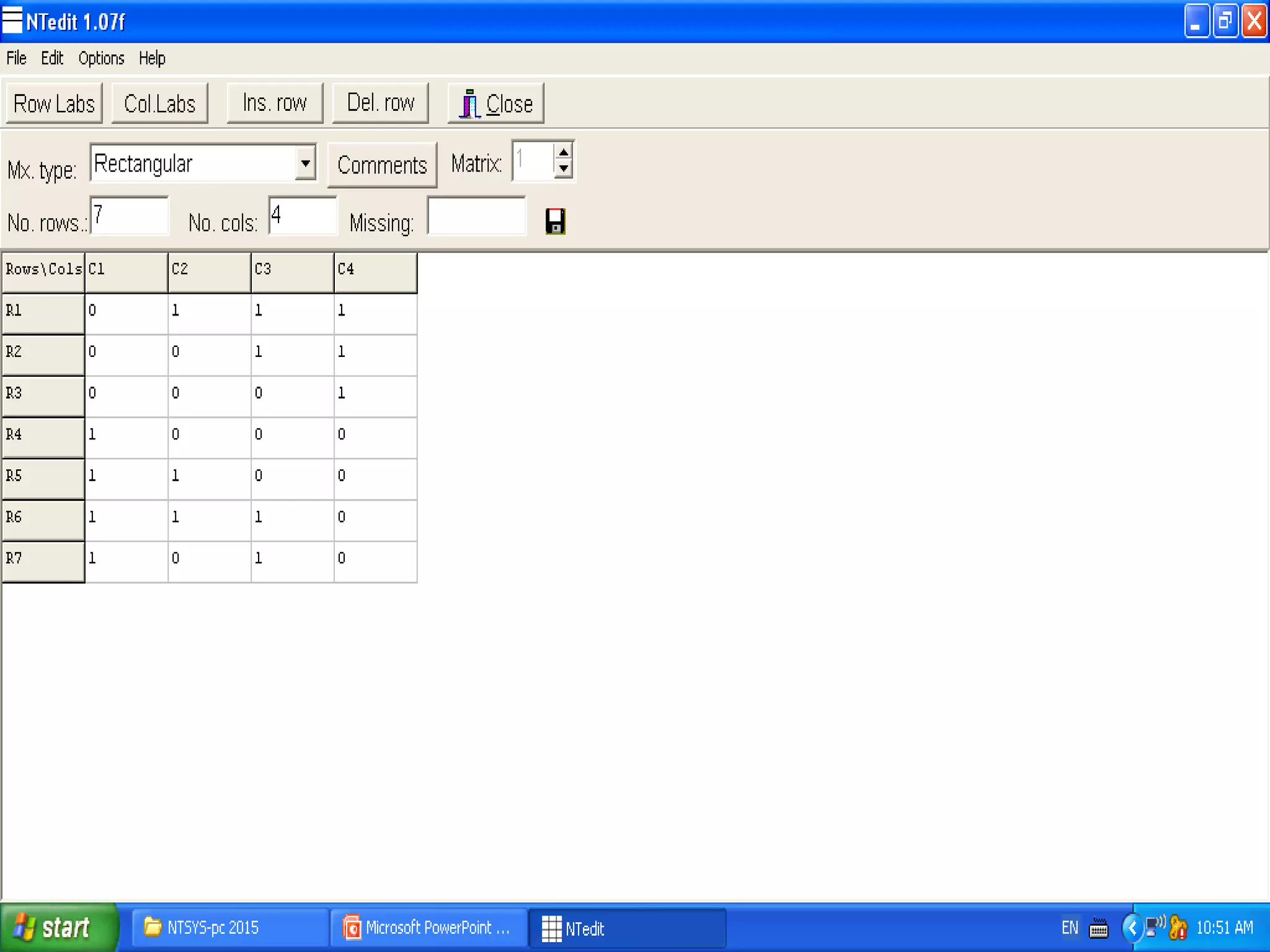
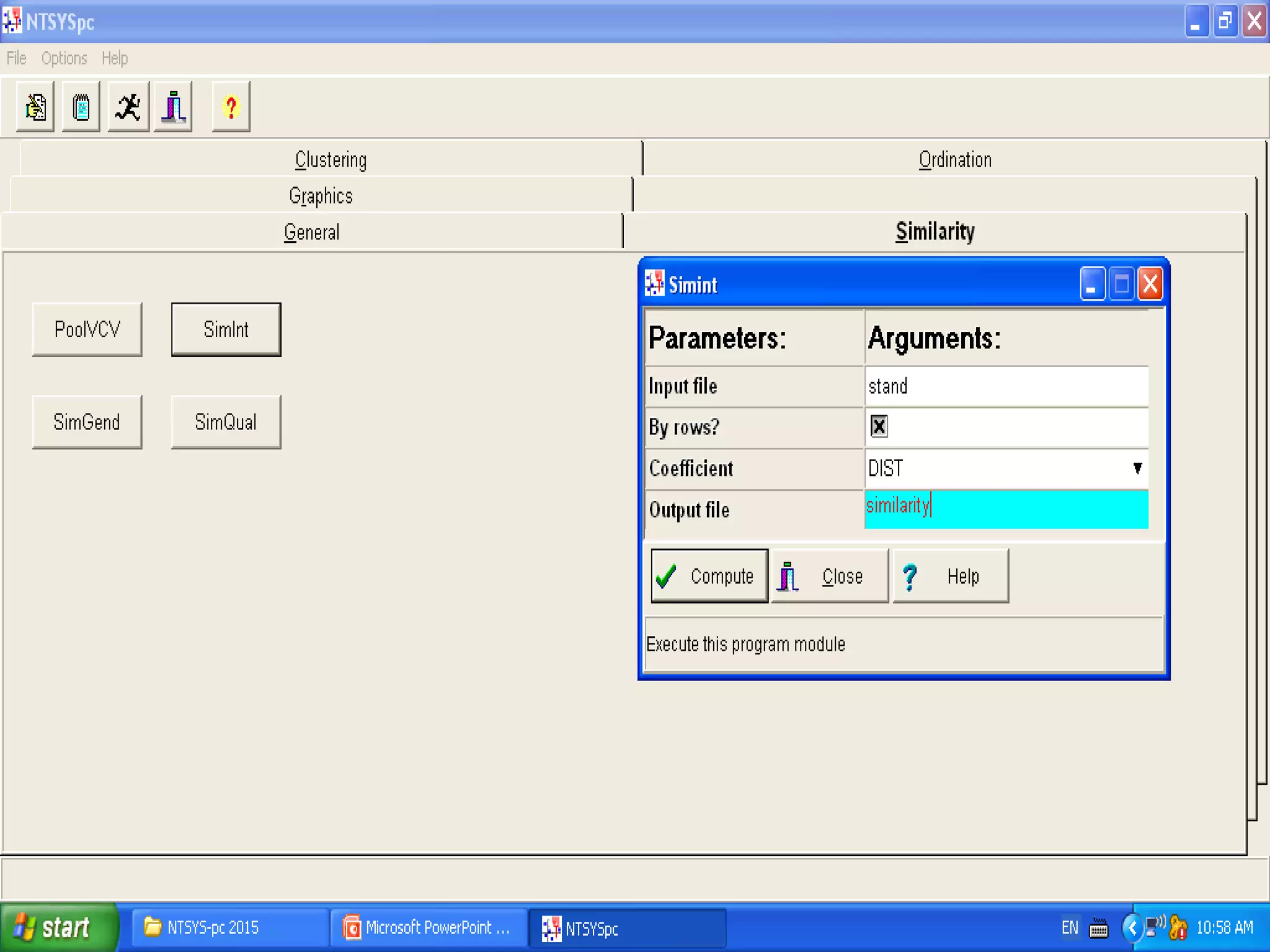
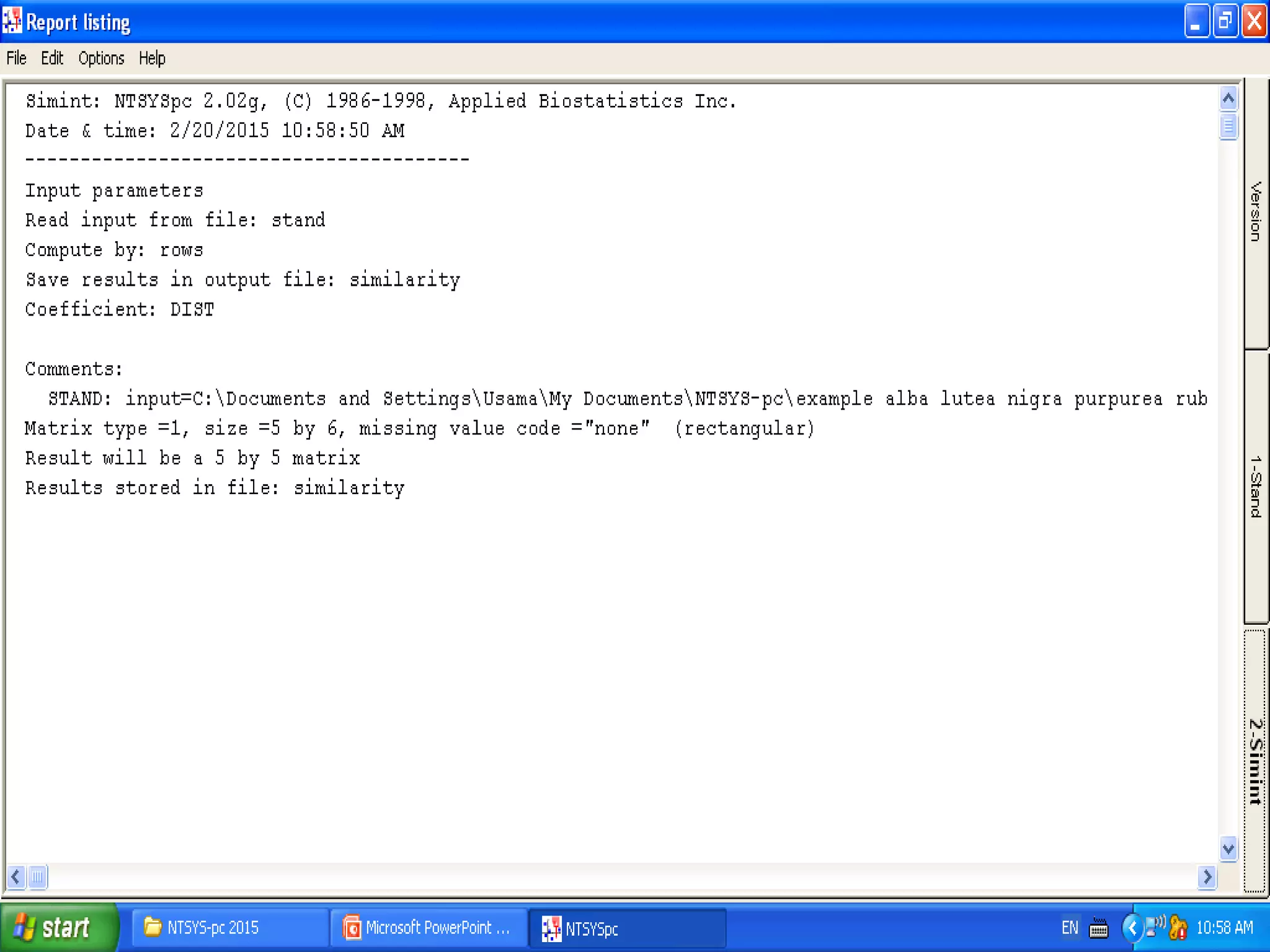
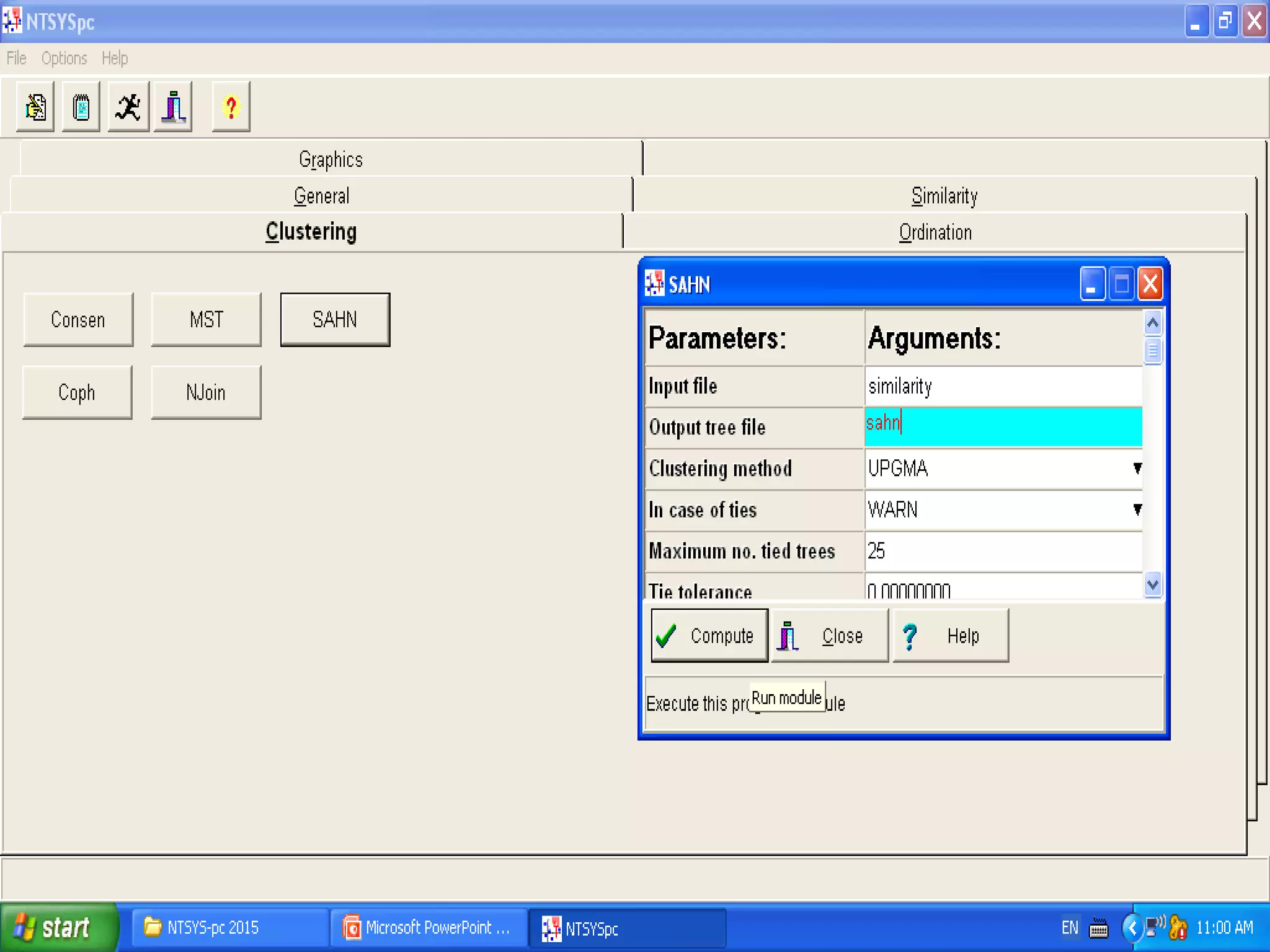
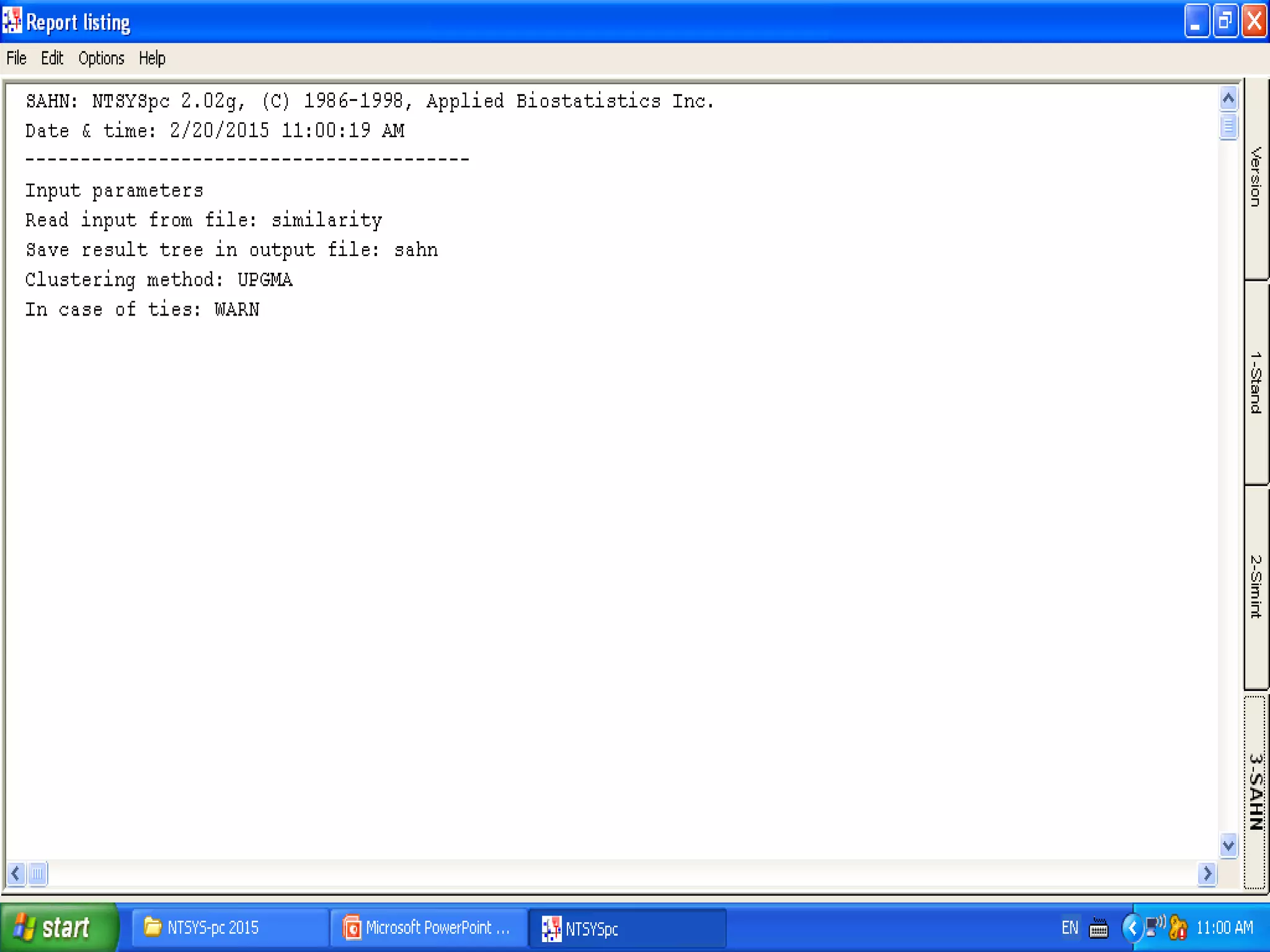
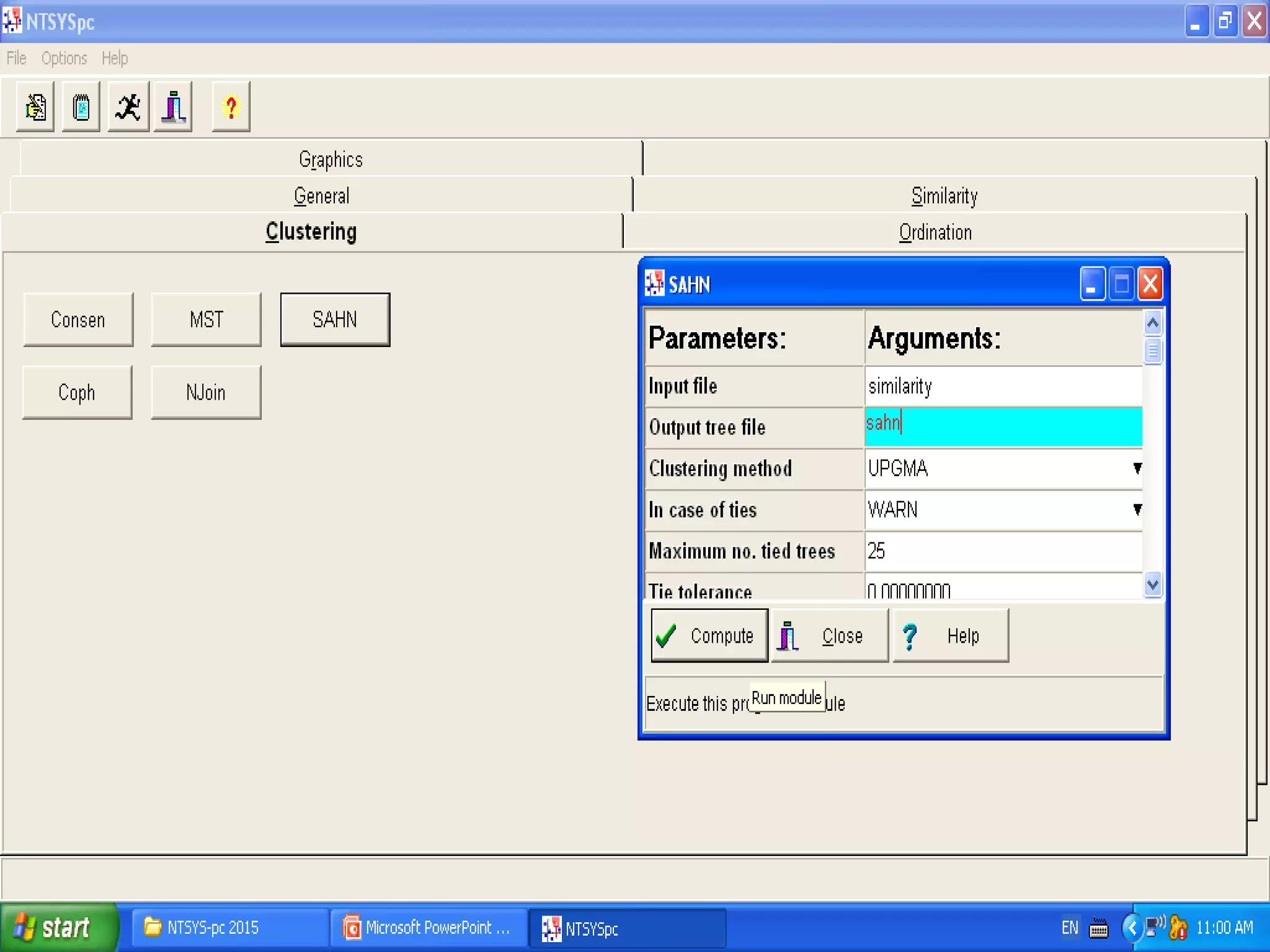
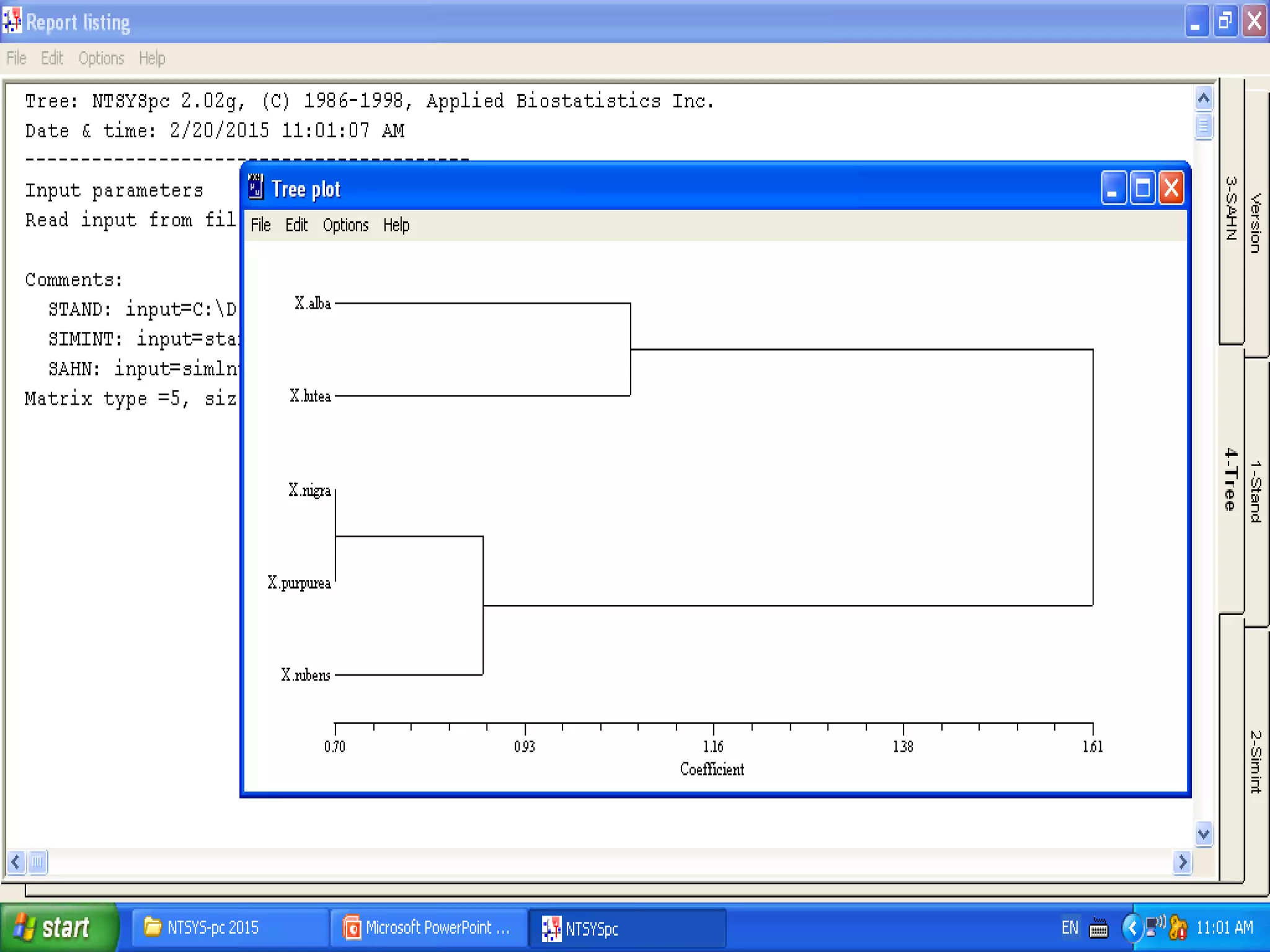
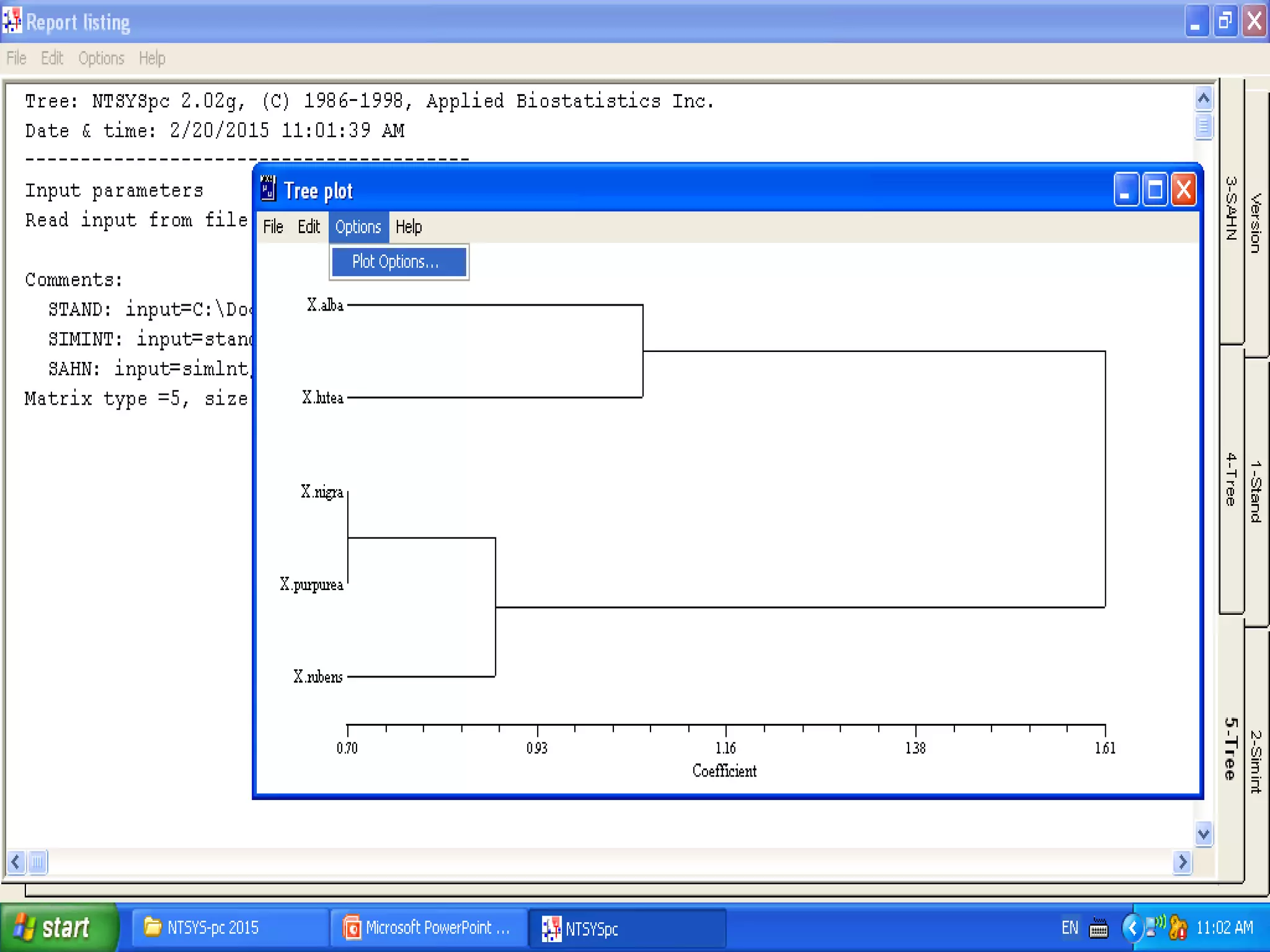


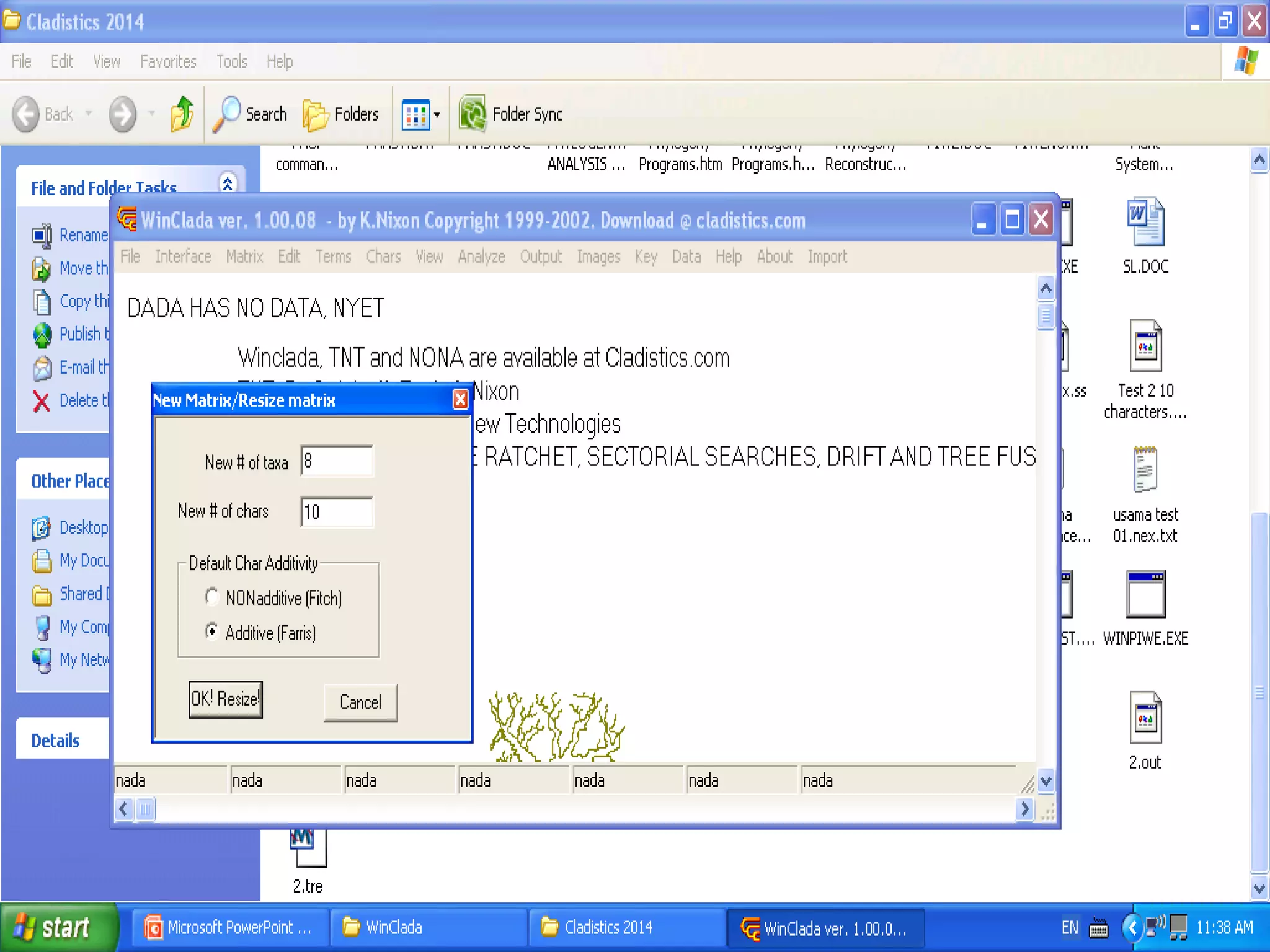
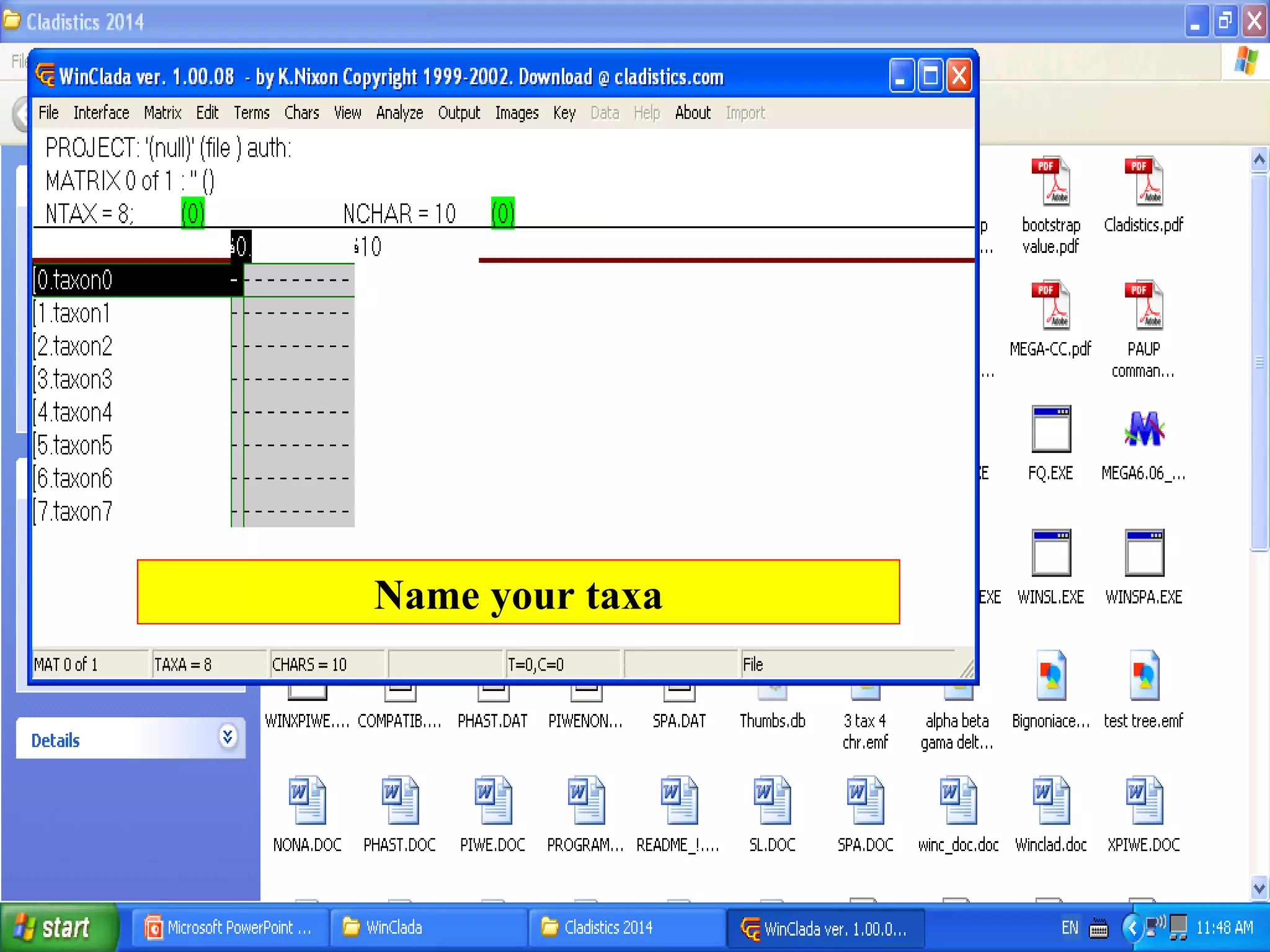
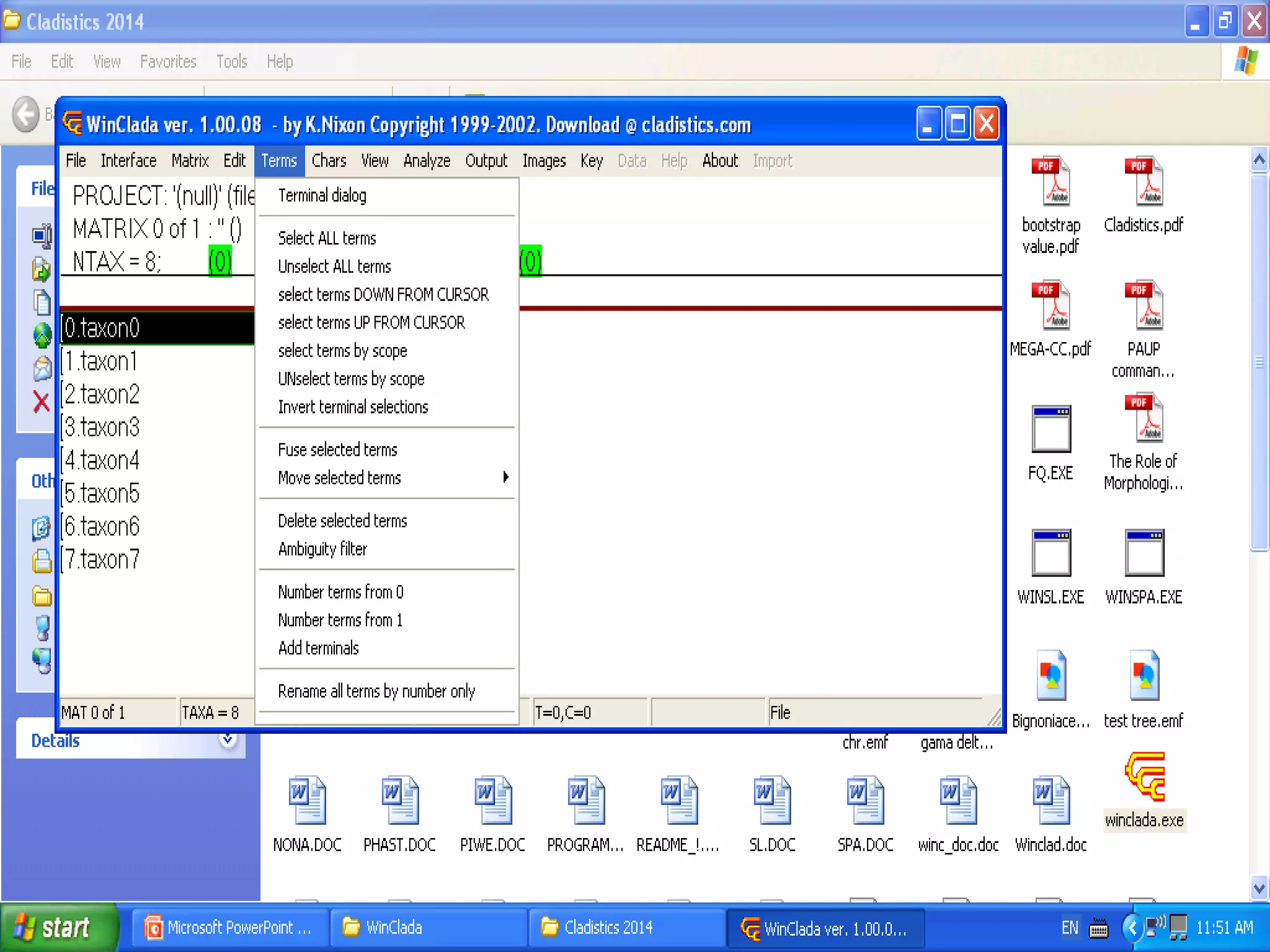
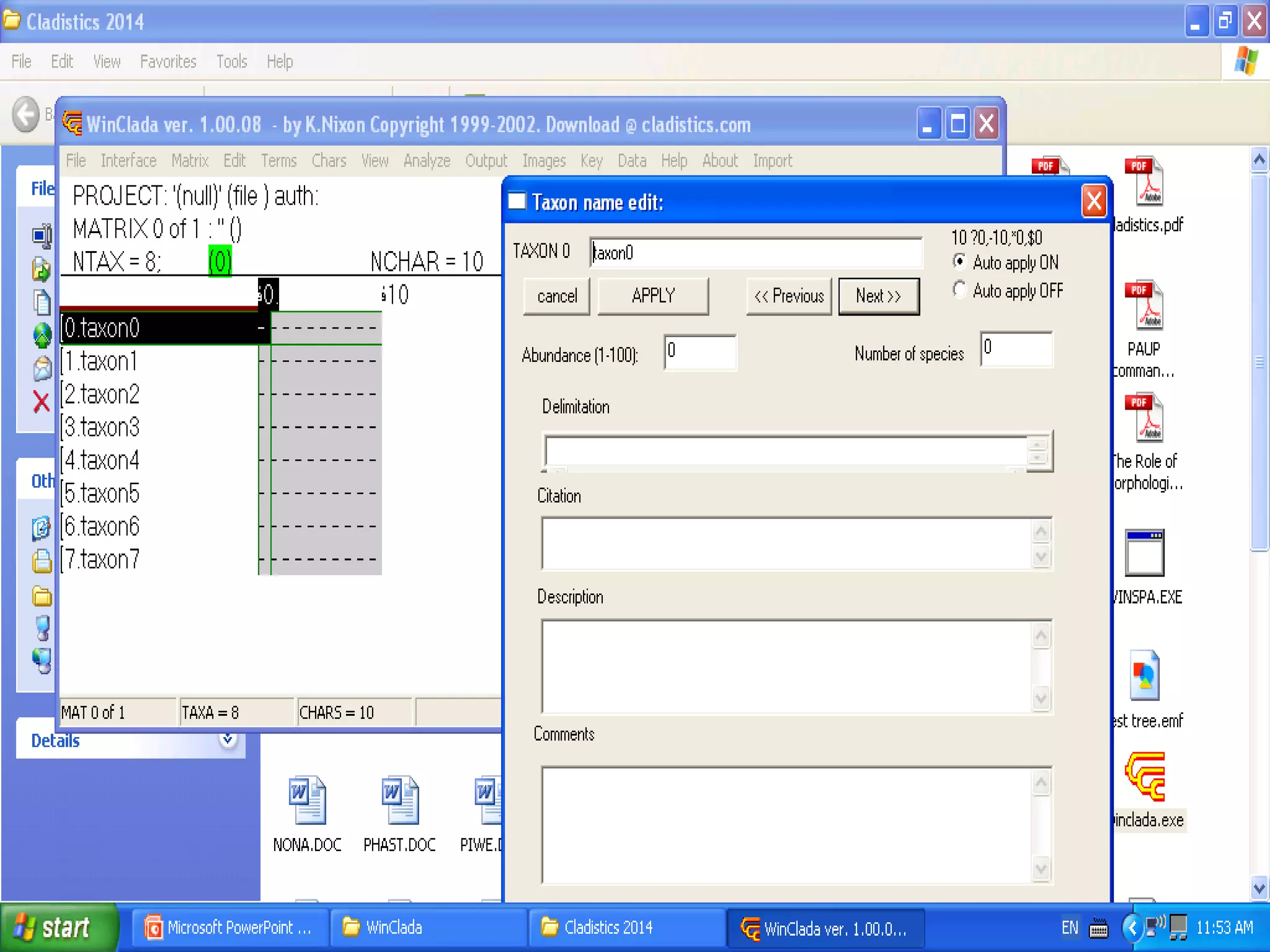
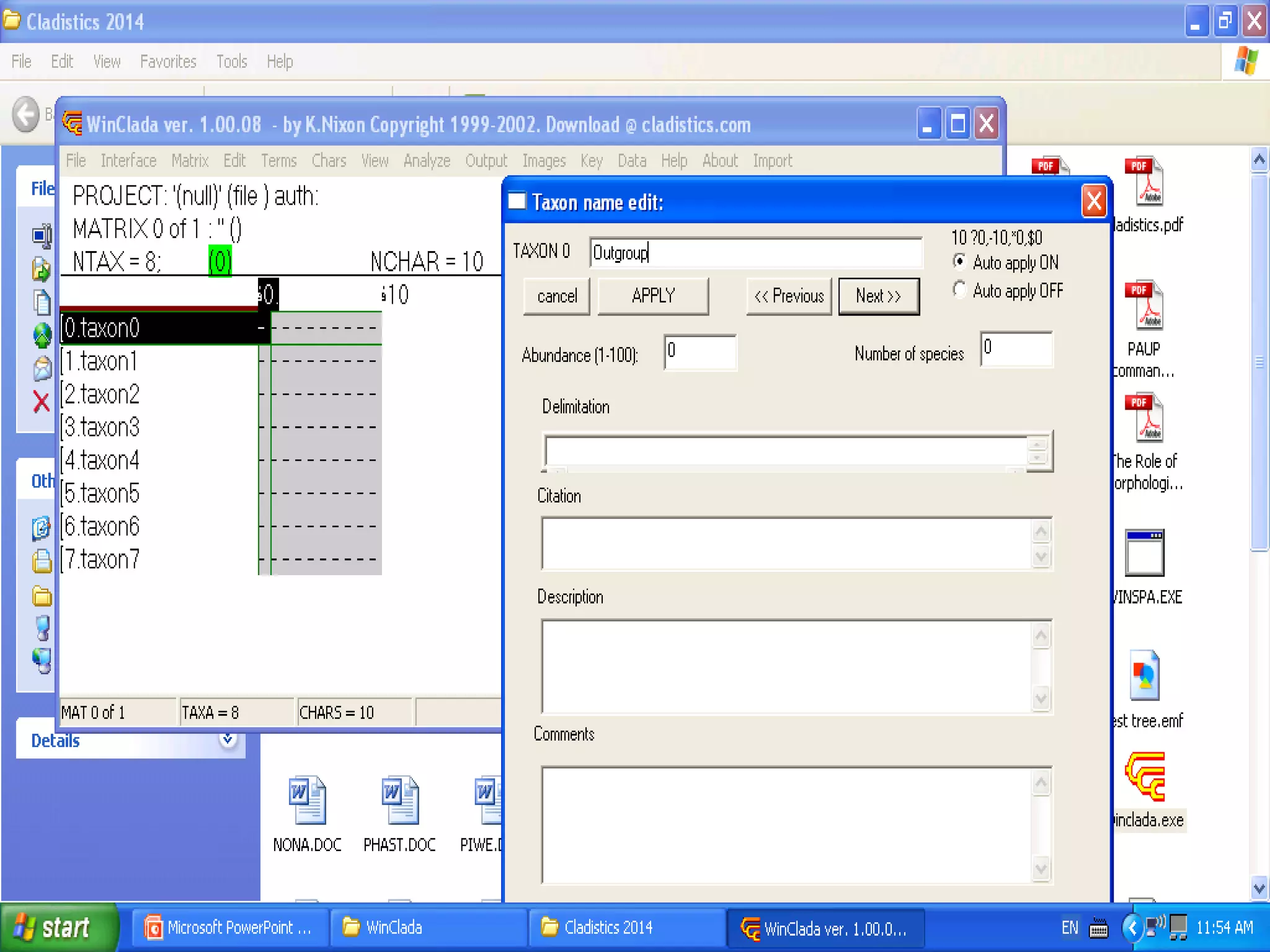
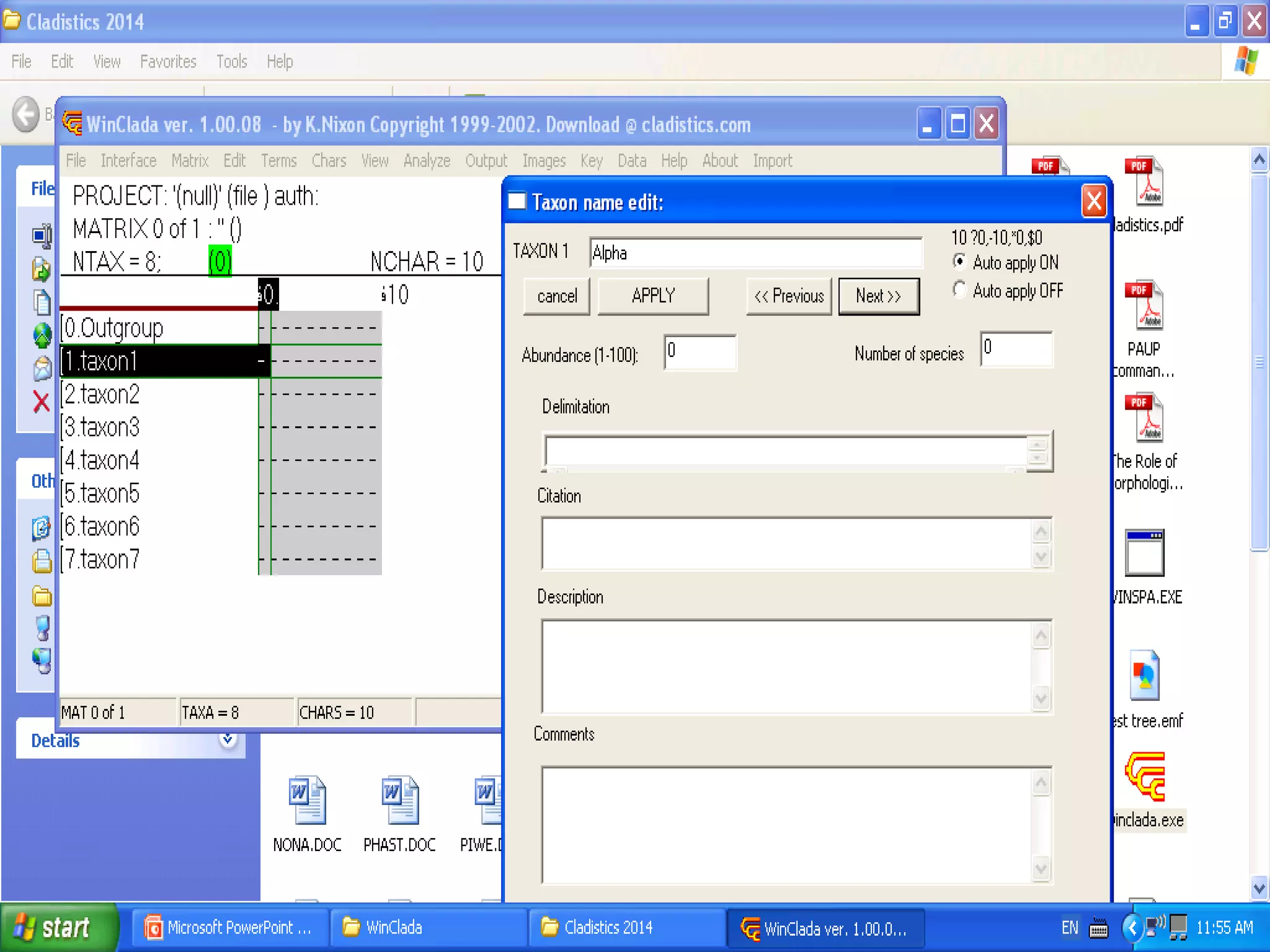
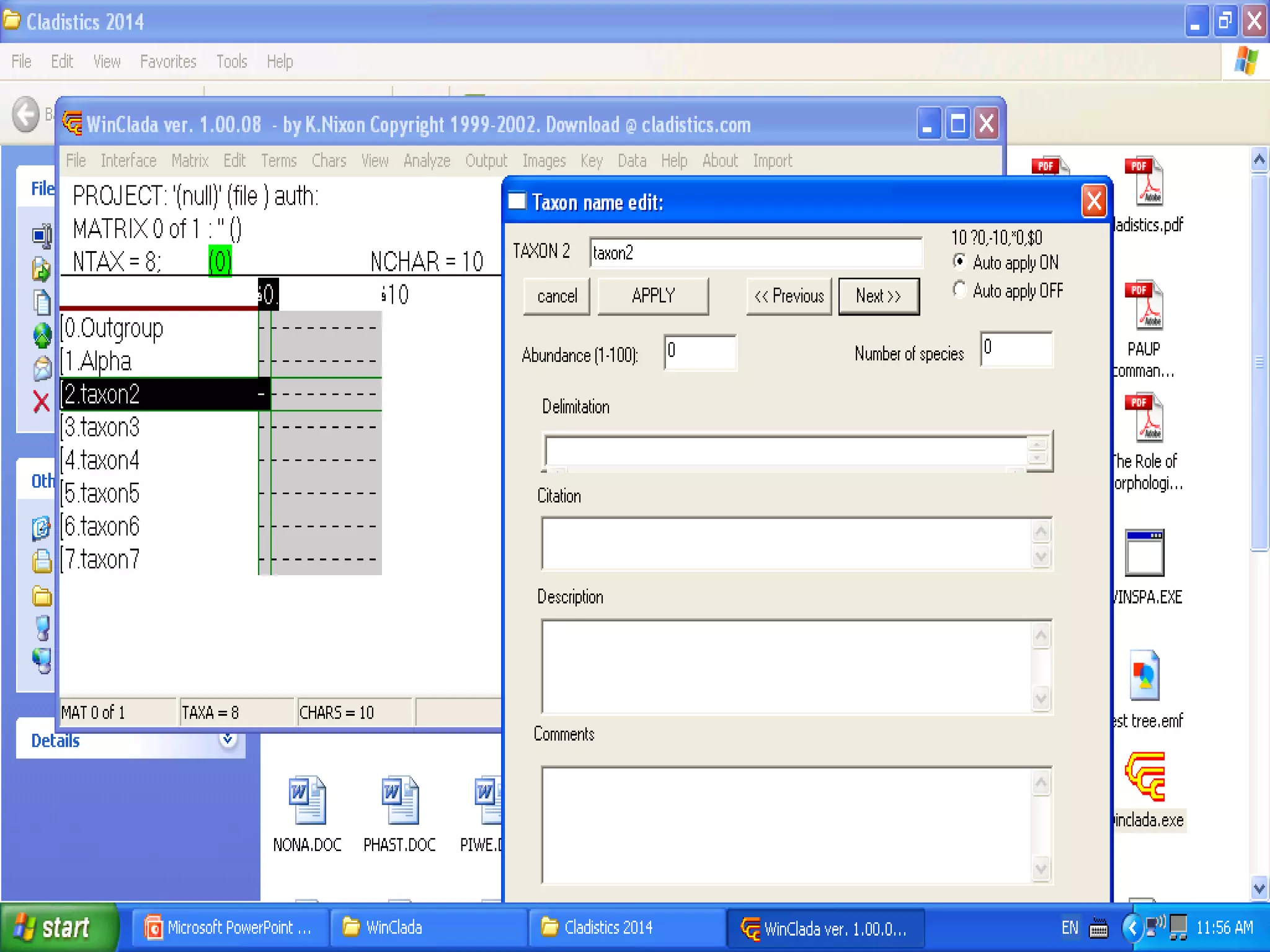
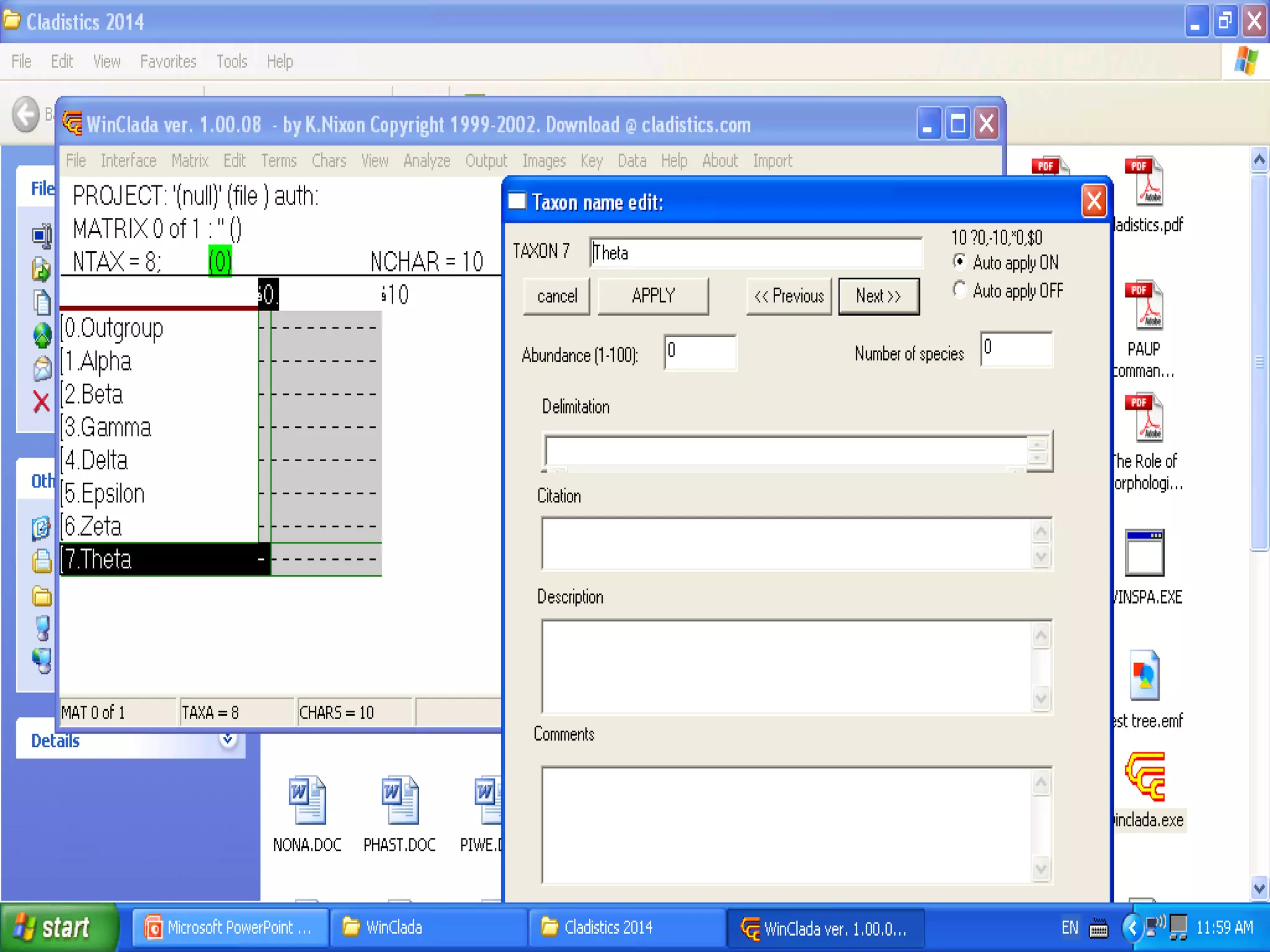
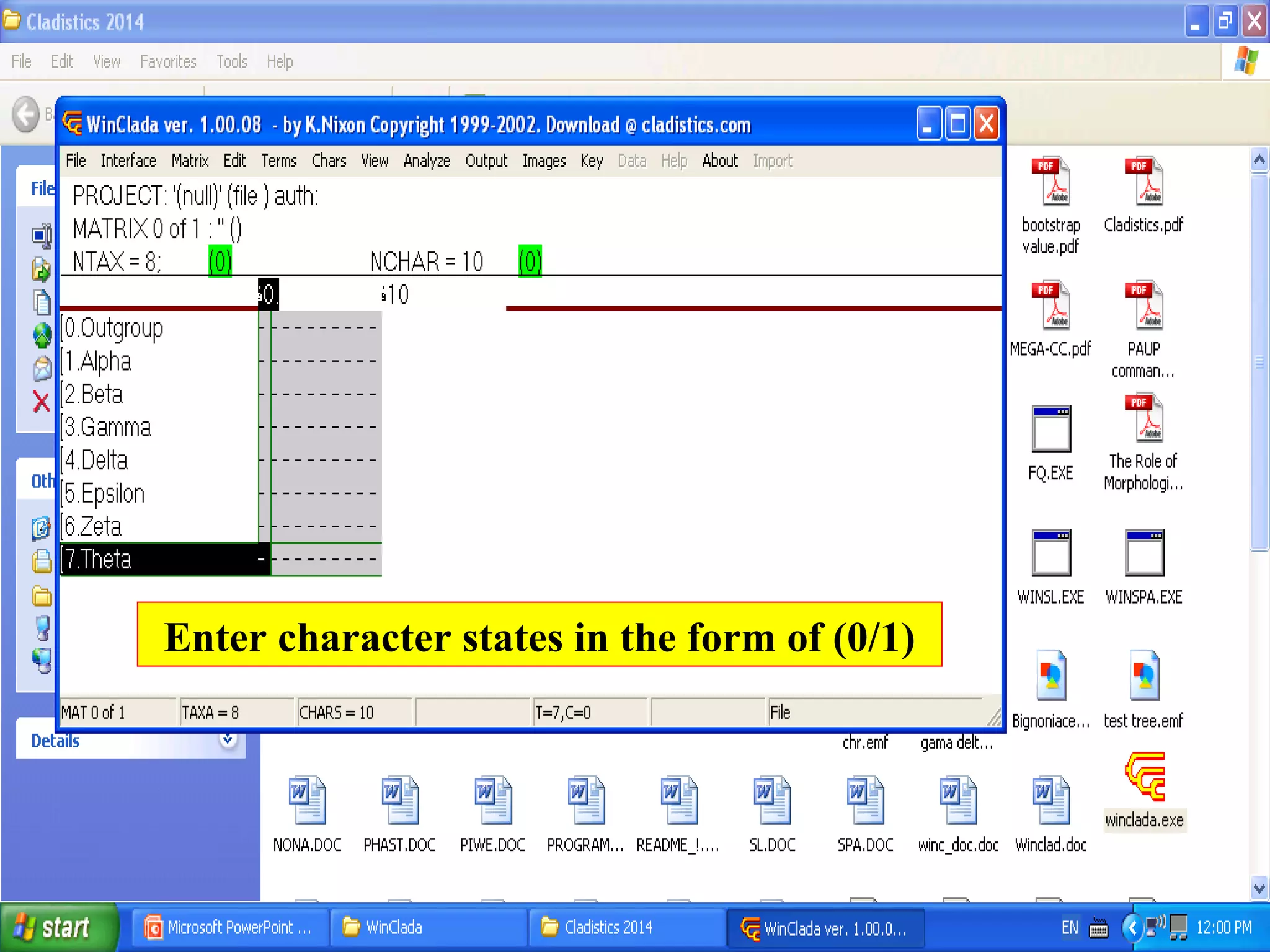
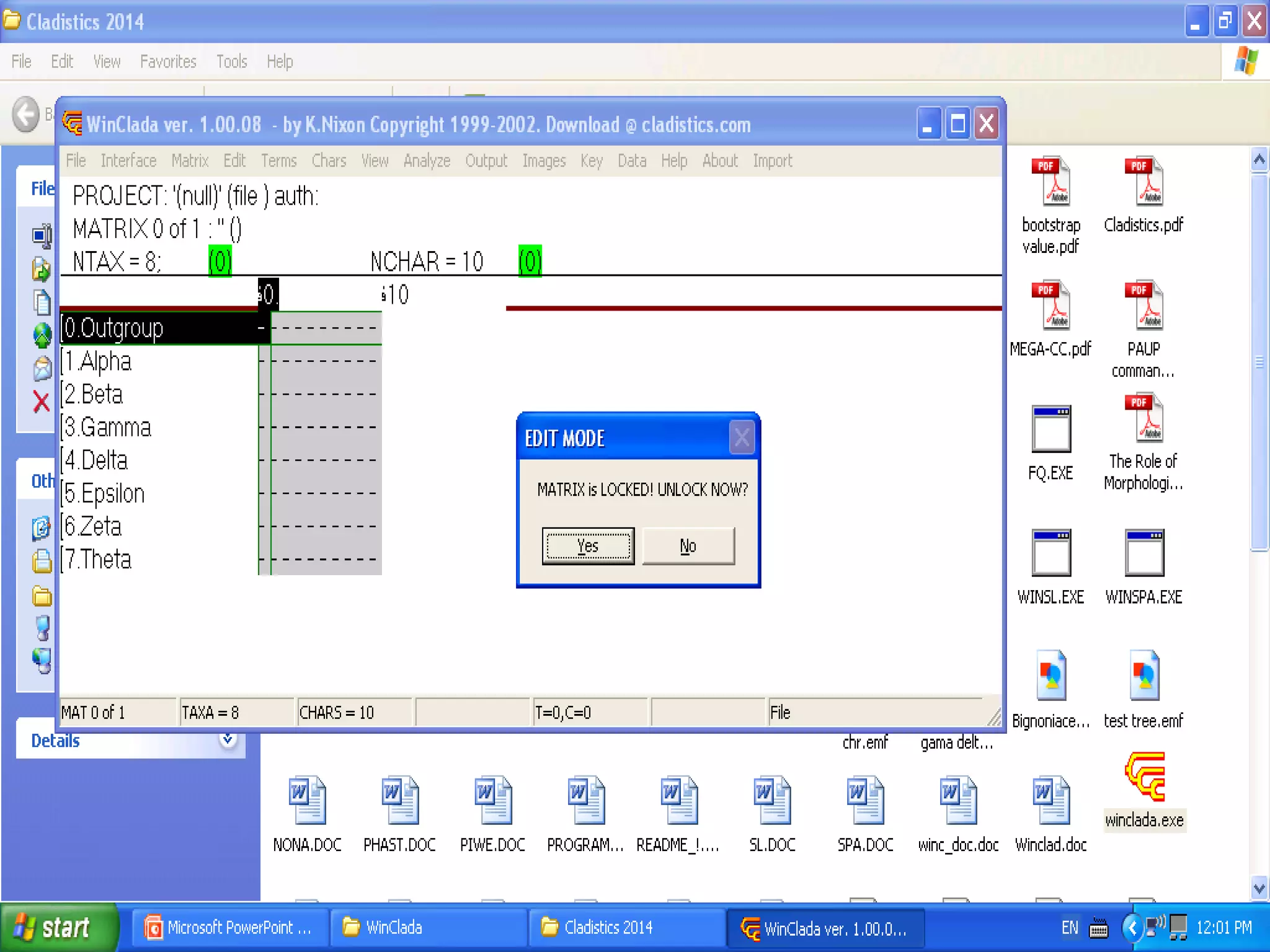
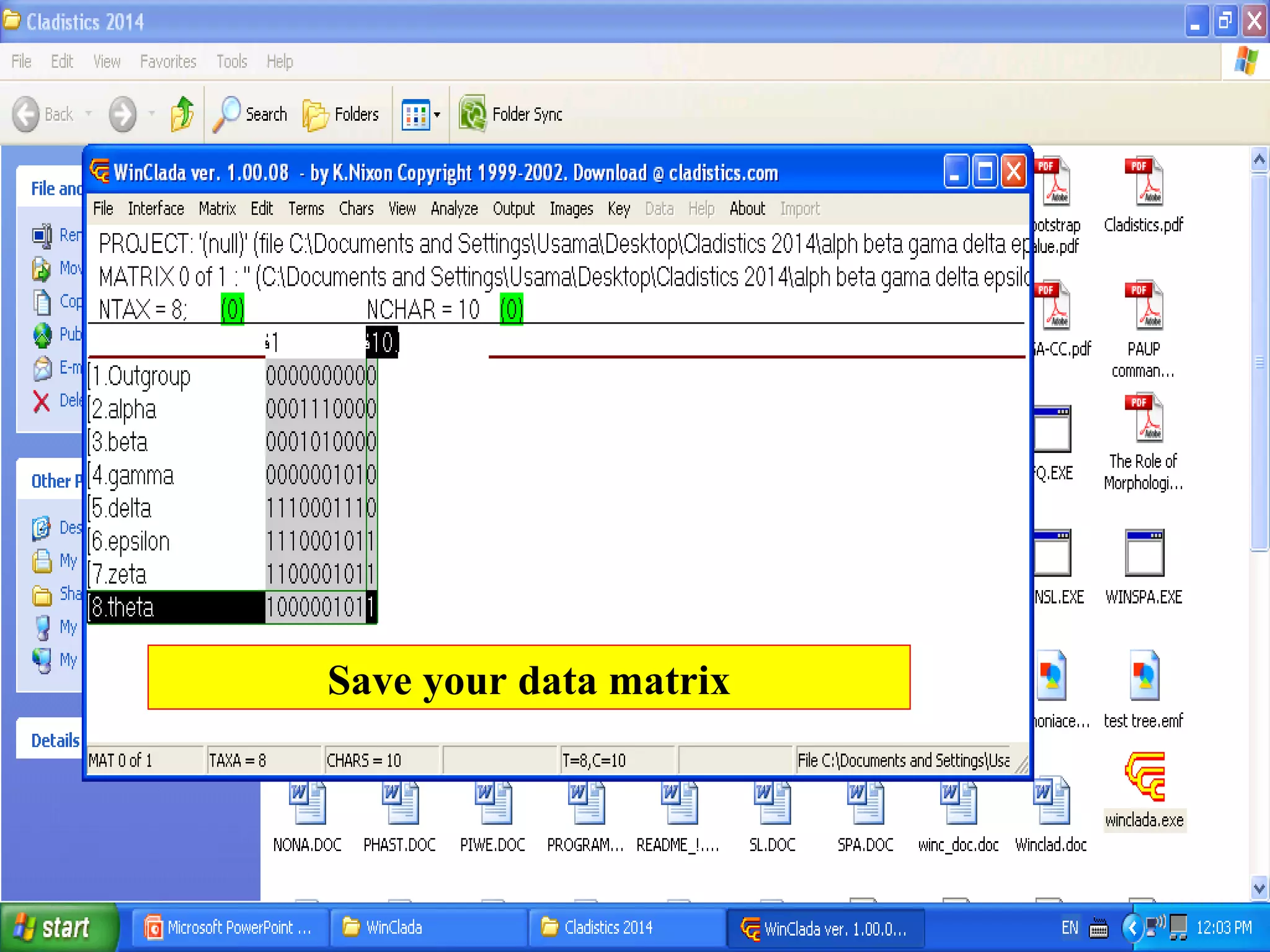
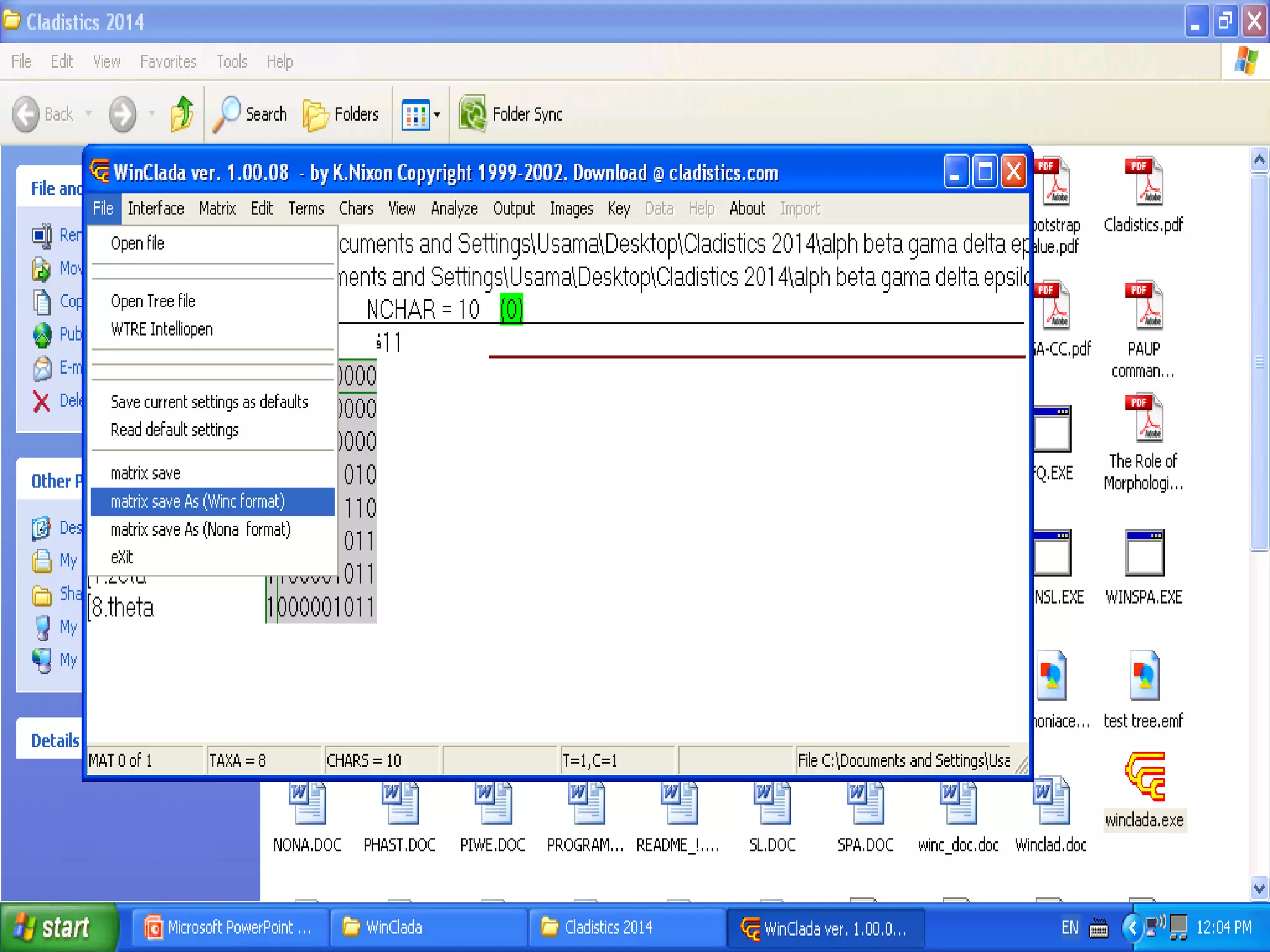
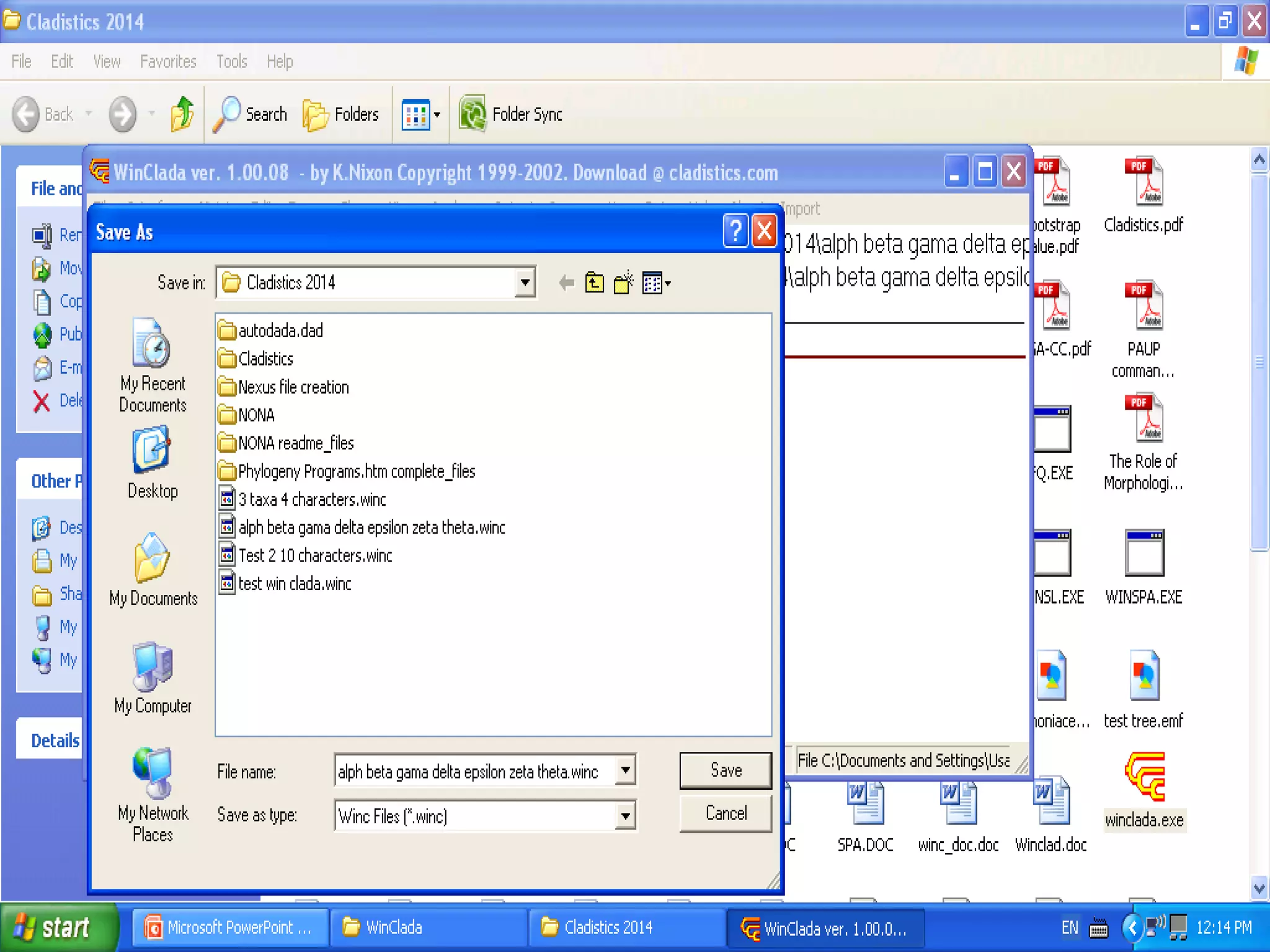
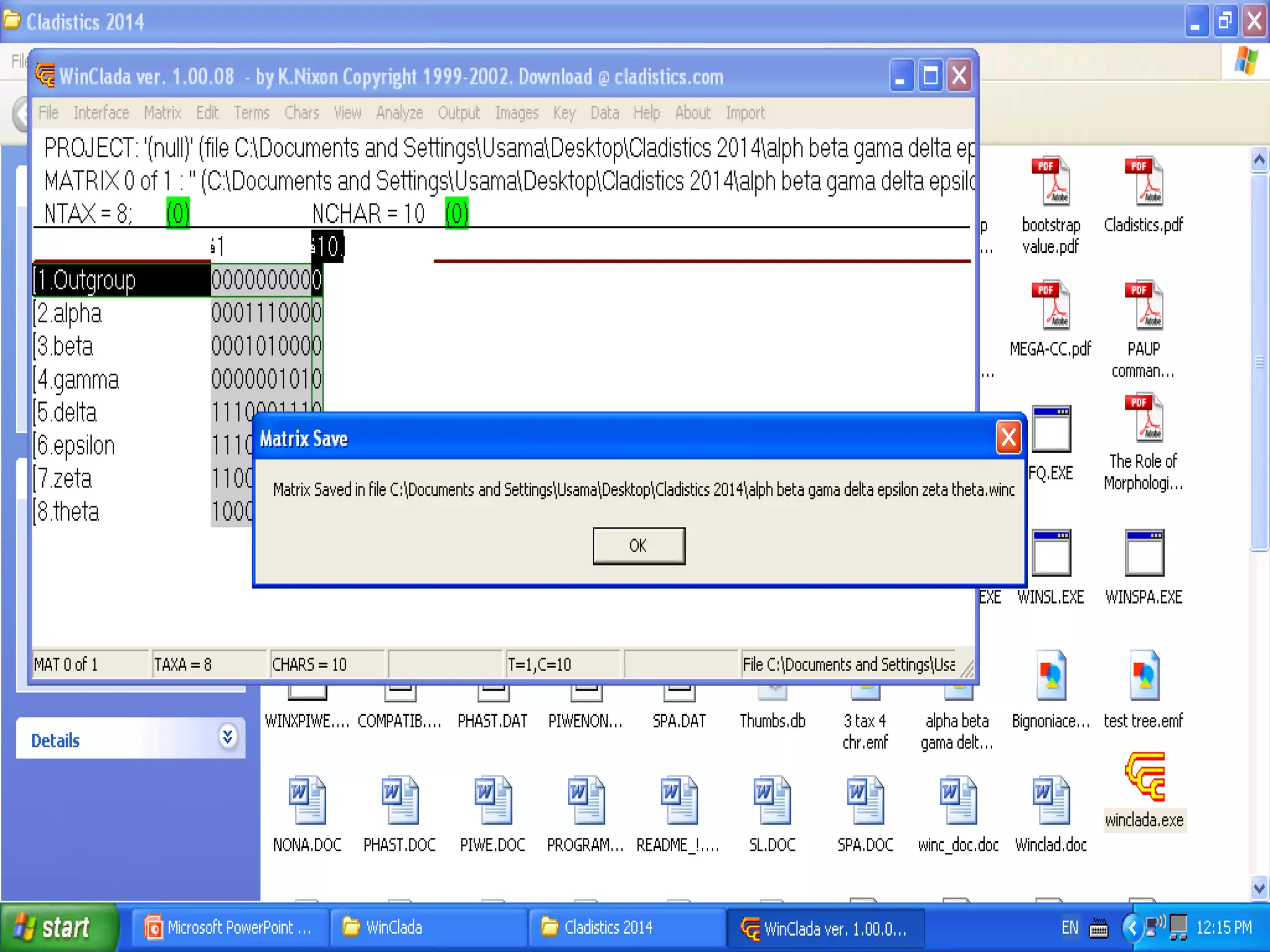
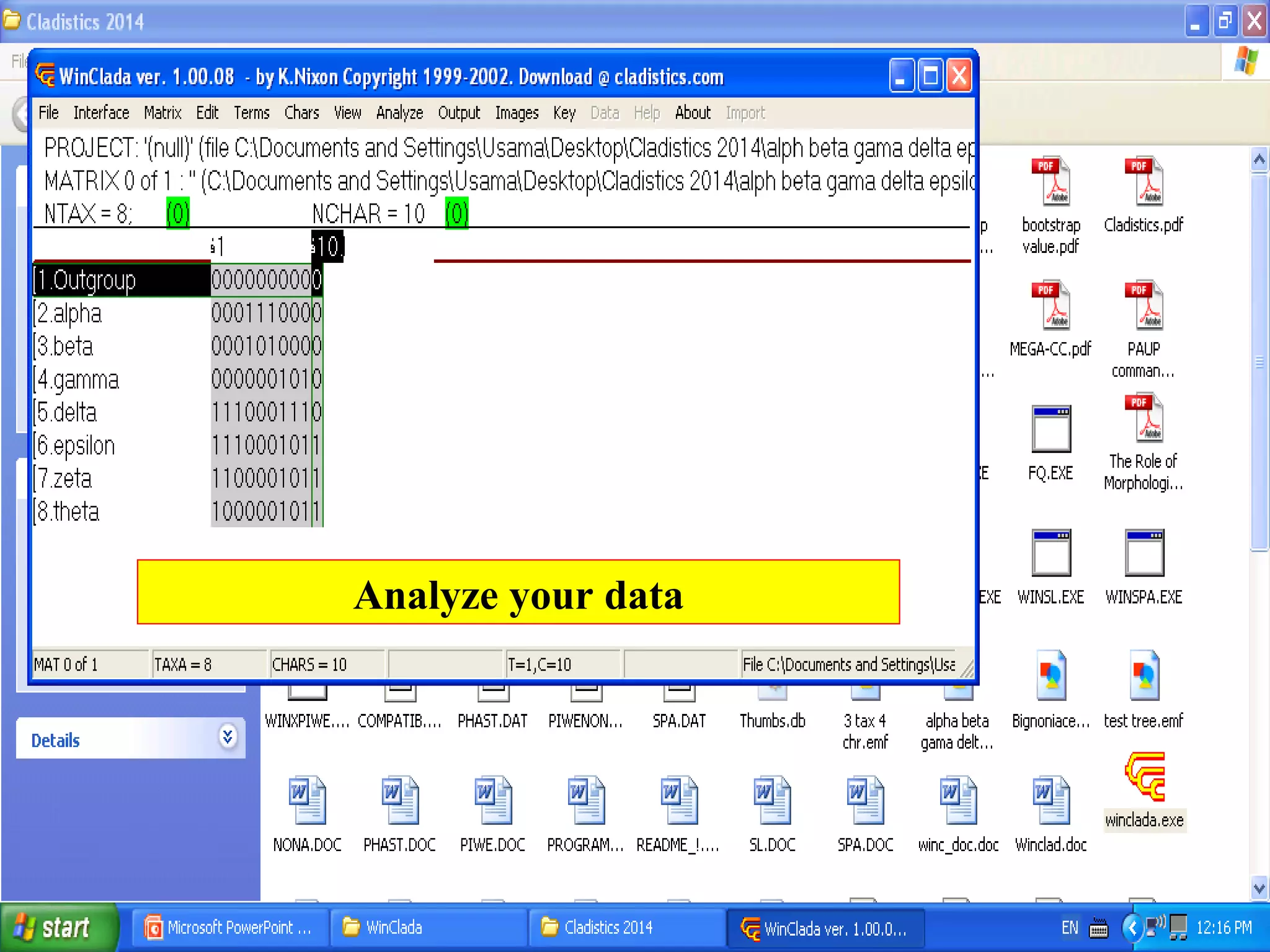
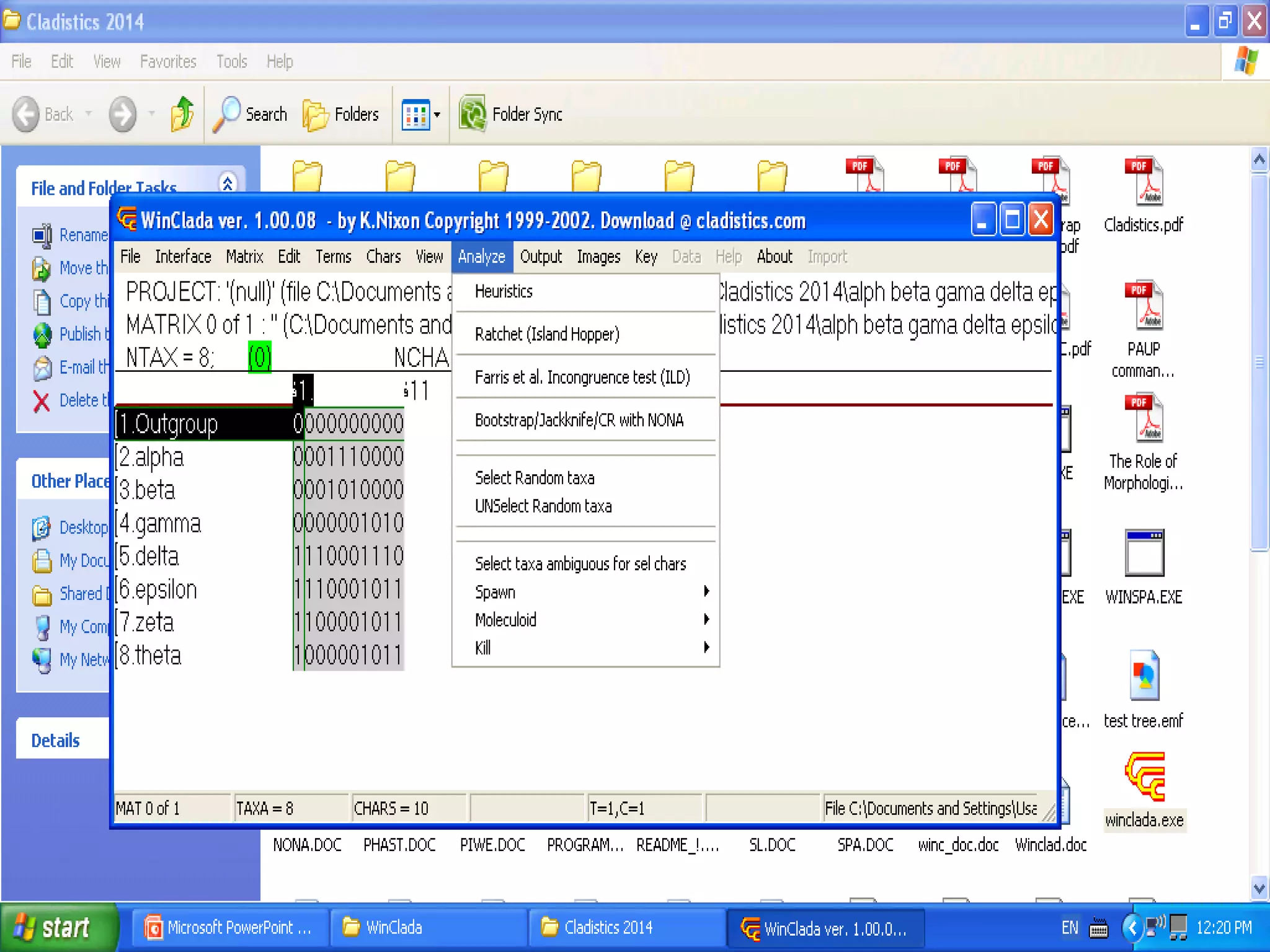
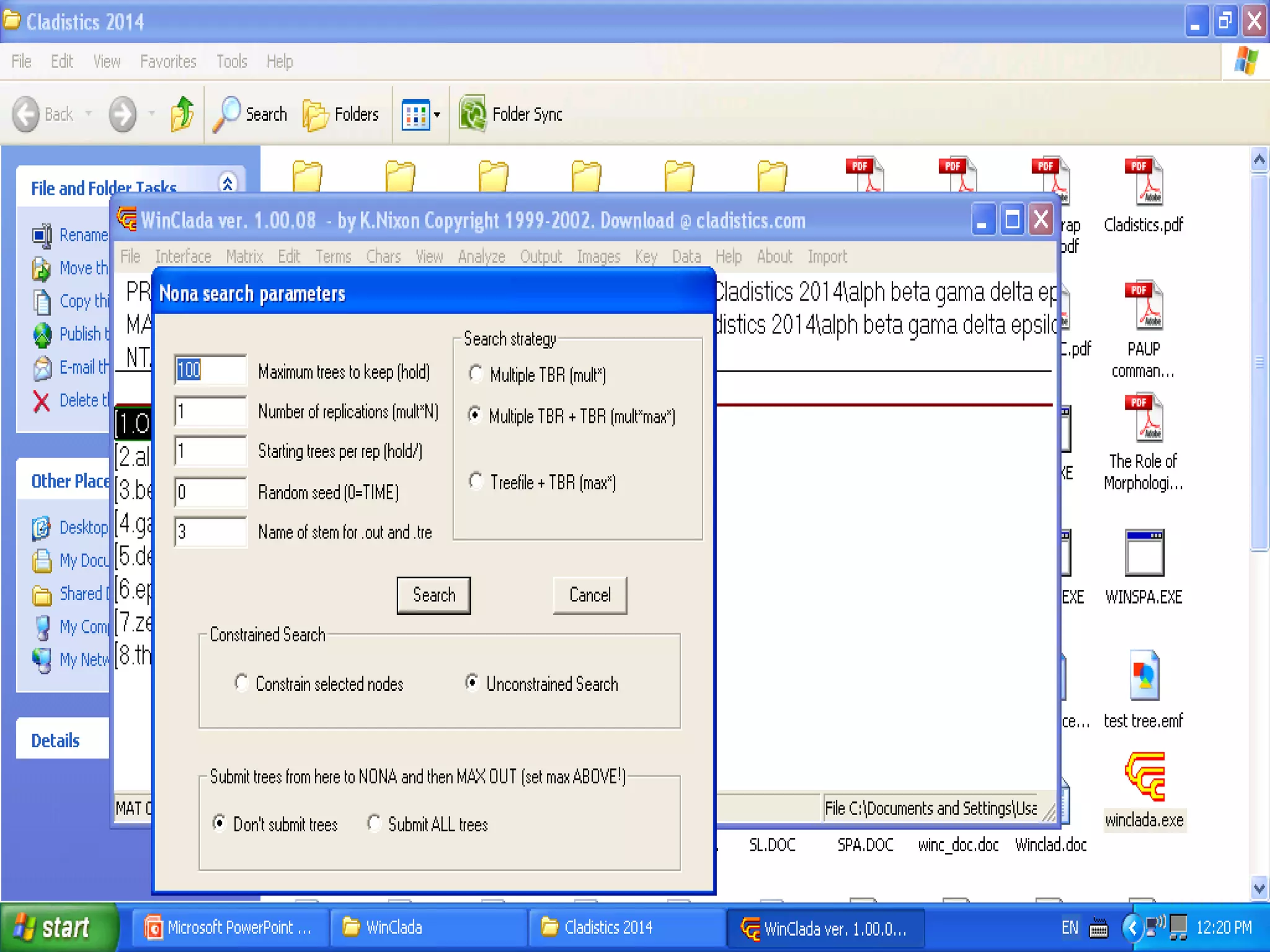
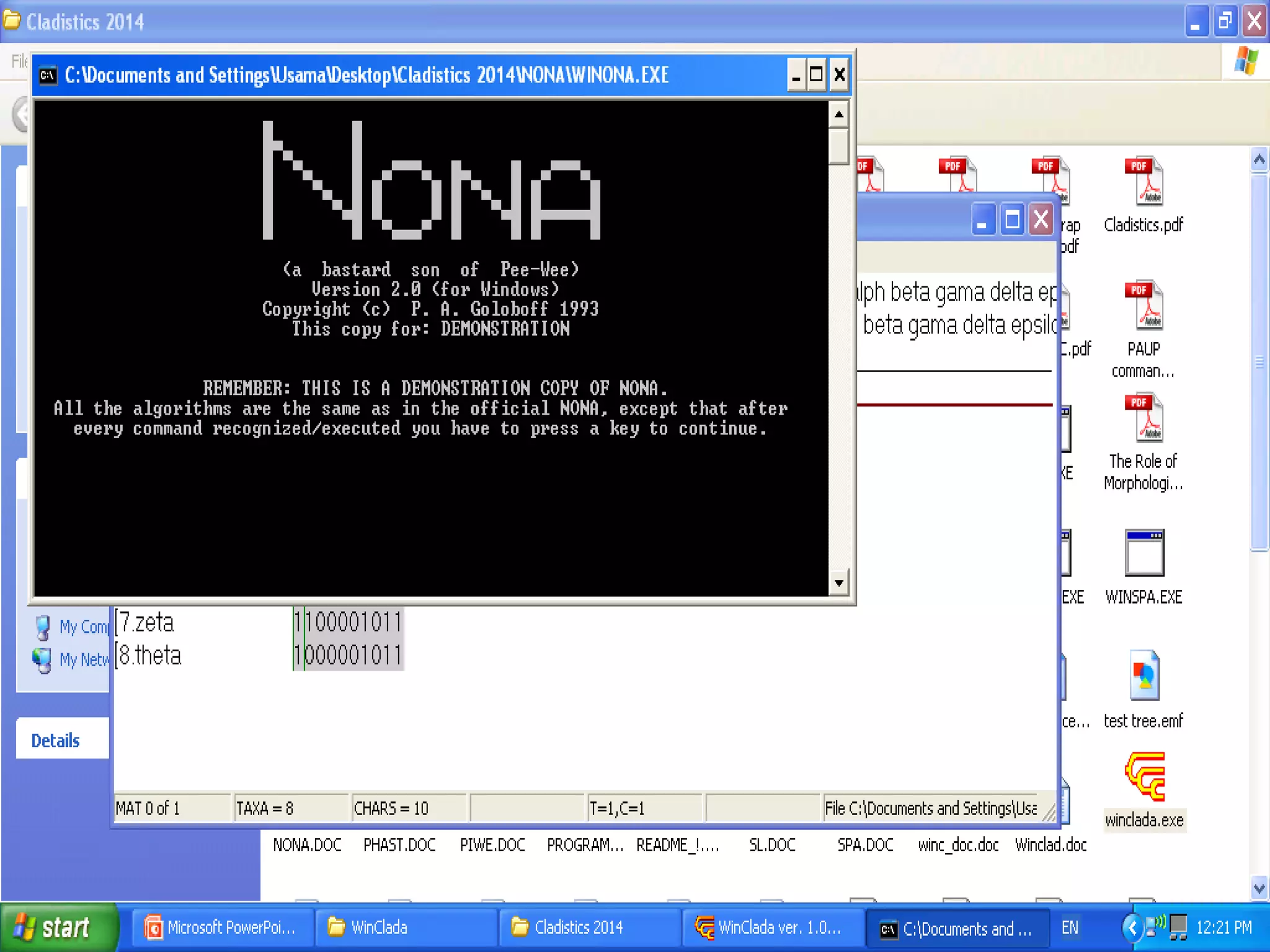

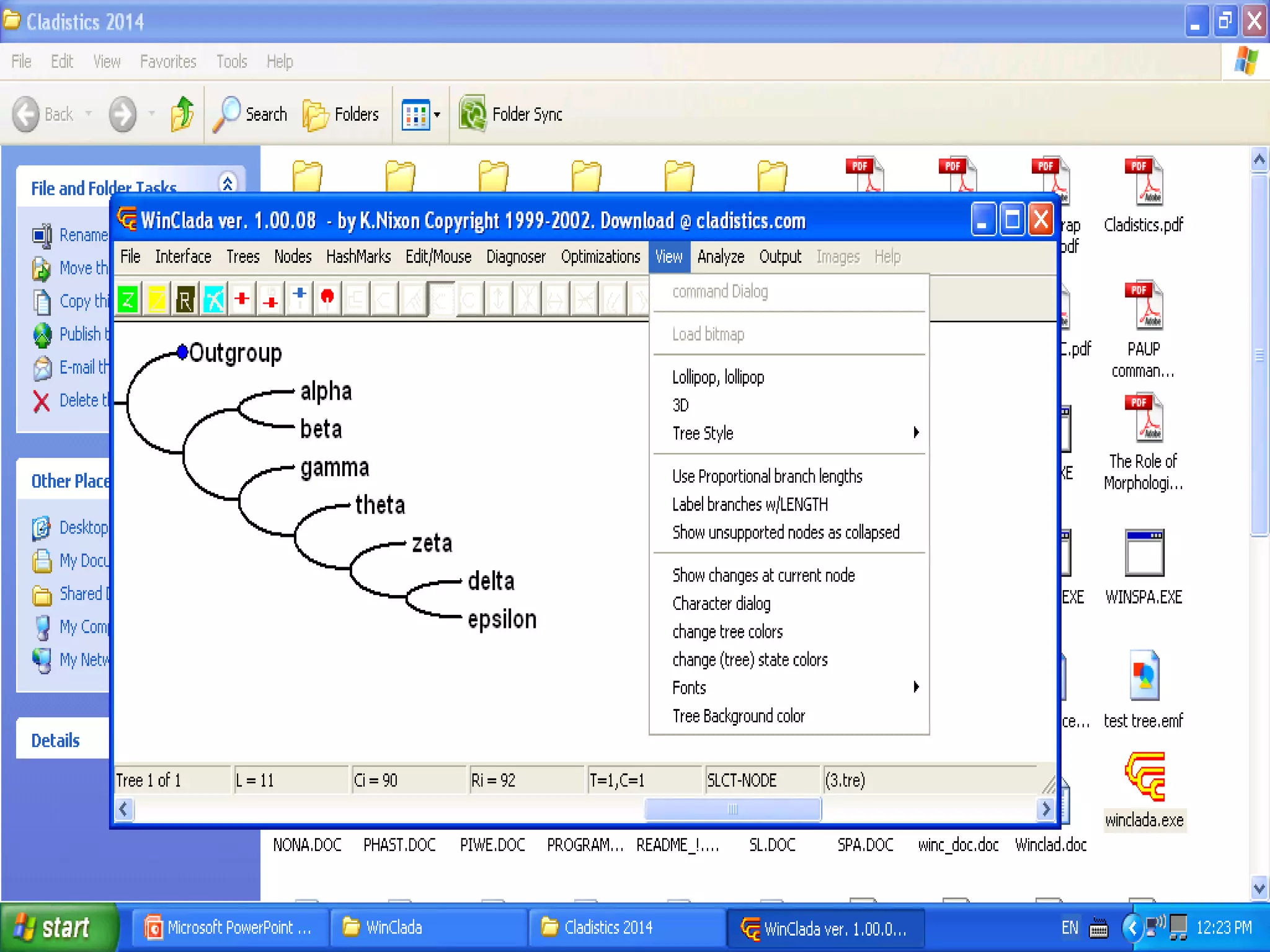
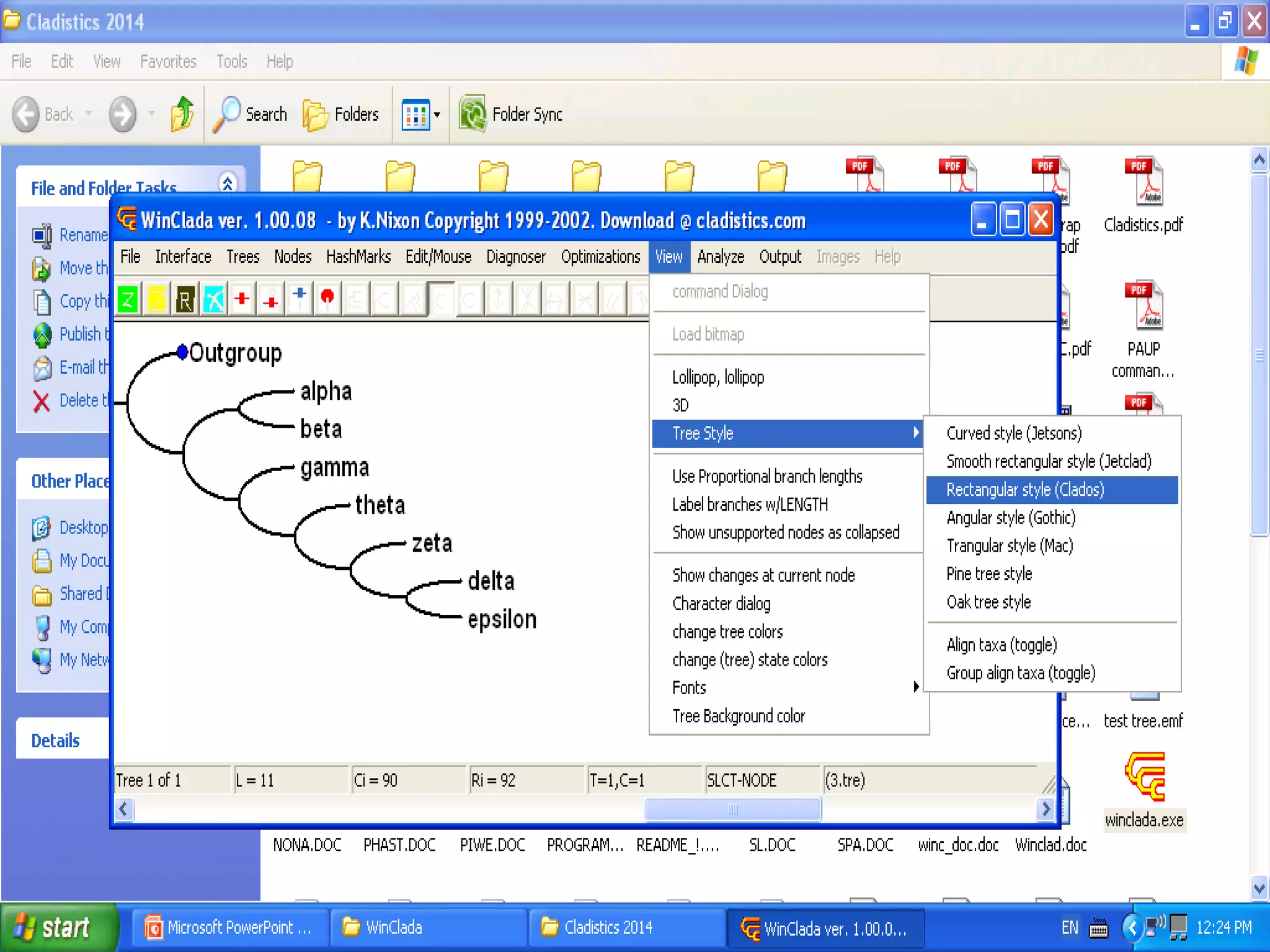
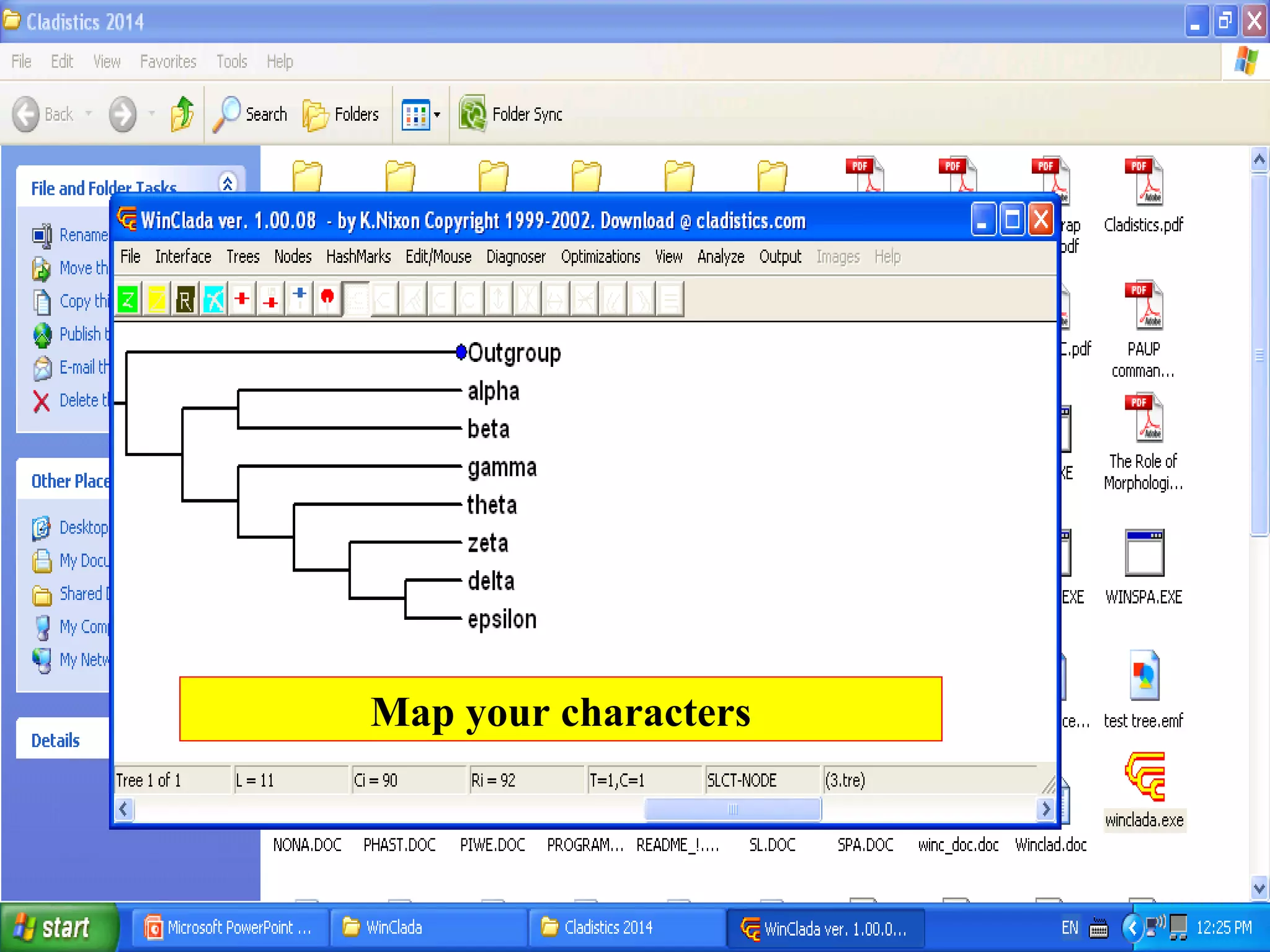

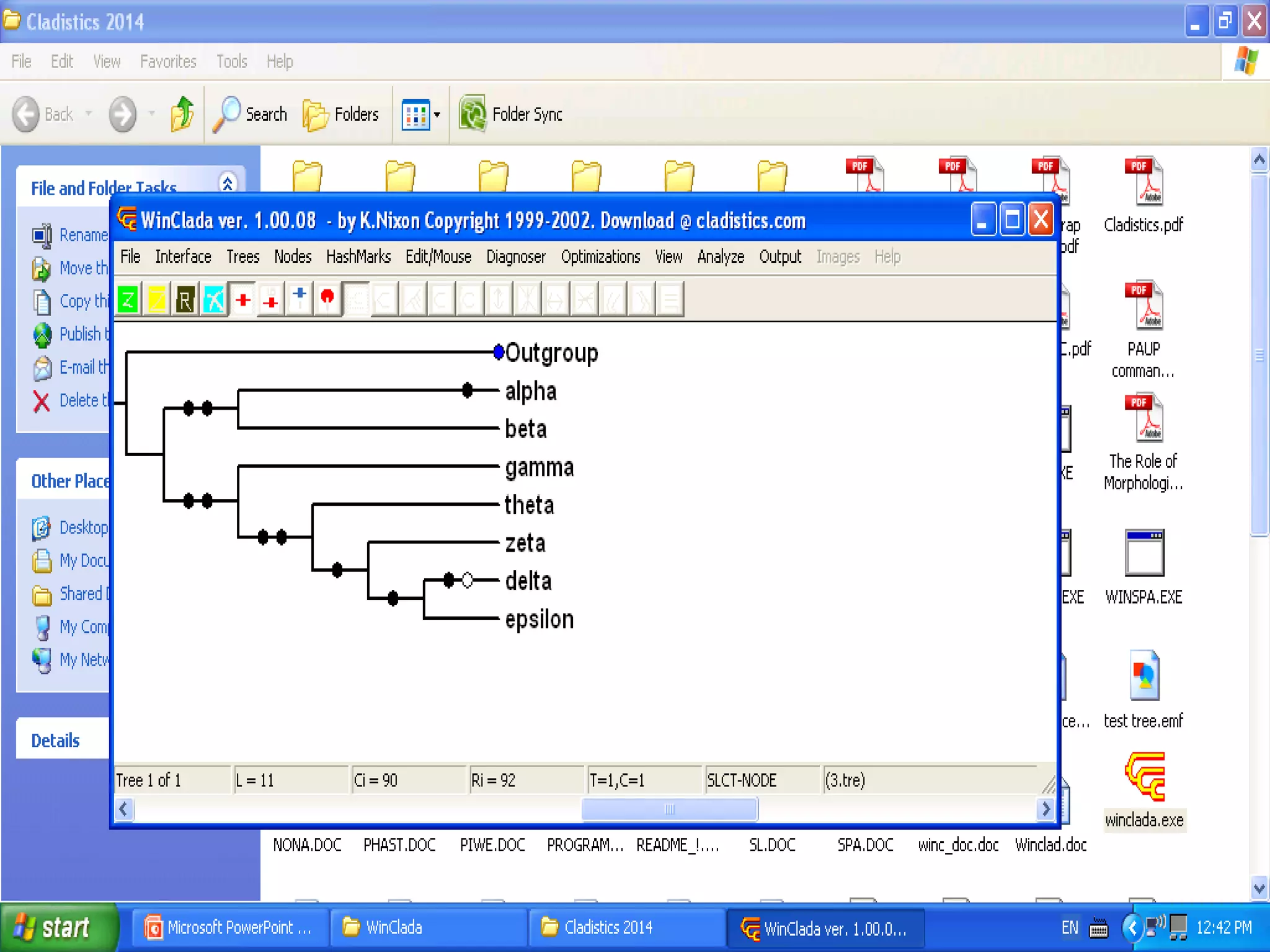
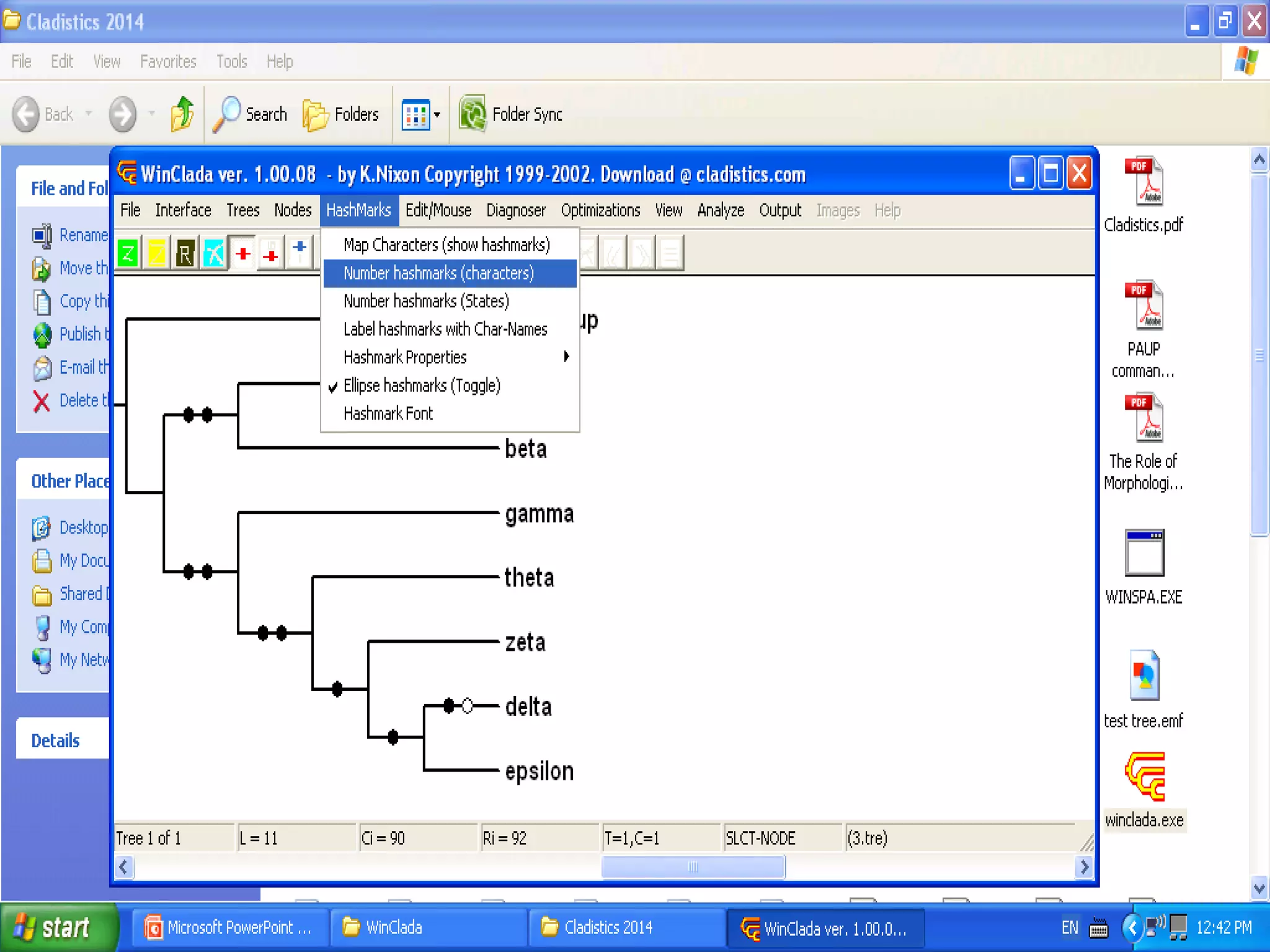
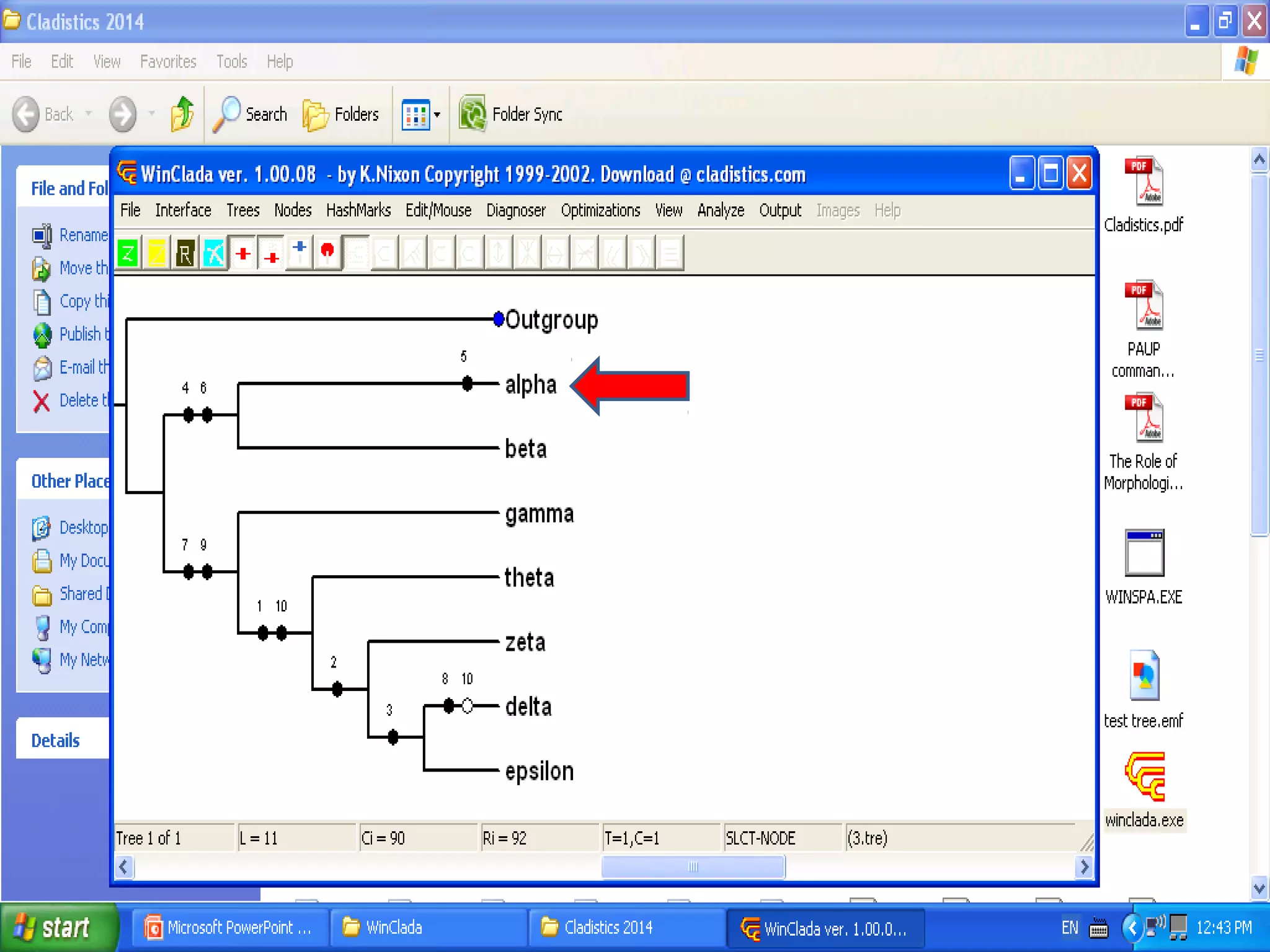
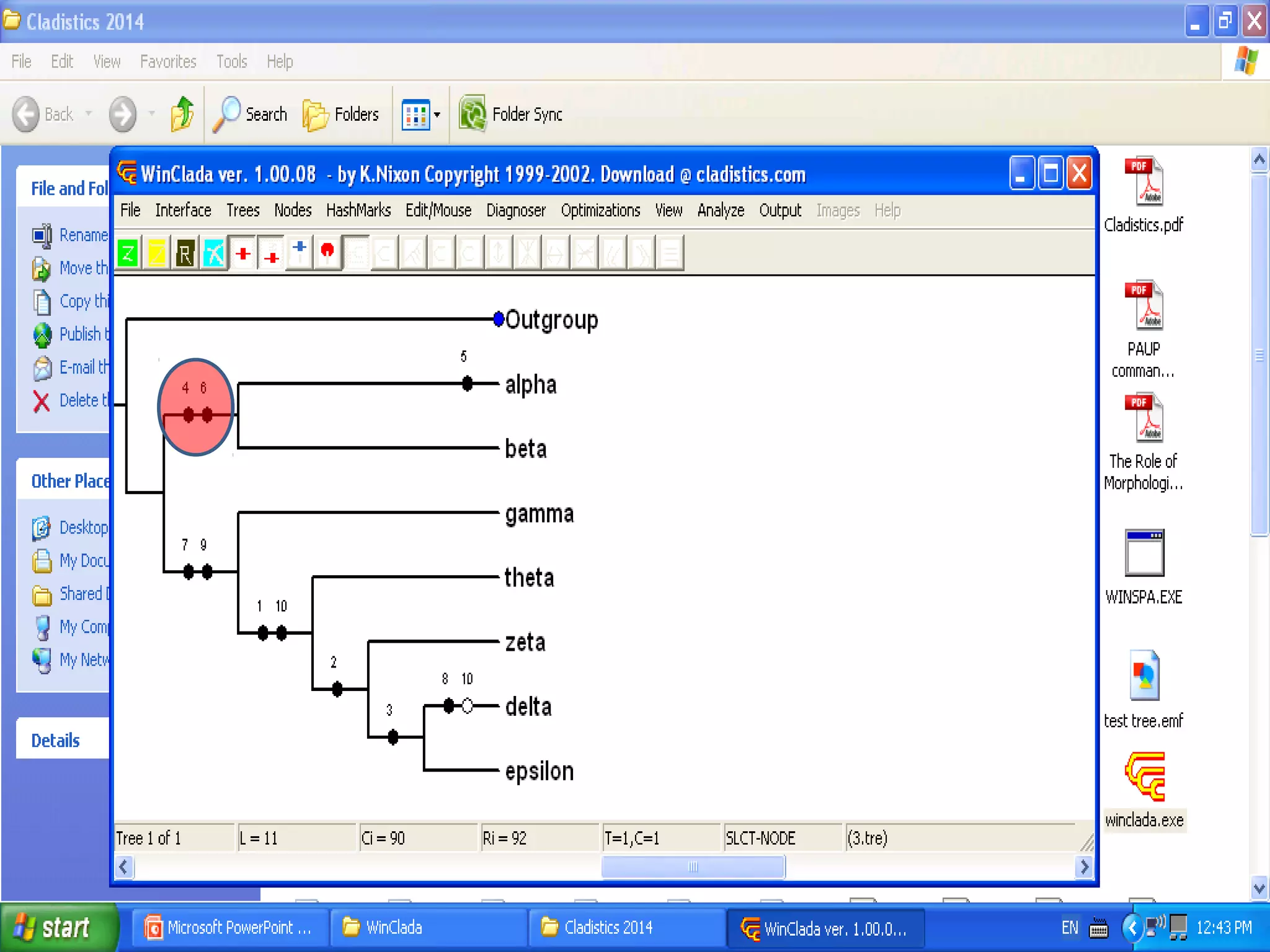
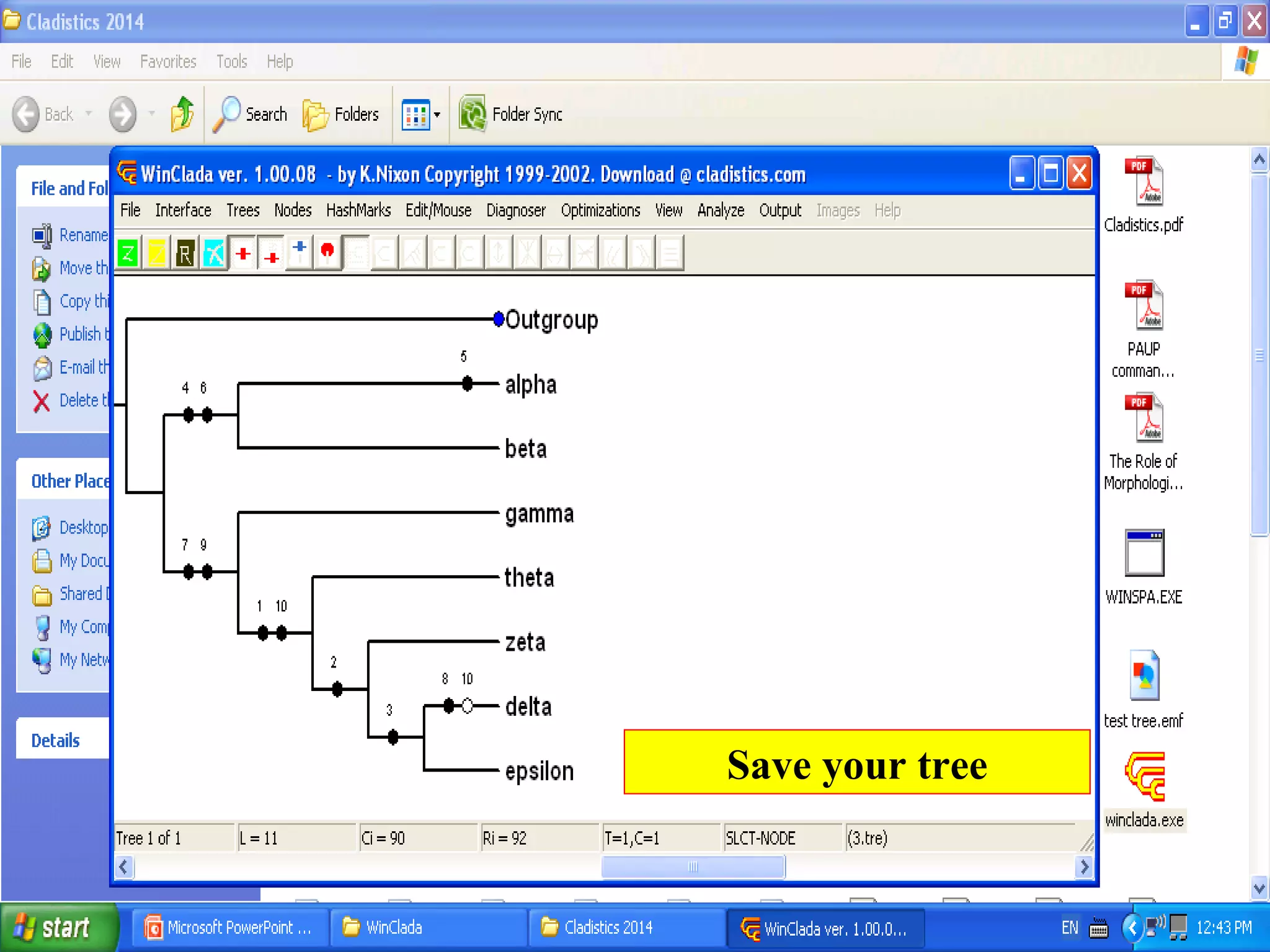
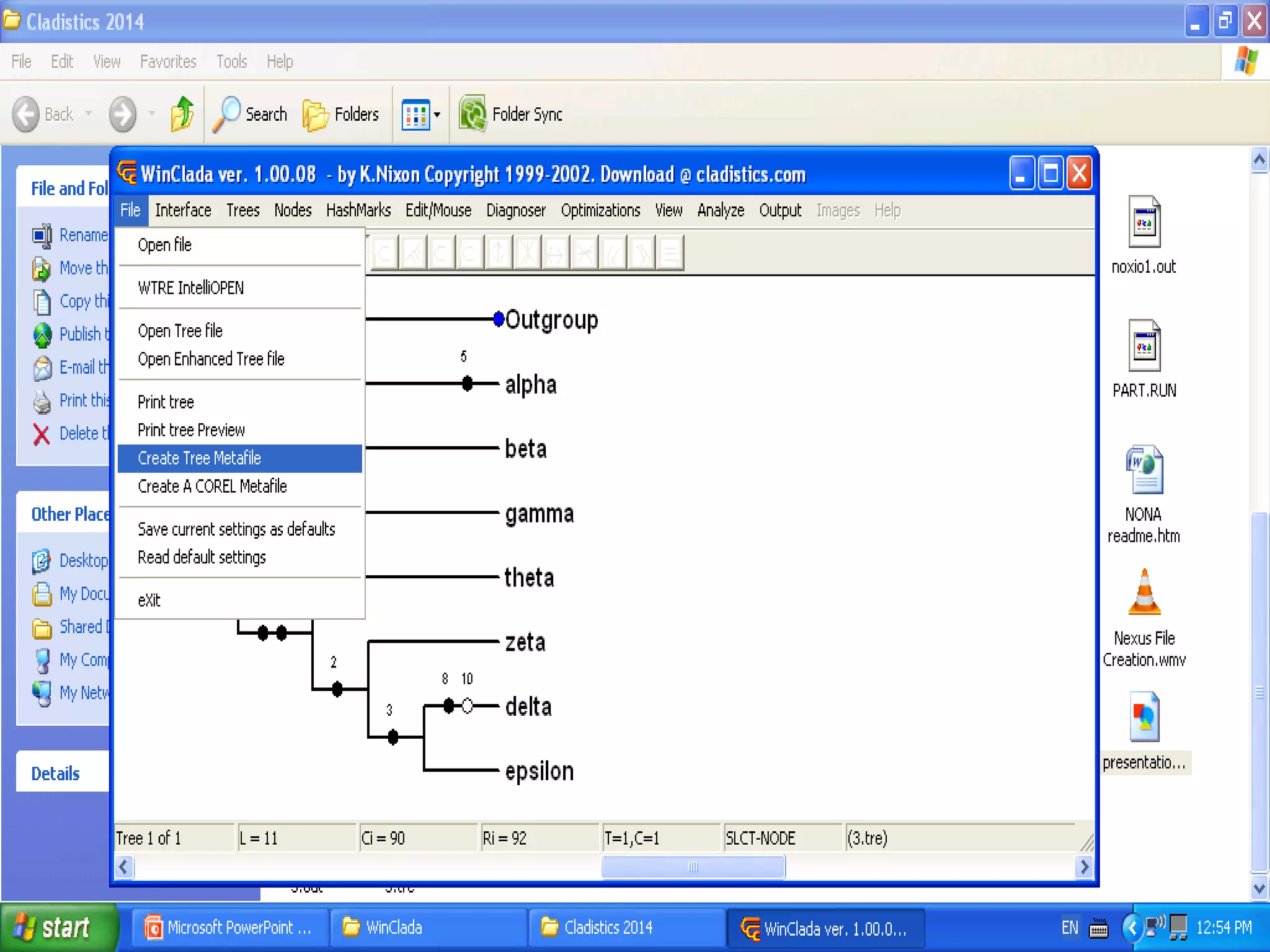
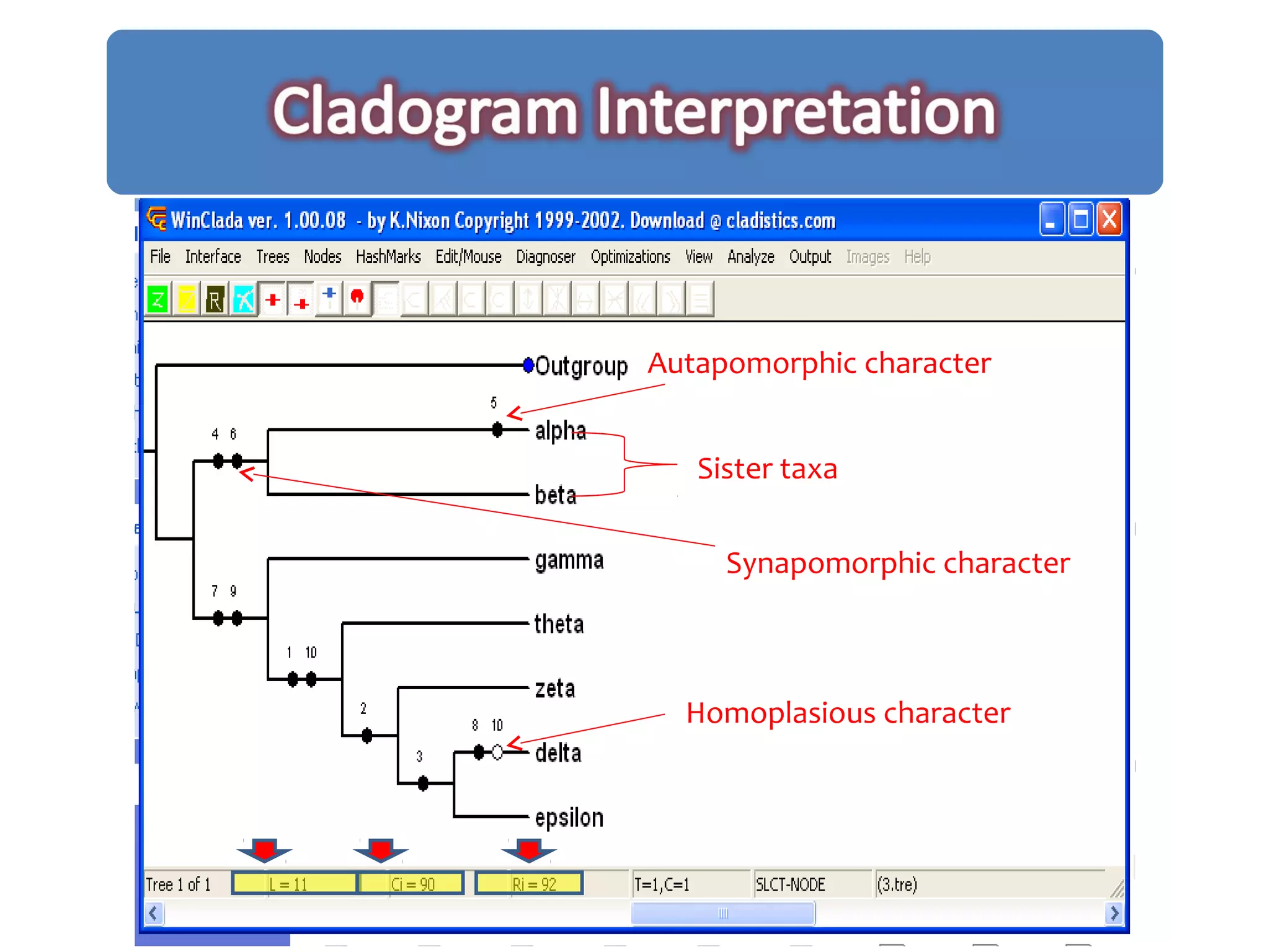





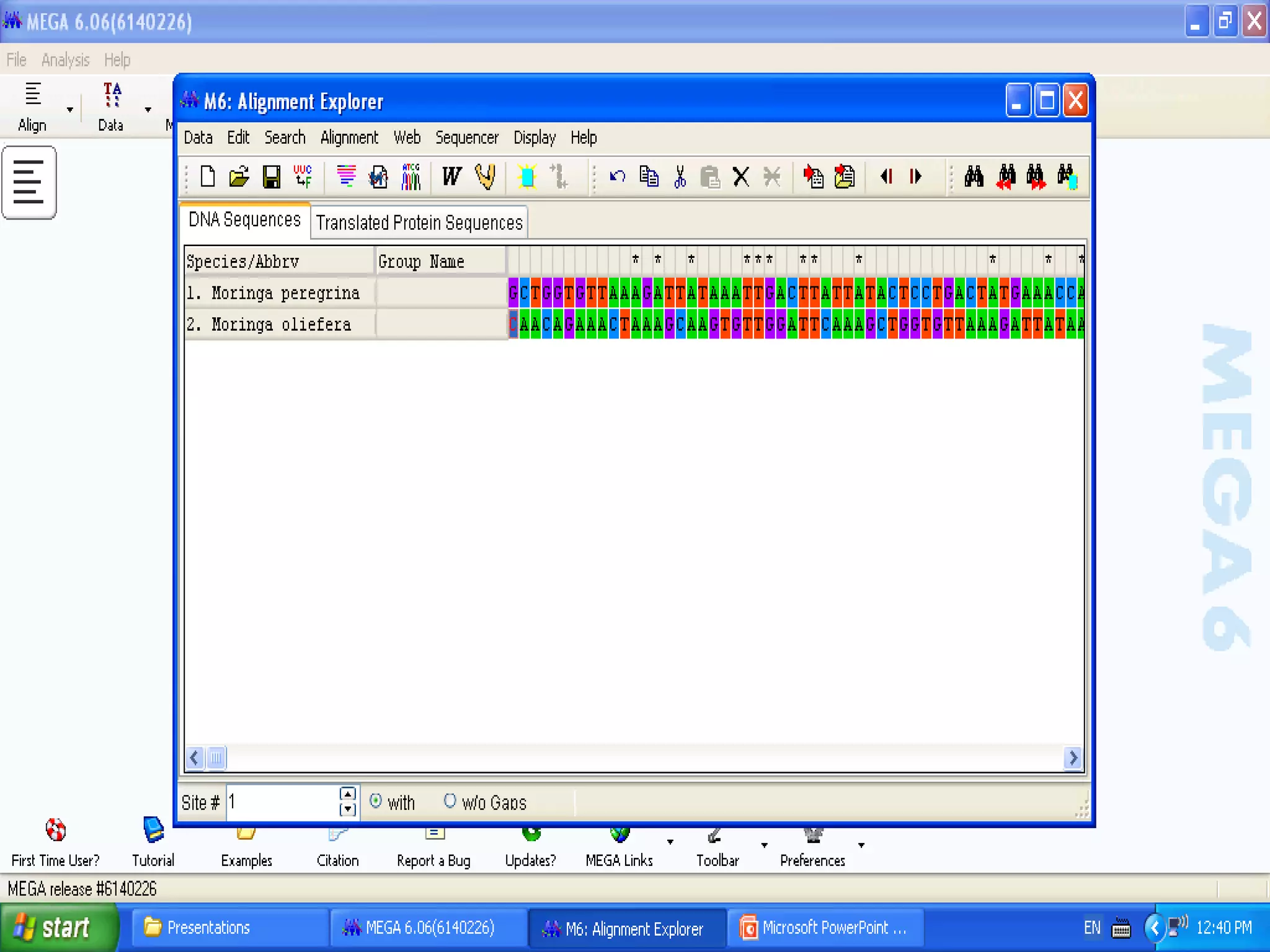
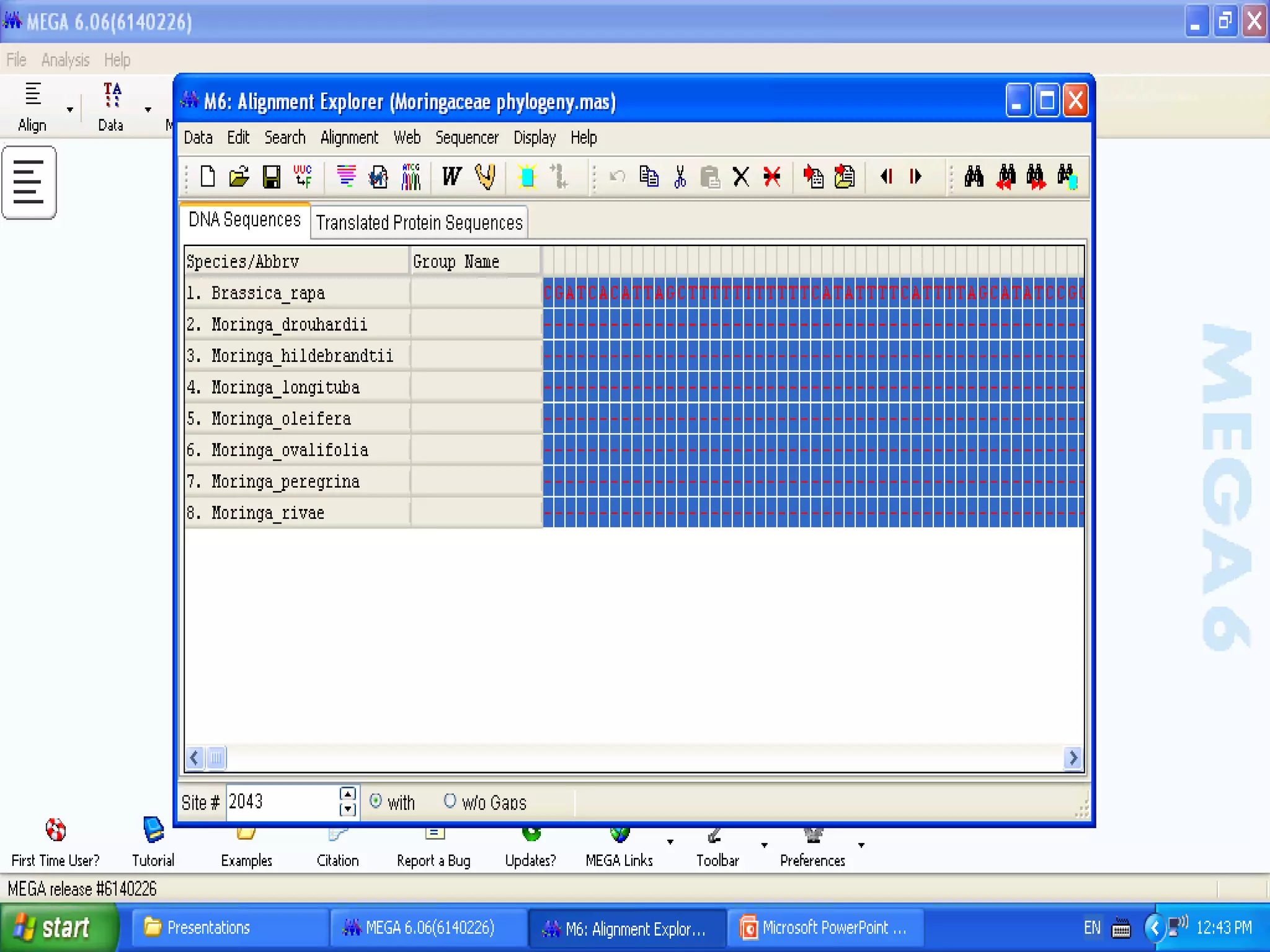


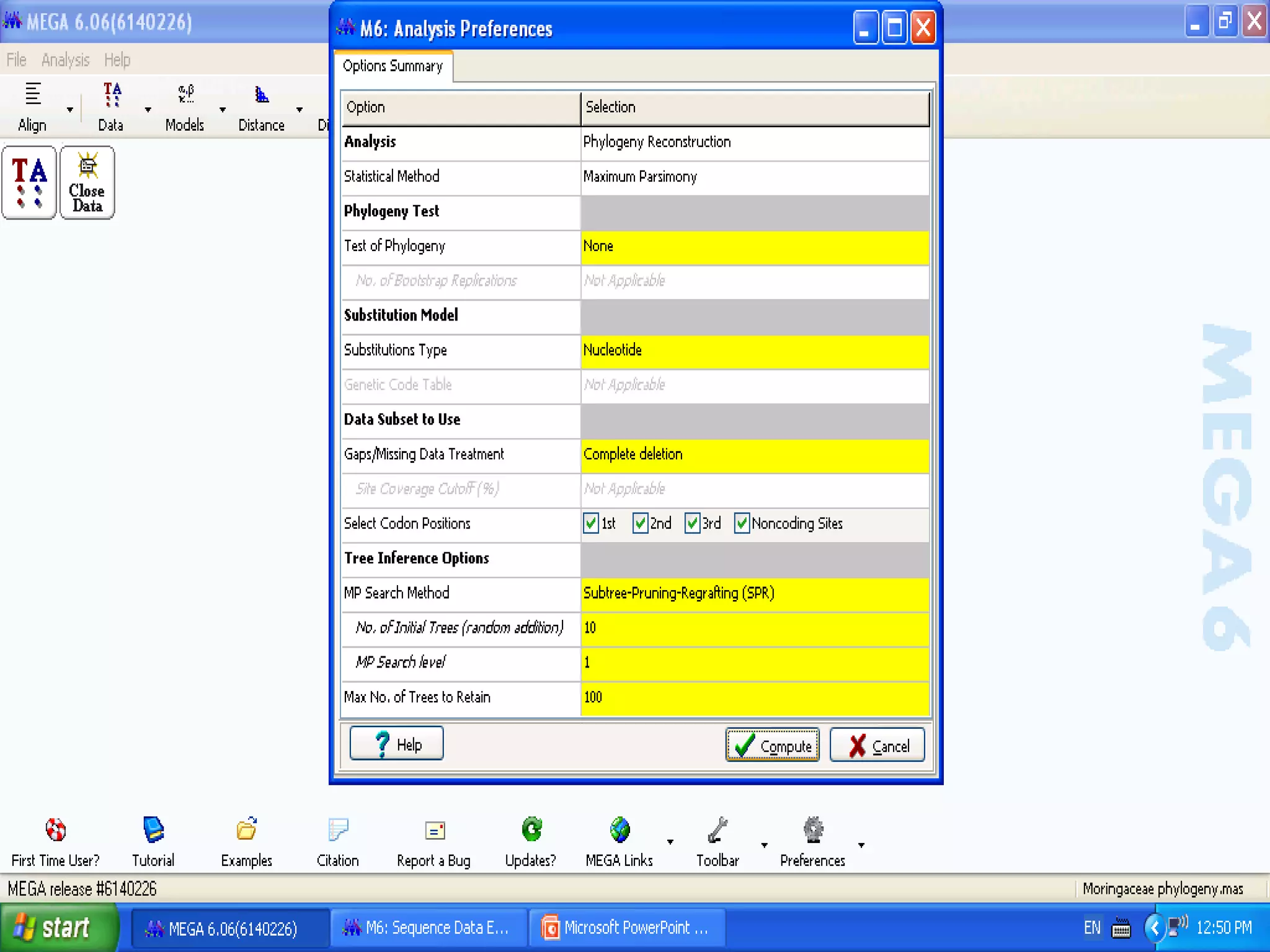
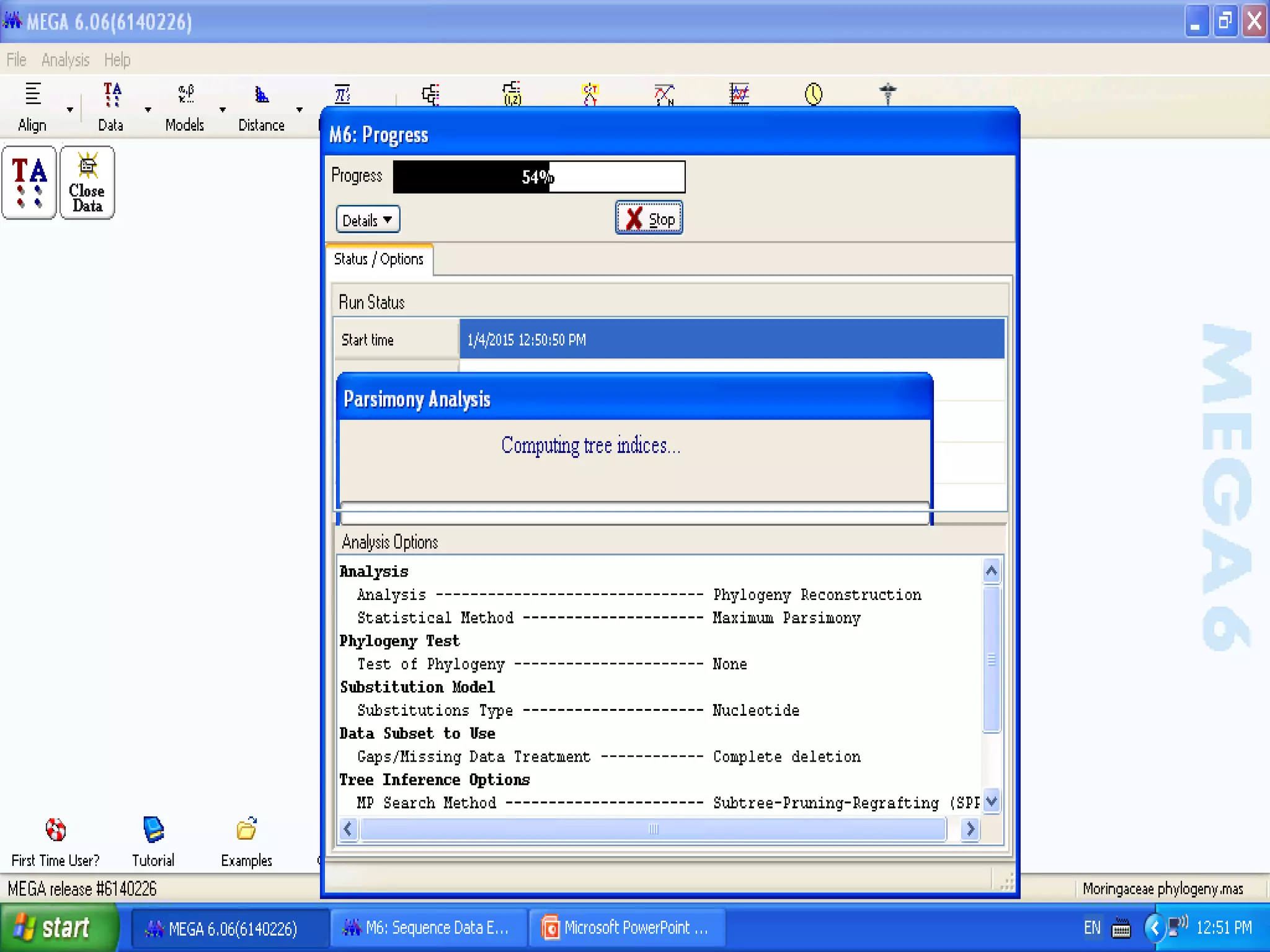
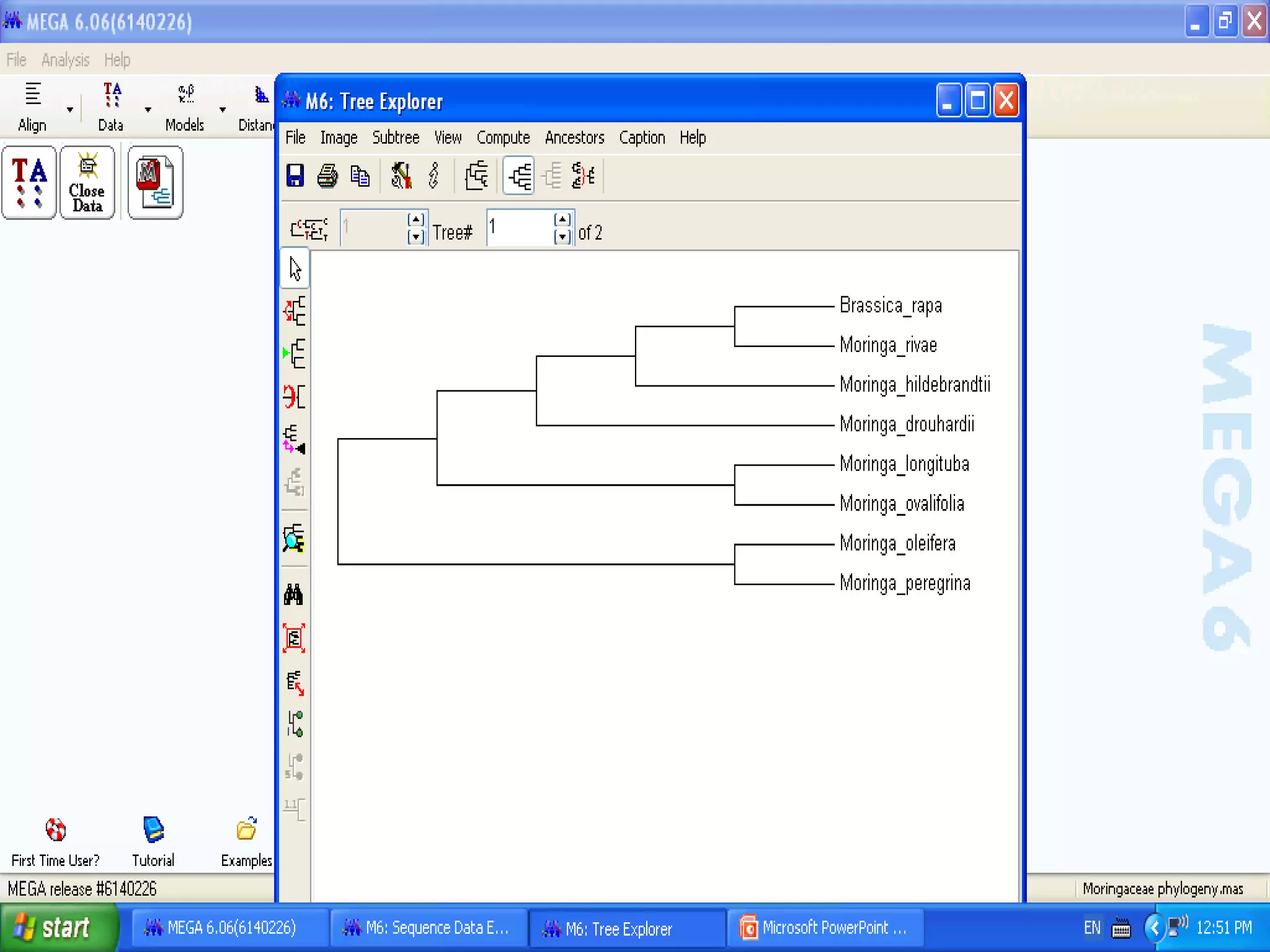
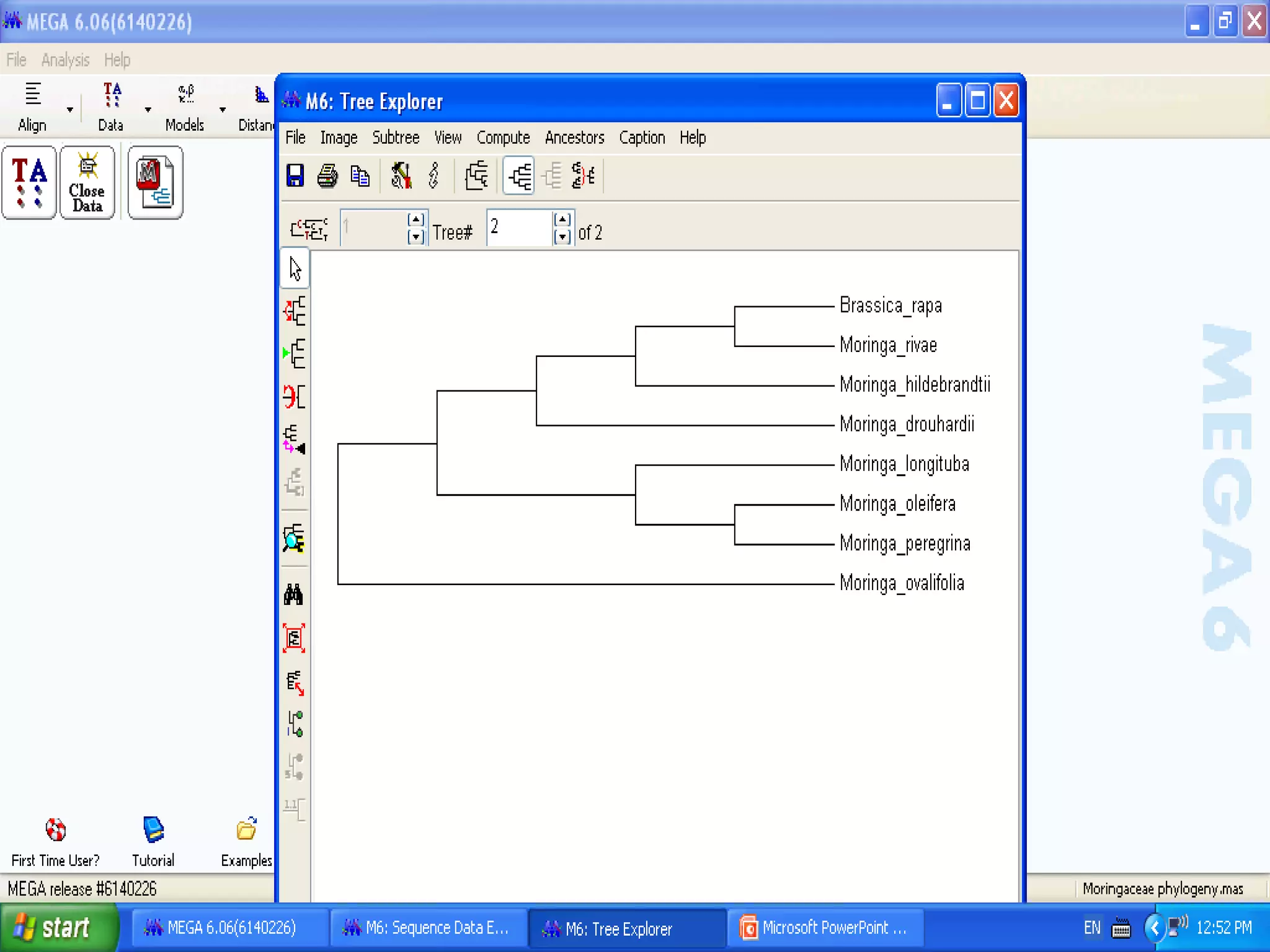
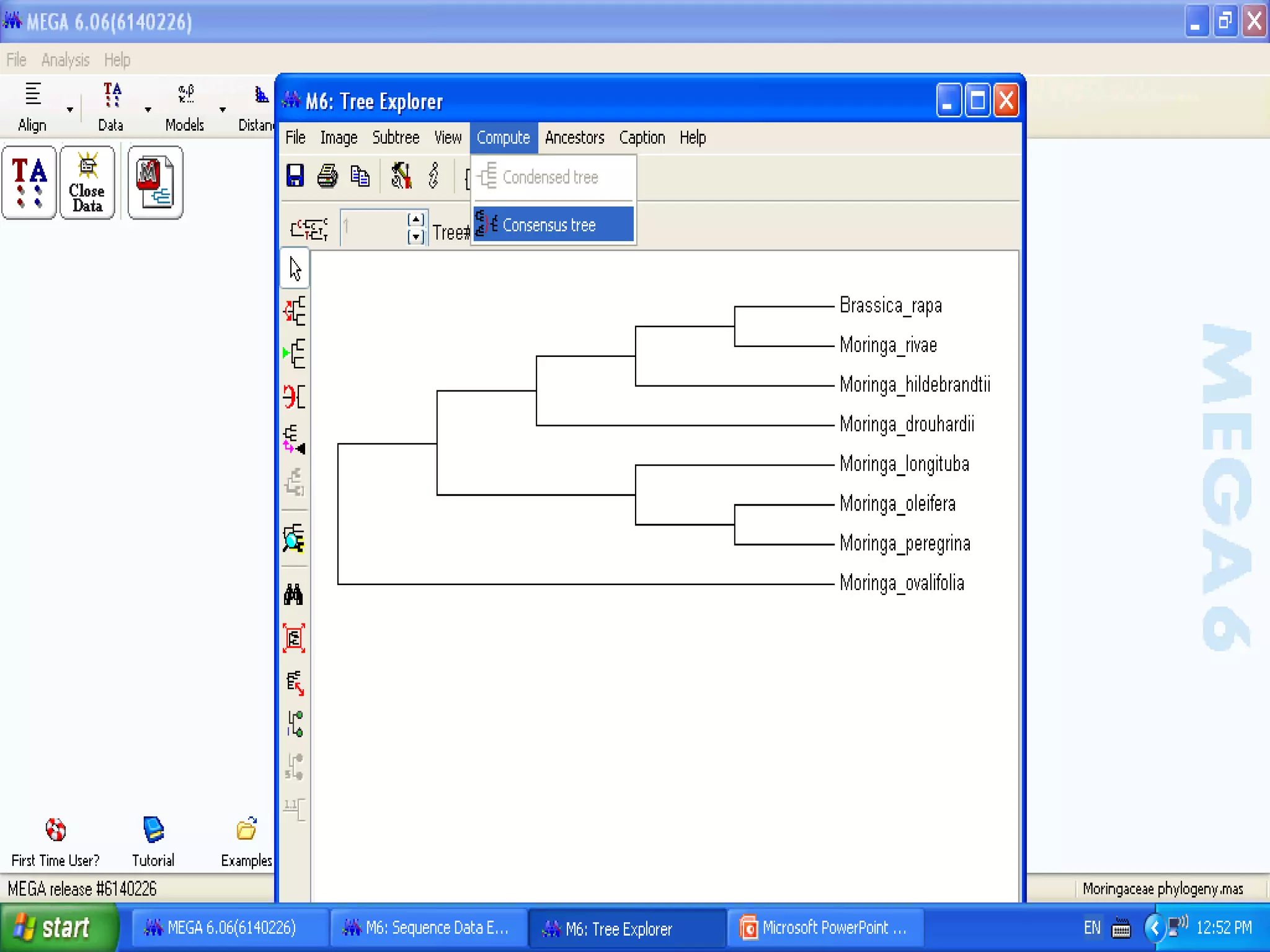
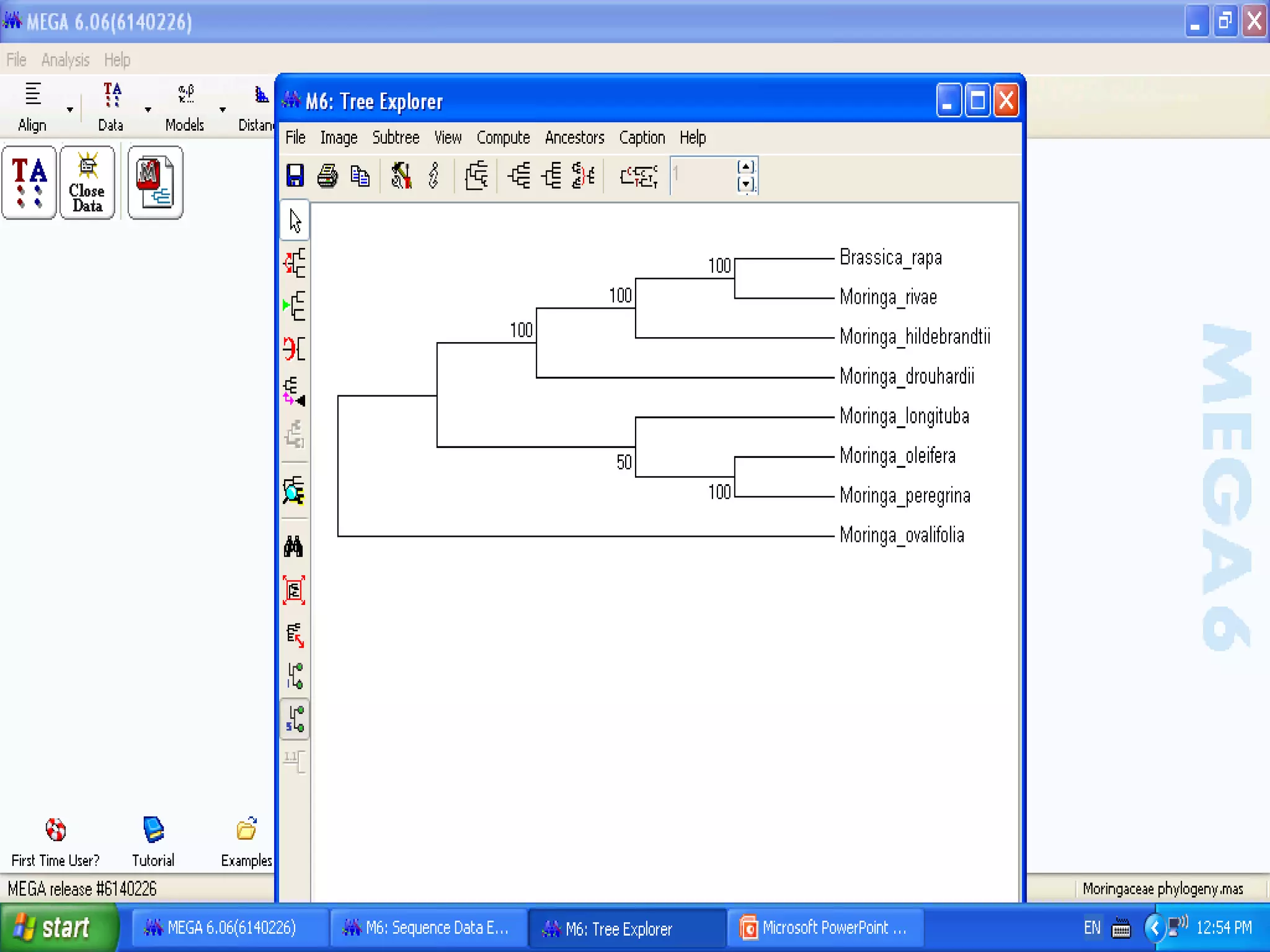


Cladistics, or phylogenetic systematics, organizes organisms based on shared derived characters, distinguishing between primitive (plesiomorphic) and derived (apomorphic) states. An outgroup is used to identify character states, with hypotheses requiring fewer assumptions being preferred. Cladograms serve as a foundation for classification, utilizing data matrices to represent character states and relationships among taxa.





































































































































































