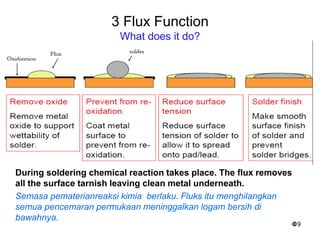
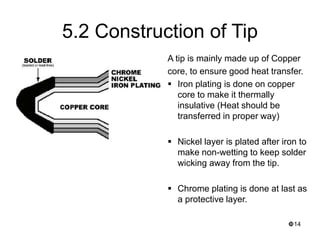
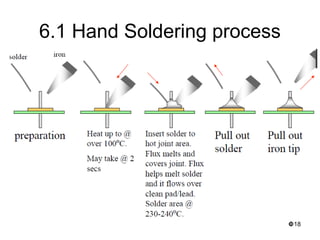
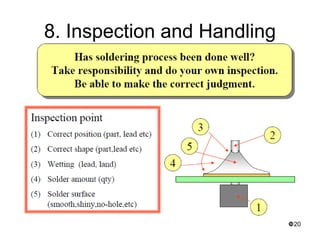
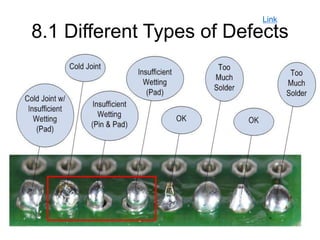
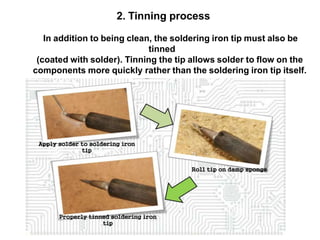
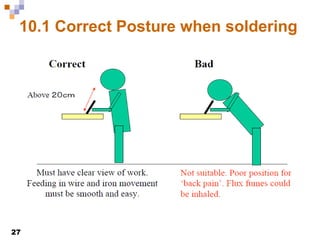
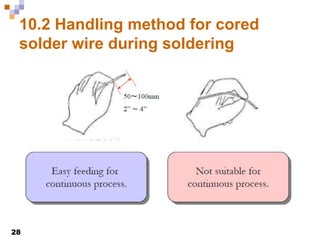
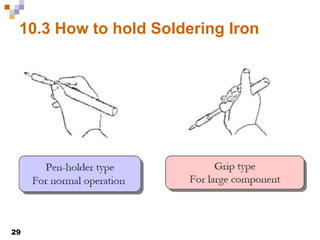
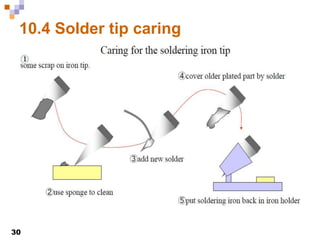
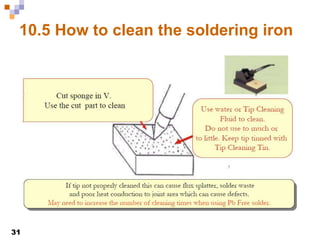
This document provides an overview of soldering, including definitions of key terms, components, and processes. It discusses the four main elements of soldering - iron, solder, flux, and electronic components. It describes the soldering process and important considerations like cleanliness, temperature control, and tip maintenance. Overall, the document serves as a guide to best practices for successful hand soldering of electronic components.